General information
Vehicle noise while driving cannot be avoided. The goal of all development efforts is to reduce wind noise. The quieter the noise produced by aggregates and components such as the engine, chain drive, tires, etc., becomes, the greater the wind noise heard when driving at high speed becomes.
In addition to general wind noise, there may be some noises that are heard as an annoying hiss or whistle. The causes of these noises may be due in part to manufacturing or repair factors. They are mainly caused by poorly installed elements that should be positioned and installed in the correct position.
The maximum noise audible inside a car is wind noise. As the speed increases, the sound level in the vehicle interior increases.
Normal Airflow Noises
At high speed, as air flows around uniform flat surfaces such as roofs, door windows, etc., turbulent air layers are formed in which changes in air pressure take place. Some of these pressure changes propagate in the form of sound waves and are carried into the interior of the vehicle through the door windows and seals. Here the noise is particularly loud due to the proximity of the window to the driver's or passenger's door. The noise is mainly expressed as a low roar that gets louder as the speed increases.
Noises partly caused by changes in the direction of the air flow and air flow around individual elements
If the air flows along the edge of the car, the air flow cannot completely wrap around the surface, and stall occurs at the edge. Whirlwinds are formed, which are destroyed again after some time or after passing a certain distance.
Change in airflow direction
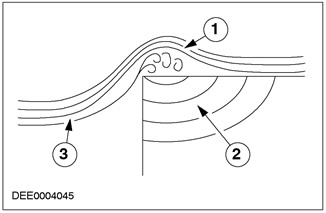
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Vortex |
| 2 | - | Sound wave |
| 3 | - | Flow |
The rise and fall of turbulence and the corresponding changes in pressure lead to the creation of sound waves. A similar effect can be observed on the rack «A» car. Here, the area where swirls usually form is directly above the door window. This makes it easier for the noise to get in (roar) into the car interior.
Swirl zone
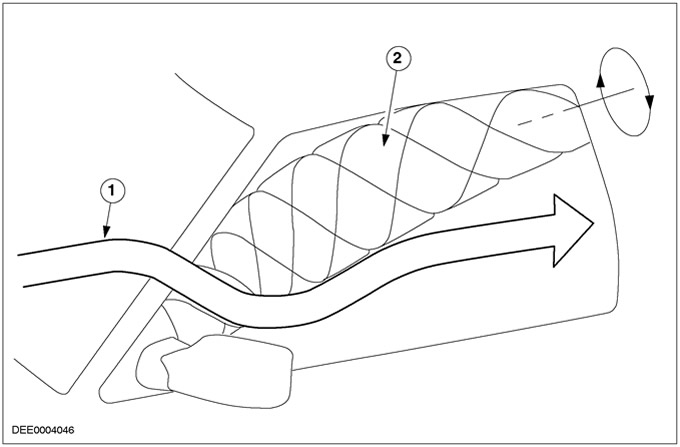
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Air flow |
| 2 | - | Swirl buildup |
A swirl is also formed under the vehicle and therefore a corresponding noise is generated. When air currents bypass small elements or pass through small gaps (e.g. through the radiator grille), the roaring noise becomes a whistle that increases in frequency and gets louder as speed increases.
Noise caused by seal vibration
Seals that do not have firm contact in the window and door areas can also lead to vibrations caused by pressure changes on the outside of the vehicle, which means noise is transmitted into the vehicle interior. The vibrating part of the seal works here in the same way as the diaphragm of a loudspeaker.
Start of hesitation (diagram)
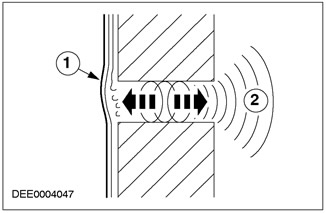
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | vibrating seal |
| 2 | - | Penetration into the car |
Resulting noise
Small leaks in the vehicle's interior sealing system allow a small amount of air to pass through. This leads to the creation «free flow noise» (air flow mixes with still air and this causes turbulence). Volume «free flow noise» increases strongly with increasing speed, and this can be heard as a whistle (e.g. when air escapes from a tire).
Noises in the cavities
If the body cavity is open to the outside of the vehicle, this can cause the volume of air in the cavity to resonate. The result depends on the volume of the cavity and the size of the hole. (For example, it is observed if you blow across the neck of the bottle).
Wind noise with sunroof open
Problem:
- When the sunroof is opened at a speed of approximately 60 km/h, low-frequency noise occurs (rattling).
Cause:
- When the sunroof is fully open, noticeable variations in air pressure occur inside the vehicle due to airflow over the opening.
Corrective action:
- At speeds above about 60 km/h, close the sunroof slightly until the rattling noise is no longer heard.
Wind noise through door seals
- Due to the air currents passing on the sides of the body and above the roof, the pressure outside is slightly less. Due to the heating and ventilation system, the pressure inside the car is slightly higher. This pressure difference at certain speeds causes, for example, doors to move away from the seals by several millimetres. If there is also a side wind affecting the movement of the vehicle, this influence is increased.
- Resulting gap differences are compensated by flexible door seals (when door seals are intact).
The ways in which outside sound enters the interior of the car
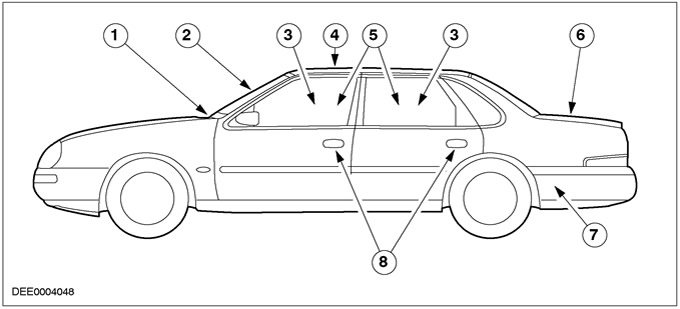
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Cabin ventilation |
| 2 | - | Windshield seal |
| 3 | - | door window seal |
| 4 | - | Sunroof seal |
| 5 | - | Door seals |
| 6 | - | Trunk lid seal |
| 7 | - | Cabin ventilation |
| 8 | - | door handles |
Wind noise
| Wind noise type | Where do they occur? | |
| Ordinary | Noise from normal air currents | Roof, window doors |
| Noises caused in part by changes in airflow direction and airflow bypassing individual elements | Racks «A», side mirrors, antenna, windshield wipers | |
| Strong | Noises caused by seal vibration | Door gaps too wide, door/window seals loose |
| Air outlet and passage noise | Leaks in the body seal system | |
| cavity noises | Unsealed body cavities | |
| Factors listed under heading «strong» require corrective action. |
Summary
The occurrence and intensity of wind noise on a vehicle depends on the shape and design of the various components.
There are two subjective methods of evaluation and service diagnostics that allow you to reduce the noise level and improve the character of the sound in the car interior:
- Reducing the Intensity of Noise Sources
- Reducing the length of the paths
In order to achieve an overall improvement in wind noise in the car, both factors must be taken into account.
Door, window and tailgate sealing systems have a major impact on the acoustic comfort in a car.
Problem sources in practice
Seal for driver's door and passenger's door
Diagnostics:
- Wind noise from upper door seal area
Cause:
- Incorrect alignment of the door frame to the roof
Corrective action:
- Re-align the door position with the door window open
- Check the contact area between the door seal and the seal surface. The width of the sealing zone must be at least 5 mm.
Correct gap between door and pillar «A» or door and roof
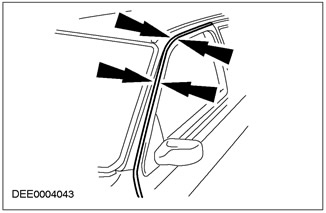
Tailgate Adjustment
Diagnostics:
- Wind noise coming from where the roof meets the top edge of the tailgate
Cause:
- Hinged tailgate set too high
Corrective action:
- Release the tailgate at the hinge point and move the tailgate further down. While doing this, pay attention to the gaps relative to neighboring elements.
- Reinstall the lock if necessary.
The luggage compartment door is located too high
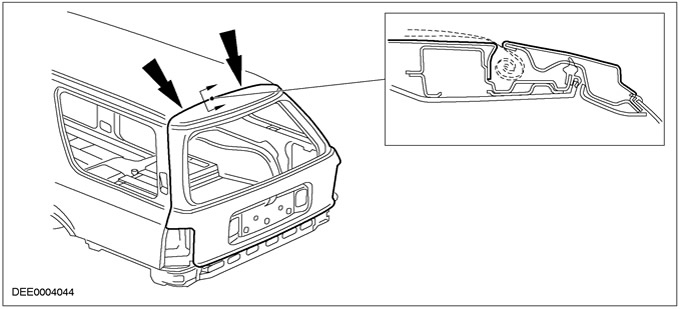
Sunroof adjustment
Diagnostics:
- Wind noise from sunroof
Cause:
- Incorrectly adjusted sunroof
Corrective action:
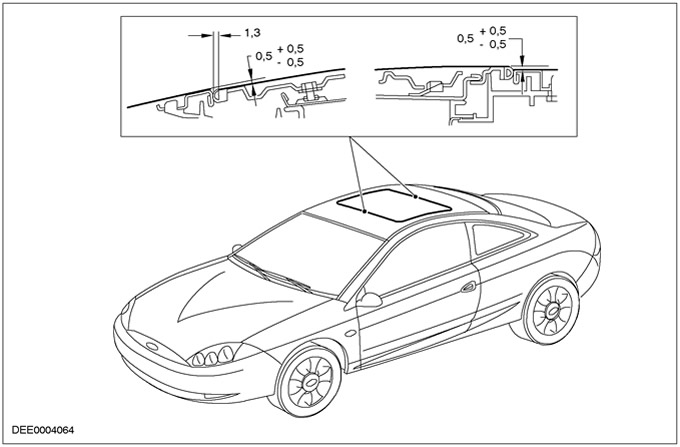
- Adjust the sunroof according to the following requirements:
- There must be an even gap around the entire perimeter of the sunroof.
- The sunroof must be adjusted to match the roof profile.
- The front edge of the sunroof should close flush with the roof surface or slightly lower.
- The seal around the perimeter of the sunroof must touch the sunroof cover evenly around the entire perimeter.
Sunroof cover adjustment
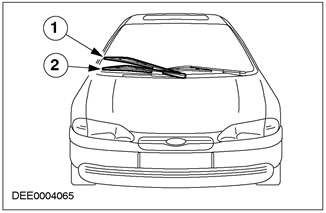
Right wiper adjustment
Diagnostics:
- Wind noise from right windshield wiper area
Cause:
- Wiper arm set too high
Corrective action:
- Remove the wiper arm from its axle and adjust it so that it is below the air turbulence zone that the air deflector has when it is in its original position.
Wiper arm adjustment
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Too high |
| 2 | - | Right |
Wind Noise Diagnosis Sequence (scheme)
1. Customer Complaint
- What is the customer's complaint and what details can he provide about wind noise?
2. Under what conditions does wind noise occur?
- 1. Sequence A: Diagnosis possibly based on detailed information provided by the customer.
- Take corrective action to eliminate wind noise.
- Carry out a road test of the vehicle to make sure the problem is corrected. The car should travel exactly the same path it traveled earlier when playing the wind noise.
- If corrective actions based on the information provided by the customer fail, further verification should be carried out at a workshop (see sequence B).
- 2. Sequence B: Diagnostics based on detailed information provided by the customer is not possible.
- Check for faults at a service station by contacting any relevant TSB (technical service bulletin).
- Visually check the outer seals, check the gaps.
- Visual inspection: Have any items been installed on the vehicle since the vehicle was manufactured or repaired after a collision?
- Perform diagnostics based on road test.
- Take corrective action based on the diagnosis.
- Perform another road test. The car should travel exactly the same path it traveled earlier when playing the wind noise.
- If this road test does not show that the work was successful, additional tests should be performed, such as a powder test, a stethoscope test, or an ultrasound test.
Diagnostics at the service station
Before carrying out repairs, a visual inspection of the vehicle should be carried out, paying special attention to the installation of the doors. When doors are finely adjusted, wind noise at high speeds can often be stopped (lifting doors over seals).
Checking with a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a simple and suitable device for detecting air leaks in the body. If the fan is turned on at the highest speed and all doors, windows and other openings are closed, the air pressure inside the car can be made greater than outside. The outside of the vehicle is then checked for escaping air flows.
Powder test
By coating the contact surface of the door seal with white powder, door seals that do not make good contact can be identified. To do this, carefully close and then open the door again. In this way, sealing surfaces that do not have contact will become visible.
Ultrasonic leak detector
Leaks can also be detected using an ultrasonic leak detector and sound generator. To do this, an ultrasonic generator is placed inside the vehicle and the outside of the vehicle is inspected using a leak detector tuned to the generator. The leak detector will easily show any leaks present.
Road test
The causes and onset of wind noise can often be identified by performing a road test. You should pay attention to the following points:
- Choose a dry, flat and straight road with as little traffic as possible.
- Make sure your tire pressure is correct to avoid tire noise.
Movement technique
- Carry out a road test in all speed ranges using the highest gears (fourth or fifth).
- The road test should be performed by two people and different seating positions should be tested.
- Prepare vehicle if necessary (use adhesive tape to cover the required areas).
- During road testing, pay particular attention to door openings and door seals.
Visitor comments