Torque specification
| Name | Nm | lb-ft | lb-in |
| Wheel sensor bolts | 9 | - | 80 |
| Nuts of fastening of brake pipelines to the main cylinder (M10) | 17 | 13 | - |
| Fastening the brake pipeline to the hydraulic control unit | 11 | 8 | - |
| Fixing the hydraulic control box to the bracket | 9 | - | 80 |
| Fixing the bracket of the hydraulic control unit to the body | 25 | 18 | - |
| Bolt of fastening of an arm of the gauge to a body | 4 | - | 35 |
| Bolts of fastening of an arm of the gauge to a body | 7 | - | 62 |
| Yaw Sensor Nuts | 8 | - | 71 |
Description and principle of operation
The yaw control function recognizes critical driving conditions such as a panic reaction in dangerous situations and maintains vehicle stability by individually braking each wheel and intervening by the engine management system, without the need for the brake and accelerator pedals.
The heading stability feature is an optional feature known as the Electronic Heading Keeping Program (ESP), relating to the anti-lock braking system (ABS), traction control system (TCS) and electronic brake force distribution (EBD). While the ABS/TCS function controls wheel slip when braking and accelerating (longitudinal dynamics), active yaw control keeps the vehicle stable on the selected course.
Sensors measure steering wheel position, brake master cylinder pressure, yaw rate (yaw rate) and lateral acceleration of the vehicle (lateral acceleration). This allows the driver's intentions to be correlated with the instantaneous behavior of the vehicle, and in the event of a loss of stability, the yaw control program can initiate appropriate corrective actions.
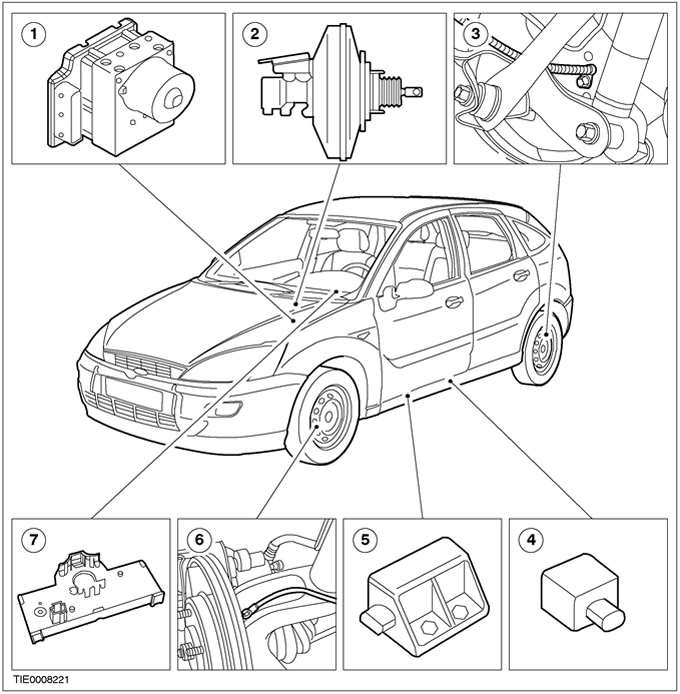
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | Hydraulic control box | |
| 2 | Active vacuum brake booster and brake master cylinder with pressure sensors | |
| 3 | Rear wheel sensor | |
| 4 | Lateral acceleration sensor | |
| 5 | Yaw sensor | |
| 6 | Rear wheel sensor | |
| 7 | Steering wheel sensor |
Visitor comments