2.0L variant shown, other variant generally similar
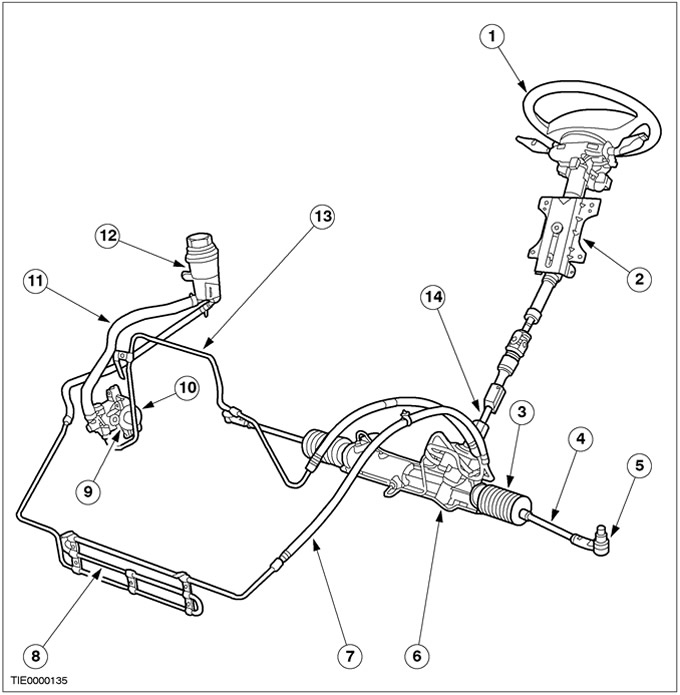
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | Steering wheel | |
| 2 | Steering column | |
| 3 | Case | |
| 4 | Tie Rod | |
| 5 | Tie rod end | |
| 6 | Steering gear | |
| 7 | Hose from steering gear to fluid cooler | |
| 8 | Fluid cooler | |
| 9 | Power steering pressure switch (PSP) | |
| 10 | Power steering pump | |
| 11 | Supply hose | |
| 12 | Tank for working fluid | |
| 13 | Hose from pump to steering gear | |
| 14 | Coupling of a shaft of a steering column |
Operating principle
The rotation of the steering wheel is transmitted to the steering mechanism by means of the steering column shaft. Steering gear type "pinion rack" converts this rotational motion into a linear translational (transversely) movement. This movement, in turn, is transmitted to the steering knuckles with the help of transverse steering rods and tie rod ends.
The power steering pump supplies pressurized hydraulic fluid to the steering gear. As the steering wheel is turned, hydraulic fluid flows through the steering gear valve to one side of the double-acting piston. The side to which the hydraulic fluid is supplied depends on the direction in which the steering wheel is turned. The working fluid moves the piston, which is part of the steering mechanism, providing the power needed to generate the force required to turn the steering wheel.
Gasoline engine versions have a power steering pressure switch due to the additional engine load applied by the power steering pump (PSP). The relay, which is a normally closed relay, sends a signal to the powertrain control module (RSM) when performing parking maneuvers at low speed. The PCM responds by keeping the engine speed at idle.
Visitor comments