Car engine repair Ford Scorpio 2
General information about engines
FORD SCORPIO cars are equipped with single-row 4-cylinder or V-shaped 6-cylinder engines. The power unit in the engine compartment is located along the direction of...
FORD SCORPIO cars are equipped with single-row 4-cylinder or V-shaped 6-cylinder engines. The power unit in the engine compartment is located along the direction of...
Vehicle identification
The engine number is stamped on the crankcase. For the ONS engine, the number is located, when viewed in the direction of travel, in front on the right next to the...
The engine number is stamped on the crankcase. For the ONS engine, the number is located, when viewed in the direction of travel, in front on the right next to the...
The most important characteristics of engines for Ford Scorpio cars
Scorpio I from 4/85 to 8/94 1) ONS (Over Head Camshaft) - the camshaft of the engine has the top arrangement. DOHC (Double Over Head Camshaft) The engine has 2 overhead...
Scorpio I from 4/85 to 8/94 1) ONS (Over Head Camshaft) - the camshaft of the engine has the top arrangement. DOHC (Double Over Head Camshaft) The engine has 2 overhead...
Removal and installation of the lower casing of a motor compartment
Withdrawal Raise the car on the goats. Firmly holding the casing, unscrew the mounting bolts. Installation Screw on cover. Lower the car.
Withdrawal Raise the car on the goats. Firmly holding the casing, unscrew the mounting bolts. Installation Screw on cover. Lower the car.
Removal and installation of the engine
The petrol engine is removed without the gearbox in an upward direction. The intake and exhaust manifolds, as well as the generator, do not need to be dismantled. A...
The petrol engine is removed without the gearbox in an upward direction. The intake and exhaust manifolds, as well as the generator, do not need to be dismantled. A...
Removal, installation and adjustment of a gear belt
ONS engine To check the tension of the toothed belt, a FORD 21-113 tester is required. Incorrect toothed belt tension causes noise during operation and leads to intense...
ONS engine To check the tension of the toothed belt, a FORD 21-113 tester is required. Incorrect toothed belt tension causes noise during operation and leads to intense...
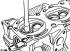
Removal and installation of a head of cylinders (gasoline OHC engine)
Remove the cylinder head only when the engine is cold. Do not remove the exhaust and intake manifolds from the head. A cylinder head gasket defect is identified by one...
Remove the cylinder head only when the engine is cold. Do not remove the exhaust and intake manifolds from the head. A cylinder head gasket defect is identified by one...
Removal and installation of a head of cylinders (engine DOHC)
Attention: Operations and instructions applicable to all engines are described above in chapter for the ONS engine . This chapter highlights only the significant...
Attention: Operations and instructions applicable to all engines are described above in chapter for the ONS engine . This chapter highlights only the significant...
Removing and installing cylinder heads (V6 OHV engine)
The exhaust manifold does not need to be removed. Removal for engines with a working volume of 2.4 and 2.9 liters is stated. Attention is drawn to the differences for...
The exhaust manifold does not need to be removed. Removal for engines with a working volume of 2.4 and 2.9 liters is stated. Attention is drawn to the differences for...
Removal and installation of a camshaft (OHC engine)
Attention: If the valve actuator parts are to be used again, they must be installed in their original places. In order not to confuse the parts in places, you should...
Attention: If the valve actuator parts are to be used again, they must be installed in their original places. In order not to confuse the parts in places, you should...
Removal and installation of valves (OHC engine)
Attention: If valve drive parts are to be reused, they must be reinstalled in their original locations. In order not to frighten the details in places, it is recommended...
Attention: If valve drive parts are to be reused, they must be reinstalled in their original locations. In order not to frighten the details in places, it is recommended...
Removal and installation of valves (DOHC engine)
Attention: If valve drive parts are to be reused, they must be reinstalled in their original locations. In order not to frighten the details in places, it is recommended...
Attention: If valve drive parts are to be reused, they must be reinstalled in their original locations. In order not to frighten the details in places, it is recommended...
Removal and installation of valves (engine V6 OHV)
Attention: If valve drive parts are to be reused, they must be reinstalled in their original locations. In order not to frighten the details in places, it is recommended...
Attention: If valve drive parts are to be reused, they must be reinstalled in their original locations. In order not to frighten the details in places, it is recommended...
Replacing valve stem seals (petrol engine)
Worn valve stem seals cause high engine oil consumption. Oil seals can be replaced without removing the cylinder head, however, this requires an adapter and compressed...
Worn valve stem seals cause high engine oil consumption. Oil seals can be replaced without removing the cylinder head, however, this requires an adapter and compressed...
Replacing valve stem seals (diesel engine)
Withdrawal Remove cylinder head cover. Loosen the rocker arm pin. Set the piston of the corresponding cylinder to TDC. To do this, first turn the crankshaft to the TDC...
Withdrawal Remove cylinder head cover. Loosen the rocker arm pin. Set the piston of the corresponding cylinder to TDC. To do this, first turn the crankshaft to the TDC...
Checking the valve guides
When repairing a cylinder head with leaking valves, it is not enough to clean or replace the valves and valve seats. In addition, the valve guides should be checked for...
When repairing a cylinder head with leaking valves, it is not enough to clean or replace the valves and valve seats. In addition, the valve guides should be checked for...
Lapping of valves
Even with perfectly machined seats and new valves, they must rub against each other to ensure optimal sealing. This is especially important for a diesel engine. Valves...
Even with perfectly machined seats and new valves, they must rub against each other to ensure optimal sealing. This is especially important for a diesel engine. Valves...
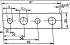
Checking and adjusting valve clearances
Engines: ONS 2.4L V6 2.8L Diesel up to 8/94 V6 2.9L without catalytic converter To compensate for various thermal expansions, certain clearances must be provided in the...
Engines: ONS 2.4L V6 2.8L Diesel up to 8/94 V6 2.9L without catalytic converter To compensate for various thermal expansions, certain clearances must be provided in the...
Cylinder compression check
Compression check allows you to draw conclusions about the condition of the engine. Namely, when checking, you can establish whether the valves and pistons are in order...
Compression check allows you to draw conclusions about the condition of the engine. Namely, when checking, you can establish whether the valves and pistons are in order...
Removing, installing and tensioning the V-belt and V-ribbed belt
If a used V-belt or V-ribbed belt is reinstalled, it must be checked for wear and damage. If there are fringing of the side surfaces, cracks or destruction, then such a...
If a used V-belt or V-ribbed belt is reinstalled, it must be checked for wear and damage. If there are fringing of the side surfaces, cracks or destruction, then such a...
Engine Troubleshooting
When the engine does not start, a systematic approach is needed to identify the malfunction. In general, in order for a gasoline engine to start, 2 basic prerequisites...
When the engine does not start, a systematic approach is needed to identify the malfunction. In general, in order for a gasoline engine to start, 2 basic prerequisites...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
See other similar sections for Ford cars:
• Power unit: Engine repair Ford Focus Turnier 1 (1998-2004)
• Power unit: Engine repair Ford Mondeo 1 (1993-1996)
• Diesel engines: Engine repair Ford Escort 4 (1986-1990)
• Power unit: Engine repair Ford Fiesta 4 (1996-1999)
• Power unit: Engine repair Ford Focus Turnier 1 (1998-2004)
• Power unit: Engine repair Ford Mondeo 1 (1993-1996)
• Diesel engines: Engine repair Ford Escort 4 (1986-1990)
• Power unit: Engine repair Ford Fiesta 4 (1996-1999)
Fusion
Scorpio 1
Scorpio 2
Sierra
- General information
- Vehicle device
- User manual
- Faults on the way
- Maintenance
- Tips for the car owner
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Lubrication and cooling system
- Supply system
- Exhaust and vapor recovery
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Front wheel drives
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Body сare
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Engine electrics
- Lighting and signaling
- Switches and sensors
- Electrical circuits
Scorpio 1
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines OHC
- Petrol engines DOHC
- Petrol engines V6
- Ignition and control
- Diesel engines
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Carburetors
- Fuel injection
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox «N»
- Manual gearbox «MT 75»
- Automatic gearbox «A4LD»
- Rear axle and drive shafts
- Chassis
- Steering
- Power steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Heating and ventilation
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
Scorpio 2
- General information
- Car care
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Ignition system
- Supply system
- Carburetors
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Injection system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Heating system
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Headlights and lighting
- Windshield wipers and washers
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
Sierra
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Gasoline engines
- Engine repair
- Ignition system
- Fuel system
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Changes 1984-1986
- Changes 1987-1989
- Changes 1990-1993
- Diesel engines
- Engine repair
- Fuel system
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Changes 1988-1993
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Cardan and rear axle
- Chassis
- Steering
- Steering with power steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Body and electrical
- Body elements and doors
- Electrical equipment
- Electrical circuits
FordBook.ru © 2014-2024 • Mobile version • Interesting to read • Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU • Site search • Contact with administration
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •