Vehicles with 75 hp diesel engine or 90 hp
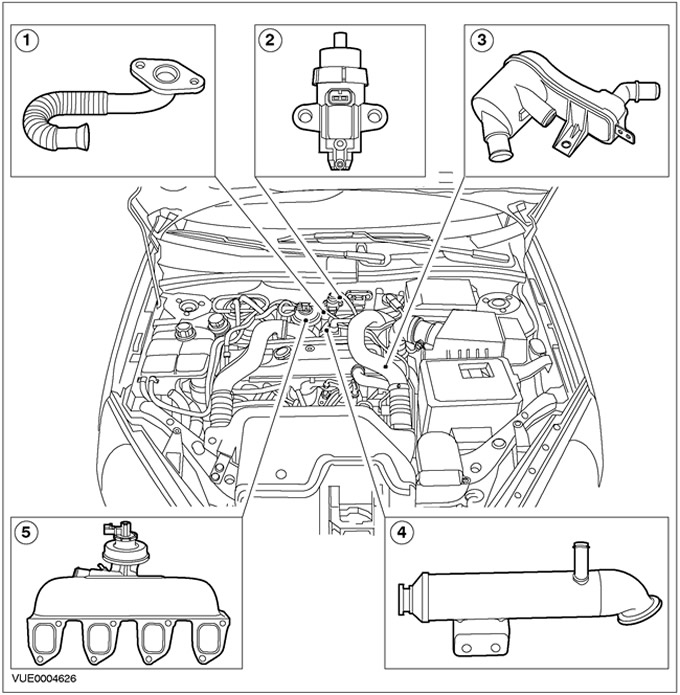
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Exhaust gas recirculation pipeline (EGR) |
| 2 | - | Electronic vacuum regulator EGR |
| 3 | - | Crankcase ventilation oil separator (PCV) |
| 4 | - | EGR cooler |
| 5 | - | Intake manifold |
Vehicles with a 100 HP diesel engine
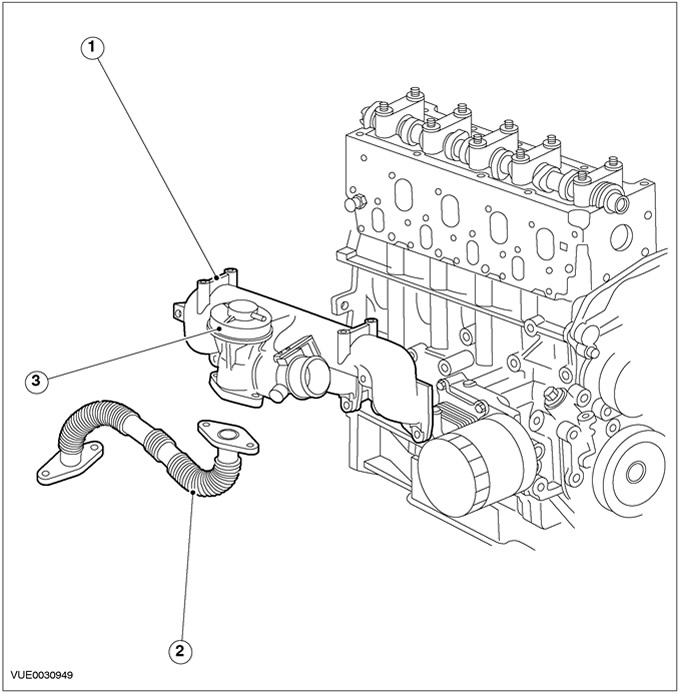
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Intake manifold |
| 2 | - | air damper |
| 3 | - | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Cooler (EGR) |
| 4 | - | EGR cooler clamp |
| 5 | - | EGR valve |
Vehicles with a 115 hp diesel engine
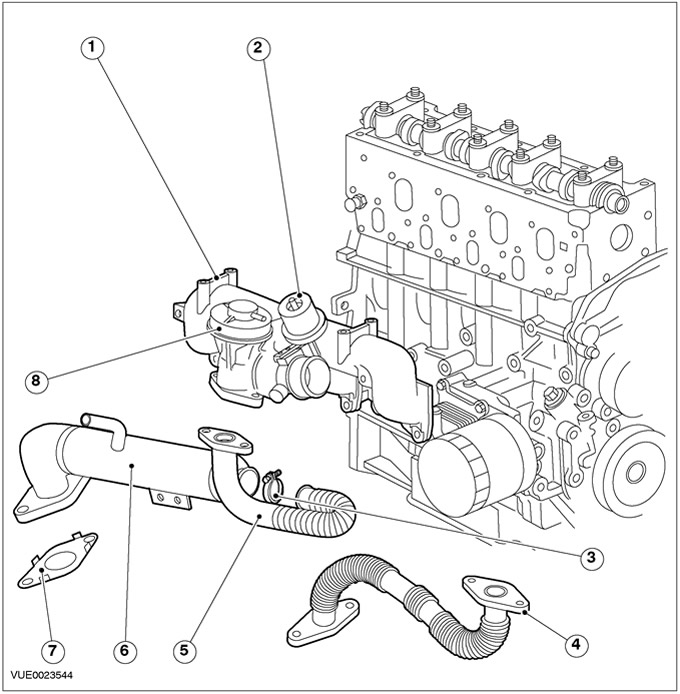
| Pos. | Spare Part No | Name |
| 1 | - | Intake manifold |
| 2 | - | air damper |
| 3 | - | Exhaust gas recirculation pipe clamp (EGR) to EGR cooler |
| 4 | - | EGR pipeline |
| 5 | - | EGR cooler |
| 6 | - | Gasket between EGR cooler and exhaust manifold |
| 7 | - | EGR valve |
Forced crankcase ventilation (PCV)
The PCV system conducts crankcase gases through the engine, where they mix with incoming air.
The crankcase ventilation system is completely sealed. All combustion gases that enter the crankcase pass through hoses to the oil separator and then from under the engine cover to the air intake system.
The positive crankcase ventilation system helps to reduce the level of hydrocarbon emissions from the engine.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
The EGR system conducts a measured amount of exhaust gases through the engine, where they mix with the incoming air.
Powertrain control module (PCM) controls the vacuum control valve with ground pulses. This regulates the size and duration «vacuum signal», supplied to the EGR valve (EGR), which allows you to adjust the height of the valve lift and the duration of its opening.
The EGR system includes an EGR cooler that is installed in the engine's cooling system. The EGR cooler cools the recirculated exhaust gases, thereby lowering the temperature in the combustion chamber and reducing the formation of NOx (nitrogen oxides).
Visitor comments