Fuel injection system
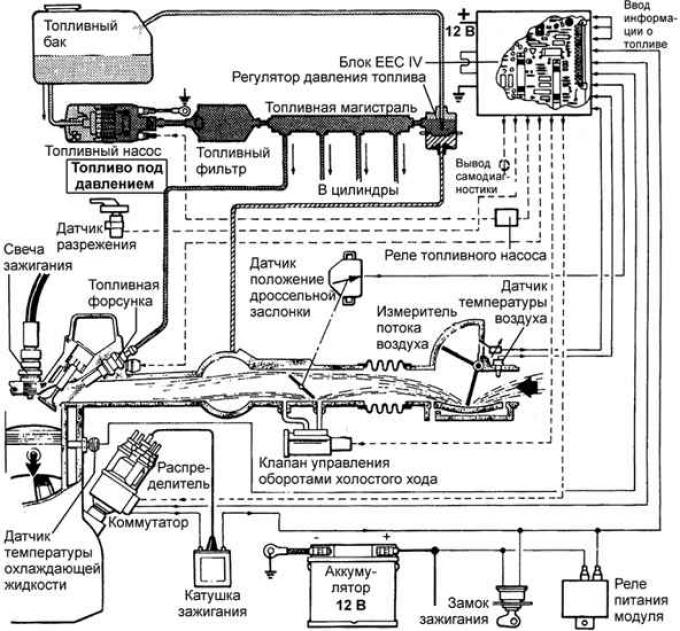
ONS engine fuel injection system
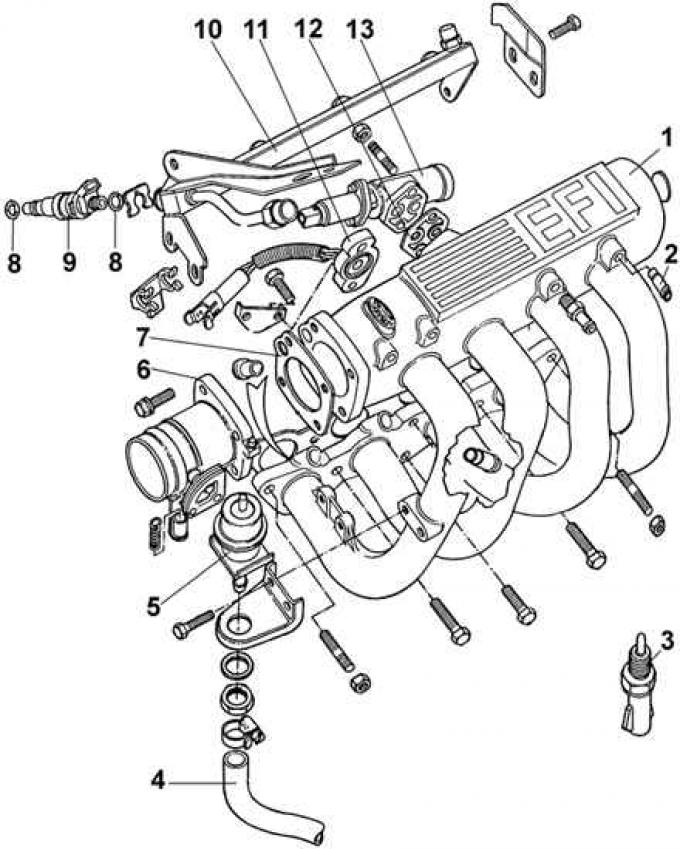
1 - inlet line; 2 – connection of a hose of the vacuum amplifier of brakes; 3 - coolant temperature sensor; 4 - fuel line; 5 - pressure regulator; 6 - throttle body; 7; 12 - gaskets; 8 - sealing rings; 9 - fuel injector; 10 - fuel distribution line; 11 - throttle position potentiometer; 13 - idle speed controller
DOHC engine fuel injection system
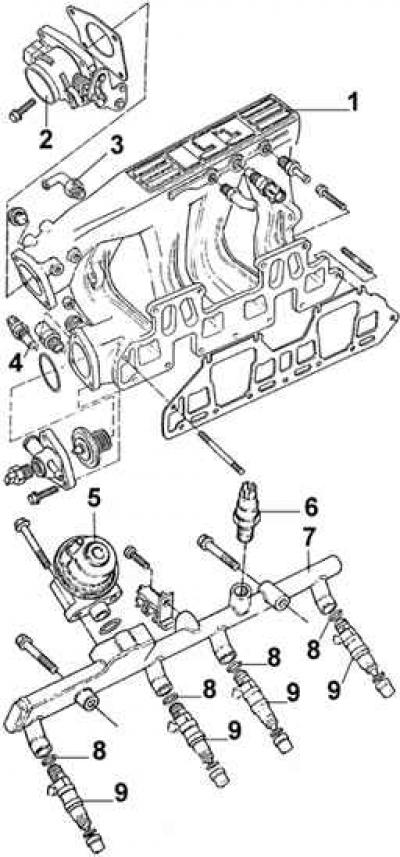
1 - inlet line; 2 - throttle body; 3 - idle speed regulator; 4 - coolant temperature sensor; 5 - pressure regulator; 6 - fuel temperature sensor; 7 - fuel distribution line; 8 - sealing rings; 9 - fuel injector
Fuel injection relay for V6 2.4 and 2.9 dm3
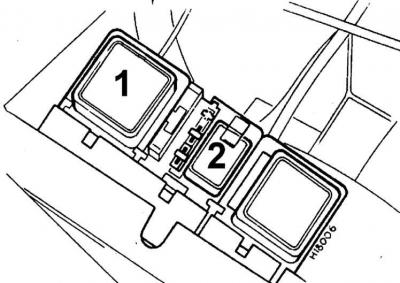
The relays are located under the instrument panel on the passenger side.
1 - power relay, 2 - fuel pump relay
Vehicles can be equipped with Bosch K-Jetronic or Bosch L-Jetronic fuel injection systems. Controlled by EEC IV module (Electronic Engine Control MK IV - electronic engine control), which also controls the ignition system.
Fuel under pressure developed by the fuel pump is supplied through the pressure accumulator and the fuel filter. The air flow is regulated by the throttle valve depending on the position of the accelerator pedal. The amount of air entering the engine cylinders through the flow meter is the main quantity that controls the mixture formation process.
The fuel injectors receive electrical impulses: one impulse per revolution of the crankshaft. The fuel injectors of the DOHC engine fire in pairs from the pulses of the EEC IV module and fuel is injected in a pair of injectors for every half-turn of the crankshaft. The duration of the pulse depends on the amount of injected fuel. The pulse duration is calculated by the EEC IV module based on information from various sensors. Each cylinder has one fuel injector.
Air drawn in by the engine passes through the airflow meter. V6 engines have two air flow meters. The flow meter plate in the meter deflects in proportion to the amount of flow: this deflection is converted into an electrical signal for the EEC IV module. Adjustable bypass channel ensures engine idling.
The throttle position sensor tells the EECIV module the throttle position and the rate of change of the throttle position, so that when the throttle is suddenly opened to accelerate the vehicle, additional fuel is supplied. To save fuel, there is a fuel cut-off system in engine braking mode.
The idle speed is controlled by a thermoelectric jet valve, which regulates the amount of air bypassing the throttle through an additional channel. The spool is controlled by the EEC IV module. Direct idle speed adjustment is not provided.
Sensors located on the engine provide accurate fuel metering in all engine operating modes at any ambient temperature. On models with an automatic transmission, the sensor registers the position of the backstage of the box from P - parking or N - neutral position, to D - forward movement, causing a corresponding change in idle speed. Additional DOHC engine sensors report fuel temperature, coolant temperature, vehicle speed to the EEC IV module (the sensor is located in the gearbox).
In the presence of an air conditioner, the signal from the compressor makes it possible to set the idle speed, regardless of the load created by the air conditioning compressor.
On models with a DOHC engine without a catalyst, the idle mixture is adjusted by a potentiometer directly connected to the EEC IV block. On DOHC engine models with a converter, the exhaust gas oxygen sensor allows the EEC IV module to control the air/fuel mixture to match operating parameters. Thus, manual adjustment of the mixture is not possible.
Models with a DOHC engine with a catalytic converter are equipped with an evaporative emission control system. The system prevents the release of gasoline vapors into the atmosphere. When the ignition is turned off, vapors from the fuel tank enter the charcoal box. When the engine is running, the EEC IV module opens the solenoid valve and they enter the intake manifold and mix with fresh air. This cleans the carbon filter. A special valve prevents intake air from entering the fuel tank.
The EEC IV module provides "limited mode" (LOS), which allows, in the event of a failure of the module or sensors of the fuel injection system, to drive the car, albeit with a loss of power.
From mid-1986, all models are equipped with an inertial fuel pump switch. The switch breaks the electrical circuit of the pump in the event of an accident or strong impact. The switch is located to the left of the trunk lid lock under a plastic cap. Turning on is done by pressing the button on the top of the switch.
Visitor comments