Car front and rear suspension Ford Focus Turnier 1
General Suspension Information
Outstanding handling: Professional magazines praise the Focus for its balanced chassis setup with «zero offset» - the geometry of the lower transverse arms and the...
Outstanding handling: Professional magazines praise the Focus for its balanced chassis setup with «zero offset» - the geometry of the lower transverse arms and the...
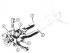
Front suspension units
Independent wheel suspension: according to the MacPherson system (patent application filed in 1949), compact module consisting of a shock absorber, a spring and a...
Independent wheel suspension: according to the MacPherson system (patent application filed in 1949), compact module consisting of a shock absorber, a spring and a...
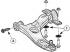
Rear suspension units
Rear axle suspension SLA: separate axle body made of welded steel profile. Axle elements such as upper wishbone, lower wishbone, shock absorbers, springs, traction...
Rear axle suspension SLA: separate axle body made of welded steel profile. Axle elements such as upper wishbone, lower wishbone, shock absorbers, springs, traction...
Amateur work on chassis and steering
Work on the chassis and steering requires experience and often special tools, as well as optical or electronic measuring instruments. In case of doubt, it is better to...
Work on the chassis and steering requires experience and often special tools, as well as optical or electronic measuring instruments. In case of doubt, it is better to...
Checking shock absorbers
Checking shock absorbers is mandatory after two sets of worn wheels. Over the course of their life, shock absorbers mutate into air pumps: after about two sets of worn...
Checking shock absorbers is mandatory after two sets of worn wheels. Over the course of their life, shock absorbers mutate into air pumps: after about two sets of worn...
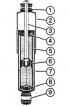
Telescopic shock absorber — design description
Your Focus rests on so-called telescopic shock absorbers. They consist of a working cylinder in which a working piston, fitted with a rod, slides up and down. The slave...
Your Focus rests on so-called telescopic shock absorbers. They consist of a working cylinder in which a working piston, fitted with a rod, slides up and down. The slave...
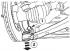
Checking the bearings of the transverse arms of the independent suspension
Both bearings and the front wishbone ball joint are maintenance free. The outer ball joint is housed in a synthetic liner with long lasting lubrication. However, the...
Both bearings and the front wishbone ball joint are maintenance free. The outer ball joint is housed in a synthetic liner with long lasting lubrication. However, the...
Checking the wheel bearing clearance
The wheels in the Focus revolve around maintenance-free double ball bearings. Modern rear axle wheel bearings are designed for a mileage of about 150,000 km. Wheel...
The wheels in the Focus revolve around maintenance-free double ball bearings. Modern rear axle wheel bearings are designed for a mileage of about 150,000 km. Wheel...
Wishbone Replacement (Front)
Deformed wishbones must always be replaced as an assembly. But worn bearing bushings can be replaced, although it is better to entrust this work to your workshop (see...
Deformed wishbones must always be replaced as an assembly. But worn bearing bushings can be replaced, although it is better to entrust this work to your workshop (see...
Replacing the suspension strut
Dismantling Raise the vehicle securely on a level surface, remove the front wheel. Disconnect the brake hose attachment and connecting rod to the stabilizer. Remove the...
Dismantling Raise the vehicle securely on a level surface, remove the front wheel. Disconnect the brake hose attachment and connecting rod to the stabilizer. Remove the...
Replacing the rear shock absorbers
Dismantling in 3-, 4-, 5-door models Remove the trunk lining. Unscrew the shock absorber top nut. To do this, lock the pressure rod with an Allen key. Raise the vehicle...
Dismantling in 3-, 4-, 5-door models Remove the trunk lining. Unscrew the shock absorber top nut. To do this, lock the pressure rod with an Allen key. Raise the vehicle...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
See other similar sections for Ford cars:
• Chassis: Suspension Ford Mondeo 1 (1993-1996)
• Chassis: Suspension and wheels Ford Escort 4 (1986-1990)
• Chassis: Car suspension Ford Fiesta 4 (1996-1999)
• Chassis: Car suspension Ford Taurus 1 and 2 (1986-1994)
• Chassis: Suspension Ford Mondeo 1 (1993-1996)
• Chassis: Suspension and wheels Ford Escort 4 (1986-1990)
• Chassis: Car suspension Ford Fiesta 4 (1996-1999)
• Chassis: Car suspension Ford Taurus 1 and 2 (1986-1994)
Focus 2
Focus Turnier 1
Focus 1
- General information
- Vehicle device
- Owner's manual
- Faults en route
- Maintenance
- First maintenance
- Second maintenance
- Applications
- Consumables and spare parts
- Auto mechanic tips
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Engine seal parts
- Cooling system
- Exhaust system
- Supply system
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Front wheel drives
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body and coating
- Body elements
- Side doors
- Tailgate
- Salon elements
- Safety system
- Windshield wipers and washers
- Body Care
- Electrical equipment
- Instruments and motors
- Battery and alternator
- Egnition lock
- Engine management
- Headlights and lighting
- Switches and sensors
- Schematic diagrams
Focus Turnier 1
- General information
- Introduction to guide
- Car care
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Fuel injection (gasoline)
- Fuel injection (diesel)
- Ignition system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch and drive shafts
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Wheels and tires
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Heating and ventilation
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting and signaling
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
Focus 1
- General information
- Using the manual
- Identification codes
- Power unit
- Engine
- Engine 1.4/1.6 Zetec-SE
- Engine 1.6/1.8/2.0 Zetec-E
- Engine Duratec ST 2.0 l
- Engine Duratec 8V 1.6 l
- Diesel engine 1.8 l
- Engine cooling
- Fuel supply
- Accessory drive
- Launch system
- Ignition system
- Air and vapor
- Engine management
- Exhaust toxicity
- Exhaust system
- Automatic gearbox
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox iB5
- Mechanical gearbox MTX-75
- Mechanical gearbox MT285
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Wheels and tires
- Front axle axles
- Brake system
- Hydraulic brake
- Anti-lock braking system
- Steering
- Body and coating
- Body panels
- Body elements
- Salon elements
- Glass, frames and mechanisms
- Windshield wipers and washers
- Car sunroof
- Seat belts
- Body repairs
- Back elements
- Electrical equipment
- Climate control
- Heating and ventilation
- Instruments and control lamps
- Battery and alternator
- Audio system
- Headlights and lighting
- Power distribution
- Electronic Function Group
FordBook.ru © 2014-2024 • Mobile version • Interesting to read • Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU • Site search • Contact with administration
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •
Focus 1 • Focus Turnier 1 • Focus 2 • Mondeo 1 • Mondeo 1 and 2 • Mondeo 2 • Mondeo 3 • Mondeo 4 • Escort 3 • Escort 4 • Escort 5 • Fiesta 2 • Fiesta 4 • Taurus 1 and 2 • Fusion • Scorpio 1 • Scorpio 2 • Sierra •