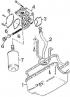
Changes in the design 1988-1993 of the car Ford Sierra
Changes in car design from 1988 to 1993
This subsection deals with modifications made to the design of Ford Sierra vehicles with four-cylinder diesel engines. Specifications and descriptions of adjustments and...
This subsection deals with modifications made to the design of Ford Sierra vehicles with four-cylinder diesel engines. Specifications and descriptions of adjustments and...
2.3 liter diesel engine repair
Cylinder head cover Since October 1987 (production date code "HU") all diesel engines 2.3 in. 3 are equipped with a new type of cylinder head cover and gasket (silicone...
Cylinder head cover Since October 1987 (production date code "HU") all diesel engines 2.3 in. 3 are equipped with a new type of cylinder head cover and gasket (silicone...
Specifications of the 1.8 liter engine
Engine with self-ignition of fuel and intermediate injection into the combustion chamber, with a turbocharger, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, liquid-cooled, with a...
Engine with self-ignition of fuel and intermediate injection into the combustion chamber, with a turbocharger, four-stroke, four-cylinder, in-line, liquid-cooled, with a...
1.8 liter engine cylinder head
Dimensions of the swirl chamber seat in the cylinder head Valve seat dimensions The cylinder head is cast iron and features plug-in valve seats and swirl combustion...
Dimensions of the swirl chamber seat in the cylinder head Valve seat dimensions The cylinder head is cast iron and features plug-in valve seats and swirl combustion...
1.8 liter engine block
Engine block 1 – block of cylinders of the engine; 2 – back cover; 3 - sealing ring; 4 - oil drain plug; 5 - oil pan gasket; 6 - oil pan; 7 – a plug of a technological...
Engine block 1 – block of cylinders of the engine; 2 – back cover; 3 - sealing ring; 4 - oil drain plug; 5 - oil pan gasket; 6 - oil pan; 7 – a plug of a technological...
1.8 liter engine crank mechanism
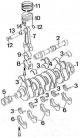
Crank mechanism 1 - crankshaft; 2 - intermediate shaft; 3 – liners of main bearings of a cranked shaft; 4 - thrust half rings of the crankshaft; 5 - pulley; 6 - caps of...
Crank mechanism 1 - crankshaft; 2 - intermediate shaft; 3 – liners of main bearings of a cranked shaft; 4 - thrust half rings of the crankshaft; 5 - pulley; 6 - caps of...
1.8 liter engine timing system
The main element of the gas distribution system is the camshaft located in the cylinder head and driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. Valve timing (measured at...
The main element of the gas distribution system is the camshaft located in the cylinder head and driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. Valve timing (measured at...
Engine lubrication system 1.8 liters
Pressure lubrication is provided by an oil pump driven by an intermediate shaft. Oil pump Gear pump with internal teeth. Oil pressure (at 100°С): at 750 rpm: 0.075 MPa;...
Pressure lubrication is provided by an oil pump driven by an intermediate shaft. Oil pump Gear pump with internal teeth. Oil pressure (at 100°С): at 750 rpm: 0.075 MPa;...
Engine cooling system 1.8 liters
A closed circuit for cooling with antifreeze circulating under pressure contains a radiator, a coolant pump, an expansion tank, a thermostat and a fan with an electric...
A closed circuit for cooling with antifreeze circulating under pressure contains a radiator, a coolant pump, an expansion tank, a thermostat and a fan with an electric...
1.8 liter engine fuel system
The fuel injection system contains a CAV Roto Diesel fuel distribution pump. Fuel tank The fuel tank, stamped from a steel sheet, is located under the bottom in front of...
The fuel injection system contains a CAV Roto Diesel fuel distribution pump. Fuel tank The fuel tank, stamped from a steel sheet, is located under the bottom in front of...
1.8 liter engine torques
Bolts of fastening of a head of the block of cylinders (every time new bolts): - Stage 1 20 – 30 Nm – stage 2 76 - 92 Nm – Stage 3 wait 2 minutes – stage 4 tighten by...
Bolts of fastening of a head of the block of cylinders (every time new bolts): - Stage 1 20 – 30 Nm – stage 2 76 - 92 Nm – Stage 3 wait 2 minutes – stage 4 tighten by...
1.8 liter engine adjustment
Valve clearance check Valve clearance is checked with a feeler gauge between the back of the cam and the tappet. 1. Disconnect the crankcase breather hose from the...
Valve clearance check Valve clearance is checked with a feeler gauge between the back of the cam and the tappet. 1. Disconnect the crankcase breather hose from the...
Fuel filter — removal and installation
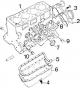
Fuel injection system 1 - fuel pump, 2 - cold engine injection advance corrector, 3 - fuel dose regulator, 4 - engine shutdown solenoid valve (STOP valve), 5 - injection...
Fuel injection system 1 - fuel pump, 2 - cold engine injection advance corrector, 3 - fuel dose regulator, 4 - engine shutdown solenoid valve (STOP valve), 5 - injection...
Removal and installation of nozzles
Attention! Protect the generator from diesel fuel. Withdrawal 1. Disconnect ground wire from battery. 2. Carefully disconnect the injection line connections from the...
Attention! Protect the generator from diesel fuel. Withdrawal 1. Disconnect ground wire from battery. 2. Carefully disconnect the injection line connections from the...
Fuel pump — removal and installation
Fuel pump adjustment 1 - adjusting bolt, 2 - fuel metering lever, 3 - residual flow adjustment bolt, 4 - idle speed adjustment bolt, 5 - idle speed lever Dimensions of...
Fuel pump adjustment 1 - adjusting bolt, 2 - fuel metering lever, 3 - residual flow adjustment bolt, 4 - idle speed adjustment bolt, 5 - idle speed lever Dimensions of...
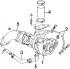
Removal and installation of a turbocharger
Turbocharger 1 - turbocharger, 2 - oil supply pipeline to the turbocharger, 3 - oil return pipeline from the turbocharger, 4 - compressed air supply pipeline to the...
Turbocharger 1 - turbocharger, 2 - oil supply pipeline to the turbocharger, 3 - oil return pipeline from the turbocharger, 4 - compressed air supply pipeline to the...
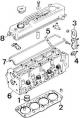
Removing the cylinder head
Cylinder head 1 - vortex combustion chamber; 2 – laying of a head of the block of cylinders; 3 - bracket with an eye for lifting the engine; 4 - oil pressure sensor; 5 –...
Cylinder head 1 - vortex combustion chamber; 2 – laying of a head of the block of cylinders; 3 - bracket with an eye for lifting the engine; 4 - oil pressure sensor; 5 –...
Cylinder head repair
Disassembly 1. Remove intake and exhaust manifolds. 2. Unscrew the two brackets with holes for lifting the engine and the oil pressure sensor from the cylinder head. 3....
Disassembly 1. Remove intake and exhaust manifolds. 2. Unscrew the two brackets with holes for lifting the engine and the oil pressure sensor from the cylinder head. 3....
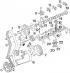
Cylinder head, timing adjustment
Gas distribution system 1 - timing belt drive timing system, 2 - crankshaft pulley, 3 - intermediate shaft pulley, 4 - toothed belt tensioner, 5 - camshaft pulley, 6 -...
Gas distribution system 1 - timing belt drive timing system, 2 - crankshaft pulley, 3 - intermediate shaft pulley, 4 - toothed belt tensioner, 5 - camshaft pulley, 6 -...
Removal and installation of the engine
Withdrawal 1. Disconnect ground wire from battery. 2. Remove the hood. 3. Drain the cooling system (see subsection 3.2.1.11 ). 4. Disconnect the air supply line to the...
Withdrawal 1. Disconnect ground wire from battery. 2. Remove the hood. 3. Drain the cooling system (see subsection 3.2.1.11 ). 4. Disconnect the air supply line to the...
Diesel engine disassembly
1. Remove turbocharger together with exhaust manifold. 2. Drain oil from engine. 3. Remove drive gear and clutch disc. 4. Remove flywheel from crankshaft. 5. Remove the...
1. Remove turbocharger together with exhaust manifold. 2. Drain oil from engine. 3. Remove drive gear and clutch disc. 4. Remove flywheel from crankshaft. 5. Remove the...
Checking Engine Parts
It is recommended to thoroughly clean and wash the parts to be used again. Removing the plugs and plugs from the cylinder block and cylinder head makes flushing them...
It is recommended to thoroughly clean and wash the parts to be used again. Removing the plugs and plugs from the cylinder block and cylinder head makes flushing them...
Checking the clearances of the crankshaft and connecting rods
Inserts of the first main bearing (from the drive side of the gas distribution system) are larger than the rest of the bearings and both have an oil groove. In the...
Inserts of the first main bearing (from the drive side of the gas distribution system) are larger than the rest of the bearings and both have an oil groove. In the...
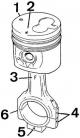
Diesel engine assembly
Identification symbols and labels for the correct position of the piston and connecting rod 1 - designation of the piston diameter, 2 - designation of the direction of...
Identification symbols and labels for the correct position of the piston and connecting rod 1 - designation of the piston diameter, 2 - designation of the direction of...
Diesel engine lubrication system
Lubrication system 1 - oil pan, 2 - oil supply pipe to the pump, 3 - gaskets, 4 - oil pump with bracket, 5 - oil pump cover, 6 - bypass valve, 7 - oil filter Removal and...
Lubrication system 1 - oil pan, 2 - oil supply pipe to the pump, 3 - gaskets, 4 - oil pump with bracket, 5 - oil pump cover, 6 - bypass valve, 7 - oil filter Removal and...
Diesel engine cooling system
Cooling system 1 - radiator; 2 – casing of the fan of a radiator; 3 - radiator fan; 4 - thermostat housing; 5 - thermostat; 6 - coolant pump; 7 - expansion tank; 8 -...
Cooling system 1 - radiator; 2 – casing of the fan of a radiator; 3 - radiator fan; 4 - thermostat housing; 5 - thermostat; 6 - coolant pump; 7 - expansion tank; 8 -...
Clutch — description of changes
Clutch control mechanism Function test When the clutch pedal is released, clicks may be heard from the automatic gap adjustment mechanism due to wear on the clutch disc...
Clutch control mechanism Function test When the clutch pedal is released, clicks may be heard from the automatic gap adjustment mechanism due to wear on the clutch disc...
Mechanical five-speed gearbox type MT 75
Since November 1988, in Ford Sierra vehicles with diesel engines, a five-speed manual transmission type MT 75 has been installed instead of a five-speed manual...
Since November 1988, in Ford Sierra vehicles with diesel engines, a five-speed manual transmission type MT 75 has been installed instead of a five-speed manual...
Drive shaft and rear axle
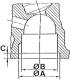
Drive joint A and B - grease packing points, C - hinge length, D - hinge diameter Surface for application of sealing paste A - surface for applying sealing paste Elastic...
Drive joint A and B - grease packing points, C - hinge length, D - hinge diameter Surface for application of sealing paste A - surface for applying sealing paste Elastic...
Steering system
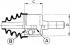
Bolt of fastening of the hinge of a shaft of a steering column Bolt tightening torque (indicated by an arrow) fastening of the steering shaft hinge increased to 25±1 Nm....
Bolt of fastening of the hinge of a shaft of a steering column Bolt tightening torque (indicated by an arrow) fastening of the steering shaft hinge increased to 25±1 Nm....
Front suspension — check and adjustment
Stabilizer Since March 1989 (production date code "KM") the stabilizer arm bushing and suspension arms are of a new type. Checking and adjusting wheel alignment...
Stabilizer Since March 1989 (production date code "KM") the stabilizer arm bushing and suspension arms are of a new type. Checking and adjusting wheel alignment...
Brake system — description of changes
Front brakes Brake pads Since August 1988 (production date code "JE") in Ford Sierra vehicles with diesel engines, the material of the brake pads has been changed. In...
Front brakes Brake pads Since August 1988 (production date code "JE") in Ford Sierra vehicles with diesel engines, the material of the brake pads has been changed. In...
Electrical equipment — description of changes
Generator Ford Sierra 1.8 Turbo D cars are equipped with a Bosch N1 70 A or Lucas A 127/70 generator. V-belt Make and type: Dayco. Deflection: 4mm under thumb pressure....
Generator Ford Sierra 1.8 Turbo D cars are equipped with a Bosch N1 70 A or Lucas A 127/70 generator. V-belt Make and type: Dayco. Deflection: 4mm under thumb pressure....
General data and vehicle characteristics
Masses (kg) Ford Sierra 1.8 Turbo D cars Version Berlin and sedan C; CL and CLX Berlin and sedan GL and Ghia Combi C; CL and CLX Combi GL Own weight in curb condition...
Masses (kg) Ford Sierra 1.8 Turbo D cars Version Berlin and sedan C; CL and CLX Berlin and sedan GL and Ghia Combi C; CL and CLX Combi GL Own weight in curb condition...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Fusion
Scorpio 1
Scorpio 2
Sierra
- General information
- Vehicle device
- User manual
- Faults on the way
- Maintenance
- Tips for the car owner
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Lubrication and cooling system
- Supply system
- Exhaust and vapor recovery
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Front wheel drives
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Body сare
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Engine electrics
- Lighting and signaling
- Switches and sensors
- Electrical circuits
Scorpio 1
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines OHC
- Petrol engines DOHC
- Petrol engines V6
- Ignition and control
- Diesel engines
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Carburetors
- Fuel injection
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox «N»
- Manual gearbox «MT 75»
- Automatic gearbox «A4LD»
- Rear axle and drive shafts
- Chassis
- Steering
- Power steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Heating and ventilation
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
Scorpio 2
- General information
- Car care
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Ignition system
- Supply system
- Carburetors
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Injection system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Heating system
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Headlights and lighting
- Windshield wipers and washers
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
Sierra
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Gasoline engines
- Engine repair
- Ignition system
- Fuel system
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Changes 1984-1986
- Changes 1987-1989
- Changes 1990-1993
- Diesel engines
- Engine repair
- Fuel system
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Changes 1988-1993
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Cardan and rear axle
- Chassis
- Steering
- Steering with power steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Body and electrical
- Body elements and doors
- Electrical equipment
- Electrical circuits
FordBook.ru © 2014-2024 • Mobile version • Interesting to read • Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU • Site search • Contact with administration
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •