General information
Care must be taken to preserve the corrosion protection material applied during the manufacture of vehicles and / or restore the protective layer during and after body repairs. Only a long-term guarantee against through-rusting is provided (refer to Warranty/Service Booklet).
Only Genuine Ford body parts and repair materials should be used for body repairs (sealant, paint, etc.), approved by Ford.
All elements of the Ford body are cathodic coated. Individual elements of the body are galvanized on one or both sides (in different areas depending on the car model).
Together with the flexible paint coating, this guarantees optimum, high resistance to corrosion caused by impacts from small objects such as gravel.
NOTE: If possible, the individual protective layers should not be damaged or destroyed by grinding or other mechanical operations (zinc, cathodic coating) Ford body parts.
Each original body assembly is embossed with the Ford logo for identification. This symbol is a registered trademark of the manufacturer; it is also required for any subsequent warranty claims.
Genuine Ford Part
If the body needs repair, you must follow the repair instructions given in the specific model-specific chapters of this manual and the instructions given in the Paint and Corrosion Protection manual.
In case of cracks, «hairline» in the connecting areas of the body after straightening work (e.g. on door hinges), it is necessary to restore the corrosion protection provided during the manufacture of the vehicle. If necessary, completely restore the paintwork. The same applies to the editing of body elements with a characteristic relief (e.g. gender). If necessary, replace or finish the paintwork, sealing rollers and underbody protection.
After repair, any interior surfaces that are no longer visible or accessible should be primed and should be done before cavity mastic is applied. Internal surfaces should be coated evenly; to do this, carefully treat the entire cavity with a spray (twice, with intermediate drying).
If body panels are subjected to intense heat during repair, this invariably leads to damage or even destruction of the structure of the corrosion protection material. If heat is used, the effectiveness of the cavity protection material is reduced. Therefore, the revision of damaged areas is mandatory.
Weld areas should be cleaned before applying corrosion protection.
Corrosion protection measures to be taken when replacing body parts are described on the following pages.
Corrosion protection of new elements
All new items should be inspected for shipping or storage defects such as scratches or dents. The following operations may be required, depending on the extent of the damage:
1. Undamaged new item
- Do not scrape the cathode primer. Clean thoroughly with silicone remover and wipe dry.
2. Slightly damaged new item
- Scratches.
- Finely polish surrounding surfaces.
- Clean thoroughly with silicone remover and wipe dry.
- Apply anti-corrosion primer to exposed areas.
3. Damaged new item (bulges, dents)
- Straighten dents and polish to a metallic sheen.
- Apply polyester putty (only on bare metal surfaces).
- Apply finishing putty.
- Lightly polish the entire element.
- Clean thoroughly with silicone remover and wipe dry.
- Apply anti-corrosion primer to exposed areas.
Depending on the vehicle, the flanges of the hood, doors, tailgate and trunk lid should be sealed using flange sealant. Detailed information is contained in the body repair manuals for specific models.
After repairs, the exterior paintwork must be restored, working as described in the Corrosion Protection and Painting Manual.
Welded elements
Using a rotating wire brush, remove soil from the inside and outside of the area to be welded. Be careful not to damage the zinc coating when doing this.
NOTE: The areas to be cleaned should be as small as possible and the corrosion protection material applied during the manufacture of the vehicle (cathodic soil), should be preserved to the maximum extent possible.
NOTE: The welding primer must be well mixed before application.
Thoroughly clean the repair area (silicone remover). Apply welding primer evenly to all flanges to be welded (old and new elements).
NOTE: The welding primer must be dry before welding.
Apply welding primer
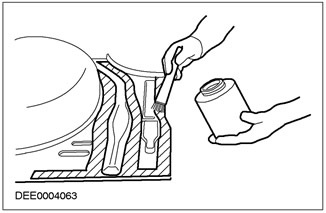
The weld reinforcement should be removed after welding, being careful not to weaken the material.
Any roughness in the joints is removed by using lead loading.
If necessary, using spot welding, weld the missing T-pins to hold the trim tape clamps in position. To avoid corrosion, the car should be completely cleaned of abrasive dust and metal chips.
Clean and prime all interior areas and areas to be sealed.
Seal all welded areas and connections, apply a coating to protect the bottom.
NOTE: The primer must be dry before applying sealing mastic or underbody protection. Do not use solvents when applying sealant (mask won't dry).
The sound deadening mats and cavity foam that are installed at the time of manufacture of the vehicle should be replaced.
After staining, apply cavity protection material to all cavities in all parts that have been replaced (especially in the area of welds).
Partial replacement
The procedure to be followed for partial replacement of elements is the same as described in section «Elements to be welded».
The main difference between partial replacement of elements and complete replacement of elements is that in the first case there are more problems with preparation for making end or lap joints.
- When cutting body parts, attention should be paid to adequate removal of paint and zinc coating on internal areas. This is especially true for hard-to-reach interior areas.
- To ensure the quality of the weld, it is important that the inside is clean metal. Zinc and paint residues in the area of the weld are burned and this causes porosity during the combustion process.
- If the zinc layer and paintwork is not removed, the zinc and paint will burn during the welding process. The soot produced prevents satisfactory cavity protection.
Procedure
- The paint layer should be removed to a width of 30 mm along the weld line using a rotating wire brush.
- This operation should be performed on both new and old parts of the body.
- Depending on the body element, a 10 mm wide zinc layer should also be removed along the weld line.
NOTE: If the cavity is small, a flat squeegee or wire brush can be used instead of a rotating brush. Do not use an angle grinder that weakens the structure.
Application of cavity protection material on the door sill after partial repair
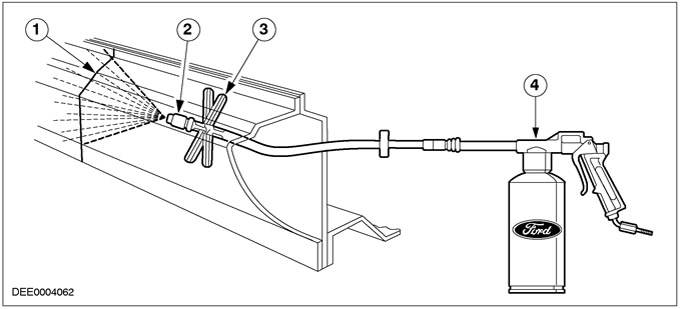
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Weld bead |
| 2 | - | spray head |
| 3 | - | spacer element |
| 4 | - | Spray |
To protect areas that are not accessible for applying cavity mastic, a hole can be drilled in an appropriate location. The diameter of the hole depends on the size of the plugs you have. When drilling, be sure to make sure that no chips remain in the cavity (if the chips remain, it will lead to rust). The edge of the hole should be treated with mastic for cavities. Then install the plug and seal using a car underbody anti-corrosion coating.
Classification of various corrosion protection measures for dent removal
| Corrosion protection method | External surfaces | Available interior surfaces | Inaccessible interior surfaces |
| Coloring | X | X | |
| Cavity Protection | X |
Classification of various corrosion protection measures for the installation of new elements
| Corrosion protection method | Weldable flanges before welding in the required position (contact surfaces) | All exposed cleared areas | Accessible area of welded flange | Inaccessible area of the welded flange |
| welding primer | X | |||
| Coloring | X | X | ||
| Curved edge protection | X | |||
| Cavity Protection | X |
Visitor comments