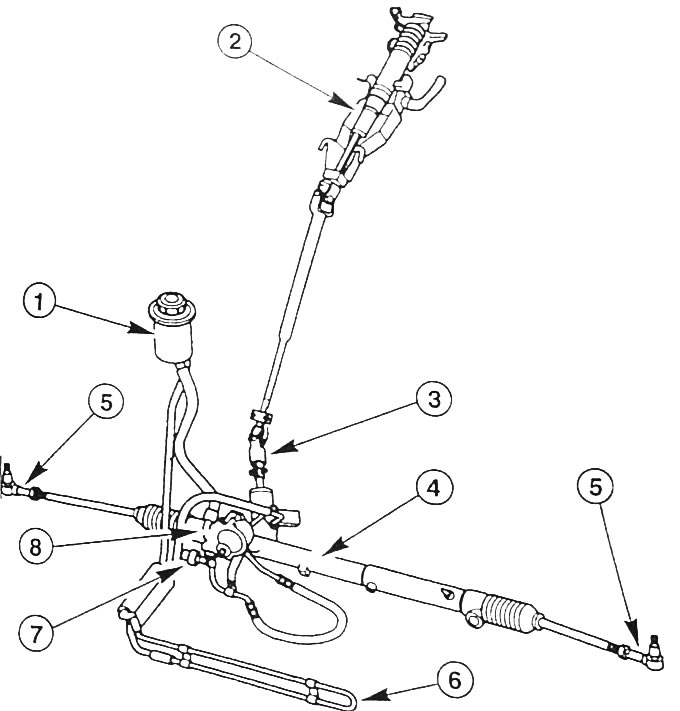
1 - hydraulic booster compensation tank
2 - steering column
3 - connecting universal joint
4 - steering mechanism
5 - tie rod end
6 - oil cooler
7 - hydraulic switch
8 - hydraulic booster oil pump
The steering system consists of a steering wheel, a steering shaft, a steering mechanism and steering rods. The steering wheel is screwed to the steering shaft, which transmits the movements of the steering wheel to the steering mechanism. In the steering mechanism, in accordance with the rotation of the steering wheel, the gear rack is mixed.
Each pinion of the gear rack is connected to a steering rod through a ball joint. Tie rods through ball joints and swivel bearings transmit steering forces to the front wheels of the car.
The steering gear rack is easy to move and should move without play from lock to lock. It is maintenance-free, but the bellows must be checked for flawless condition as part of maintenance.
Wheel steering is made easier by hydraulic power steering. The hydraulic power steering consists of an oil pump, an oil compensation tank and pipelines. The oil pump is driven by a V-belt from the engine crankshaft. The pump takes oil from the compensation tank and delivers it under high pressure to a valve located in the steering gear housing. The valve is connected to the steering column and directs oil, depending on the position of the steered wheels, into the corresponding chamber of the working cylinder. It puts little pressure on the piston of the gear rack and thereby increases the force generated by the driver on the steering wheel. At the same time, through the drain groove of the spool valve, the piston squeezes the oil from the other chamber of the working cylinder into the return line and through it back to the oil reservoir. Depending on the model and equipment, wheel steering is facilitated by a speed-dependent booster (Servotronic system). Due to this, when turning the steering wheel of a stationary car, the effort expended by the driver becomes less, and at high speed, on the contrary, as a result of a decrease in the amplifying effect of the amplifier, a better feeling of the road and a high sensitivity of the car to the steering wheel turn are achieved.
The driver's airbag is located in the steering wheel. In the event of a severe frontal collision, the control unit ignites a small igniter in the airbag unit, and the gases generated during the explosion inflate the air bag within a few milliseconds. This time is enough to dampen the collision of the driver rushing forward. The airbag then deflates within a few seconds as the gases escape through the openings in the bag.
Safety instructions
Always replace self-locking nuts. Welding and straightening work on steering parts is not allowed. Work on the air bag system must be carried out in a workshop, risk of explosion!
Visitor comments