Power system diagram
The system is designed to clean and supply atomized fuel to the engine cylinders in the amount necessary for the corresponding mode of operation.
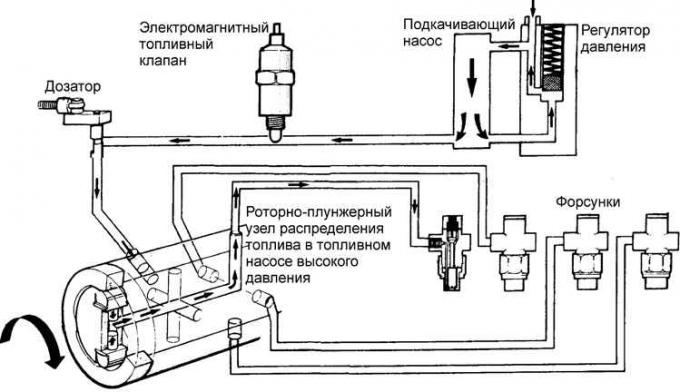
The fuel system includes a rear-mounted fuel tank, fuel filter, high pressure fuel pump, injectors, high and low pressure fuel lines.
With a booster pump built into the injection pump, fuel is taken from the tank and sent to the filter. The filter retains mechanical impurities and water contained in the fuel. A manual fuel pump is mounted in the fuel pump housing. After being cleaned in the filter, the fuel enters the high pressure fuel pump.
The amount of fuel supplied to the cylinders is regulated by a dispenser controlled by a cable from the accelerator pedal. The injection advance angle varies with engine speed.
There is a solenoid valve to stop the engine. When the engine is started, a voltage of 12 V is applied to the valve winding, the valve opens and passes fuel to the pump and injectors. When the engine is turned off, turning the key in the ignition lock turns off the fuel valve and shuts off the fuel supply.
A high-pressure fuel pump delivers fuel through pipelines to injectors that are installed in the cylinder head near the combustion chambers. The injectors inject fuel into swirl chambers where the fuel is ignited.
Injectors are a valve that opens at a strictly defined fuel pressure (110–120 bar). The atomizer, located at the lower end of the nozzle, forms a torch of sprayed fuel of the required shape. The fuel is cut off by a needle under the influence of the nozzle spring. The atomizer and needle are a precision assembly and must be handled with care when repairing. Excess fuel after cut-off seeps along the needle, lubricating it and, through the return pipeline, is discharged into the tank.
Serviceability and correct adjustment of injectors are very important for the normal operation of the engine. If the nozzle atomizer does not provide the desired shape of the flame or a bad cutoff occurs, the engine starts to work with vibration, strong mechanical knocks appear, and smoke increases.
Attention! The injection pressure is an adjustable parameter. During the operation of the engine, the injection pressure often drops, so the nozzle must be checked periodically and adjusted if necessary.
It should be noted that nozzles from different engine models are externally the same, but have different characteristics, in particular, the shape of the torch, so new nozzles should be used only those that are designed for this model.
To facilitate the start of a cold engine, a system is used to improve the ignition of fuel in the cylinders at the time of starting. Glow plugs are installed in the swirl chambers of each cylinder. Before starting the engine, they are energized, which indicates the ignition of the control light on the instrument cluster. Within a few seconds, the candles heat up to a high temperature and the control lamp goes out, which serves as a signal to start the engine. Hot plugs raise the temperature in the swirl chamber and make it easier to ignite the fuel. It should be noted that the candles do not turn off immediately after starting the engine, but after some time, allowing the engine to enter normal operating mode. The failure of even one candle leads to difficult starting of the engine, with interruptions in operation and strong vibration.
The fuel system on diesel engines is usually very reliable. The main condition for normal and durable operation is the purity of the fuel used and the absence of water in it.
Visitor comments