Crank mechanism
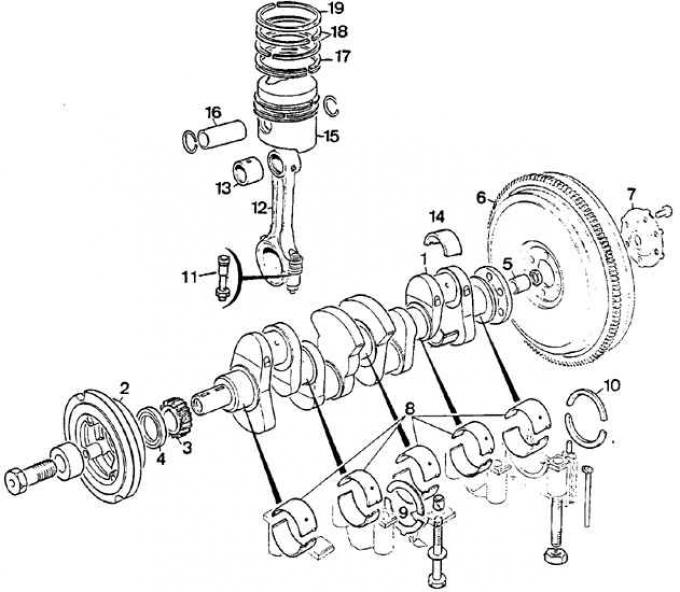
1 - crankshaft, 2 - pulley, 3 - sprocket, 4 - sealing ring, 5 - centering sleeve of the input shaft of the gearbox, 6 - flywheel, 7 - washer for fixing the flywheel mounting bolts, 8 - main bearing shells, 9 - thrust half rings of the crankshaft shaft, 10 - rear main bearing seals, 11 - connecting rod bolt, 12 - connecting rod, 13 - connecting rod head bushing, 14 - connecting rod bearing shell, 15 - piston, 16 - piston pin, 17 - oil scraper ring, 18 - lower sealing ring, 19 - top sealing ring (compression)
1. Check the condition of the connecting rod.
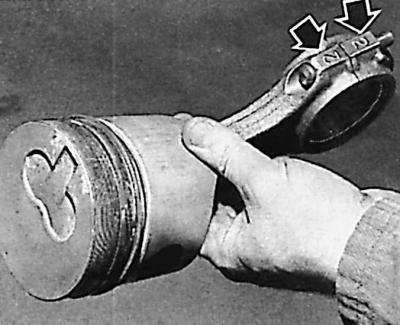
2. Observe the correct installation - the recesses on the bottom of the piston must be directed in the same direction as the markings on the connecting rod and its cover (arrows).
3. Lubricate the piston pin with a thin layer of engine oil and install it in the connecting rod head bushing.
4. Carefully install the spring retaining rings in the grooves of the piston, fixing the pin in the piston.
5. Using the special tool, install the rings on the pistons with the side marked "Thor", toward the bottom. Rings are supplied ready for installation. The rings should move freely in the piston grooves, but without appreciable play.
6. Position the rings in the piston grooves so that the locks (incisions) O-rings were shifted relative to each other on opposite sides at an angle of 120°relative to the cut of the oil scraper ring.
Selection of pistons by cylinder diameter
Cylinder Block Assembly
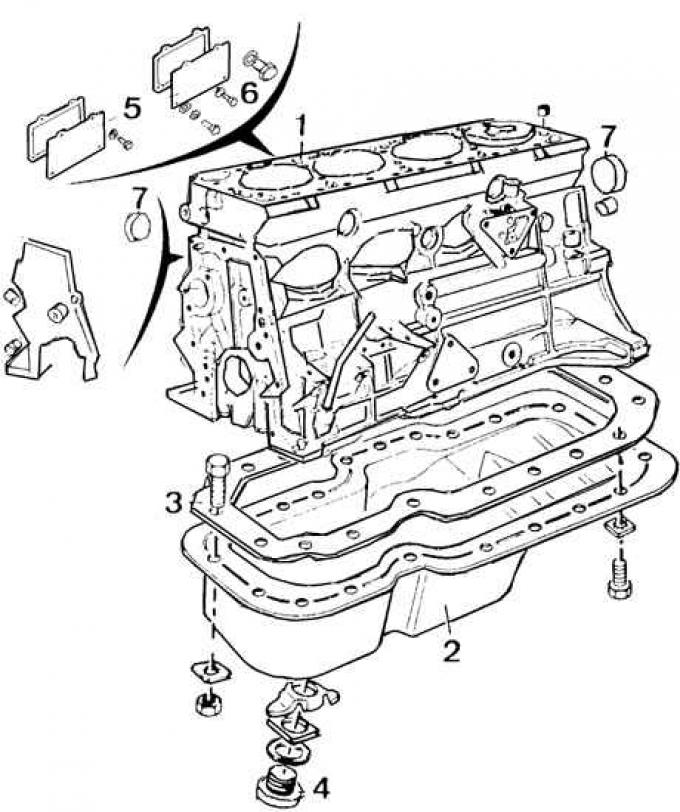
1 - cylinder block, 2 - oil pan, 3 - oil pan fastening bolt, 4 - oil drain plug, 5 - cylinder block technological hole covers, 6 - bolt, 7 - technological hole plug
Designations of cylinders on the engine block and pistons on their bottom
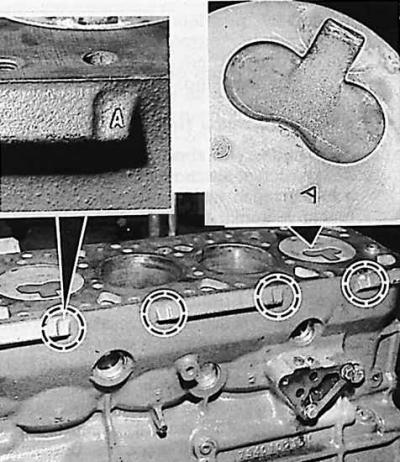
1. The diameters of pistons and cylinders are divided into groups, which are indicated by letters stamped on the engine block and piston bottom.
2. The cylinder and the piston interacting with it must belong to the same selection group (see fig. Designations of cylinders on the engine block and pistons on their bottom).
Attention! New engine blocks have cylinders with an exclusively group diameter "A" And "IN".
3. Lubricate the piston surfaces and the inner surfaces of the cylinders with oil.
4. Using a ring compressor, insert the piston-connecting rod assemblies into the respective cylinders.
Attention! The indentation at the bottom of the piston must point towards the fuel pump.
5. Push the pistons into the cylinders.
6. Install connecting rod bearings and connecting rod caps (observing the designations - see fig. Designation of the relative position of the piston, connecting rod and its cover), tighten the nuts of the connecting rod cap bolts to 60 Nm.
7. Measure the moment of resistance during rotation of the crankshaft using a torque wrench.
8. Lubricate the tappets with oil and insert them in accordance with the designations and into the guides of the engine block.
9. Install the camshaft and intermediate plate with a new gasket into the cylinder block.
10. Install the timing system actuator (see subsection 4.2.11.3.3) and the casing of the drive chain of the timing system, together with a new gasket.
11. Lubricate the timing chain housing bolts with Frenetanch sealant and tighten to 10 Nm.
12. Attach the oil pump to the cylinder block so that the tapered hole in the pump housing is opposite the threaded hole.
13. Torque tighten 22.5 Nm bolt (with conical end) oil pump mountings.
14. Install the copper washer and tighten the plugged nut to 30 Nm.
15. Install the original shim and carefully tighten the screw plug.
16. Install oil pan. Tighten the drain plug with a new gasket to 3 Nm.
Visitor comments