Design and function of the ignition system
Both types of DOHC engine are equipped with an electronic ignition system:
- engines with carburetor fuel system: ESC II ignition system;
- injection engines: EEC IV ignition system.
ESC II ignition system
Wiring diagram of the electronic ignition system ESC II of the carbureted engine DOHC 2.0 dm3
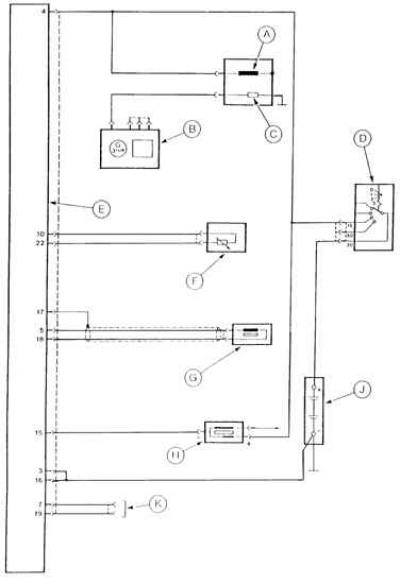
A - Fuel cut-off solenoid valve after engine shutdown, B - Alternator, C - Automatic carburetor resistor heater, D - Ignition switch, E - ESC II ignition control module, F - Coolant temperature sensor, G - Position sensor and engine speed, H - ignition coil, J - battery, K - fuel octane coding connector
This system contains:
- ignition distributor with a high voltage distributor and a non-contact Hall sensor that acts as a sensor for the number of revolutions of the crankshaft of the engine;
- ignition coil;
- vacuum sensor in the intake manifold;
- coolant temperature sensor;
- automatic transmission shift lever neutral position sensor (only in vehicles with automatic transmission).
The electronic ignition control module ESC II receives signals from these sensors and, on the basis of them and the data contained in its memory, selects the optimal, for the given engine operating conditions, the moment of current interruption in the primary winding of the ignition coil, and thereby the optimal ignition timing. Then it turns on the current in the primary winding and interrupts the current in it at the moment when ignition should occur in the next cylinder, again supplies current to this winding, etc.
The ignition timing is constantly adjusted in accordance with the received signals and the data contained in the memory of the electronic module.
In engines with a carburetor, the ESC II ignition control module also corrects the throttle position during idling depending on the speed, load on the engine (for example, engaging a gear in an automatic transmission or turning on the air conditioning compressor), the thermal state of the engine, as well as the throttle position.
Checking the elements of the ESC II ignition system
| Checked element | Measurement between contacts | Ignition | Meaning | Remarks |
| Crankcase ground connection | "16" and ground "3" and ground | Turned off | 0 - 0.5 ohm | |
| Fuel octane corrector | "7" and "16" "19" and "16" | Turned off | The resistance is infinite | Before testing, disconnect the ESC II module |
| coolant temperature sensor | "10" and "22" | Turned off | 37 kΩ at 20°C 4 kΩ at 80°C | |
| Throttle lever damper solenoid valve | "24" and "4" | Disabled Enabled | Infinite resistance 65 - 80 Ohm | If there |
| crankshaft position sensor | "5" and "18" "17" and "16" | Included | 300 - 500 ohms Infinite resistance | |
| Power supply of the ESC II module | "4" and "16" | Included | 10 - 14 V |
Attention! A method for checking the elements of the ignition system of a DOHC engine combined with a fuel injection system included in the EEC IV engine control system is given in the fuel injection section.
EEC IV ignition system
This ignition system functions on the same principle as the ESC II ignition system, only combined with fuel injection in the overall EEC IV engine management system, and the electronic control unit also controls the injection system.
Attention! The described ignition systems do not require adjustment.
Removal and installation of the distributor of ignition
Removal and installation of the distributor of ignition do not present big difficulties. The elements of the DOHC engine ignition system are shown in the figure.
Elements of the DOHC engine ignition system
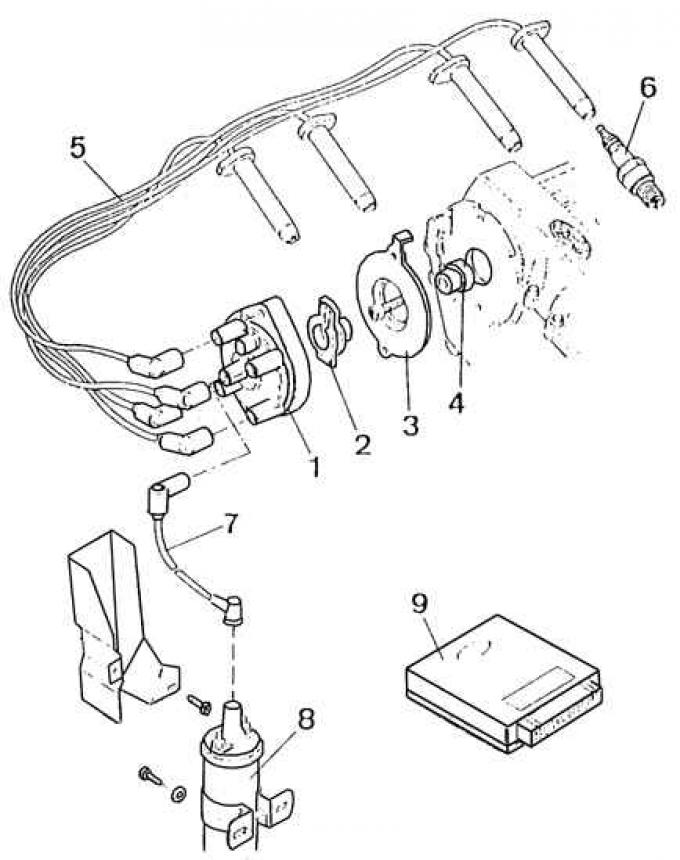
1 - cover, distributor, 2 - distributor rotor, 3 - plate, 4 - driver, 5 - spark plug high voltage wires, 6 - spark plug, 7 - ignition coil high voltage wire, 8 - ignition coil, 9 - electronic control module ignition
The ignition distributor can only be installed in one correct position.
Checking the elements of the ignition system
In a DOHC carbureted engine, disconnect the multi-pin connector of the ESC II ignition control module and use a multimeter to measure the resistance and voltage on the selected connector pins in accordance with the table below.
In the event of incorrect values of electrical parameters, before considering this element as damaged, the condition of the corresponding electrical circuit should be checked.
Visitor comments