Mondeo selects gears with a cable.
In this chapter, you will learn how the Mondeo «sends» its engine power to the front wheels. The fuel transfer system, in particular, consists of a flywheel with a clutch, a gearbox and a final drive. In order for all these components to interact properly, they are connected by a precisely matched system of friction pads, shafts, bearings, gears and joints. How much force actually reaches the wheels depends primarily on engine power «your his» accelerator. However, the accelerator contributes little to this if the engine speed is not consistent with the current speed - each internal combustion engine «obedient» only in a limited speed range. So that you can theoretically «better understand your Mondeo», in the chapter Engines we have presented different power curves. If you want to drive while saving fuel, then you need to accelerate quickly and quickly shift to the next high gear: try to constantly coordinate your speed with a gear in which the engine speed is close to maximum torque.
To ensure that the torque and speed are as possible «became like-minded», they are assisted in the Mondeo by a fully synchronized five-speed gearbox (MTX-75). In combination with the 2.0-liter Duratec-HE V6 engine, Ford offers an electronic variable four-speed automatic transmission with an accelerator and torque converter lock-up clutch as an alternative (CD4E).
«Conductor's stick»: gear lever in detail
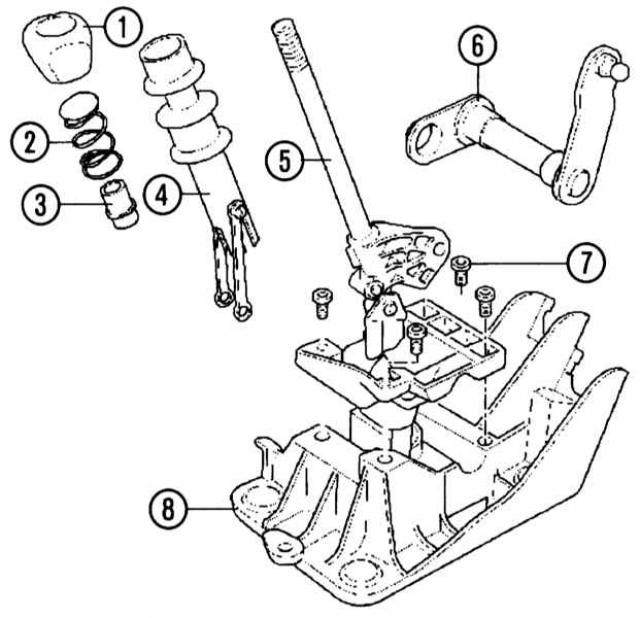 |
|
1 - Switch handle,
|
5 - Gearshift lever with the upper housing of the linkage system and gearshift levers,
|
Gears for traction forces
To out «resting states» accelerate without problems, the drive wheels need as much torque as possible. If you have already looked at the power curves, then below 1500 rpm, at least for carbureted engines with torque, it is still not so good: using «quiet gears» first gear makes it easier for the engine to jump to high revs and propel the Mondeo. When installing the fourth - and even fifth - gear, unfortunately, the opposite is true: in both gears, «transfer to speed». Compared to the speed of the drive wheels, the engine rotates slowly high in these gears. In other words: the gearbox changes the engine speed closer to the desired speed of the drive wheels.
«branch» engine from gearbox - clutch
With every start-up or gear change, the power flow between engine and gearbox is interrupted for a short time. In cars with a manual transmission, the clutch is designed for this. It provides «soft» starting and smooth shifting due to the fact that it equalizes the different speeds between the crankshaft and the transmission drive shaft. Somewhat wasteful functions «joint game» planetary gears and automatic transmission. Each switching process here takes place without interruption of the traction forces.
Transmits engine torque - hydraulically in gearbox - torque converter
Instead of a conventional friction clutch, a hydraulic torque converter coordinates the starting process and «change of course». In the Mondeo, this is ensured by the coordination of five solenoid valves, which, based on a common steering gear housing, form «management» automatic transmission:
- pressure switch (via pipeline pressure control mechanism),
- switching control (via control valve with position control),
- modulated actuation of the torque converter - clutch bridging,
- switching process control 3 – 2 and...
- ...forced idle mode with engine braking function.
In this sector, the torque converter not only operates very comfortably, but also without mechanical wear – at least under normal loads.
Torque Converter with Clutch to Block Torque Converter
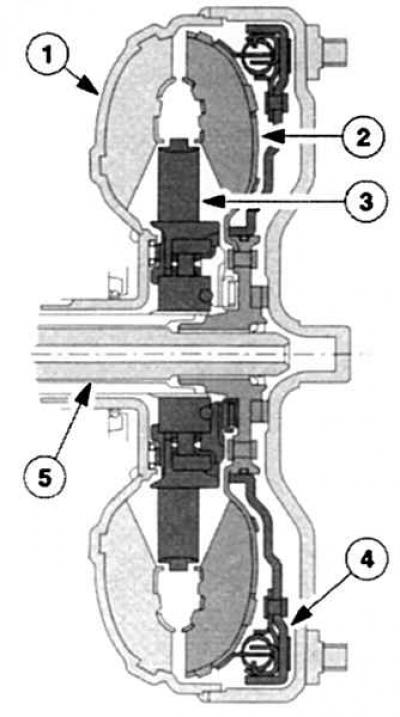 |
|
1 - Converter housing and pump wheel,
|
4 - Clutch for blocking the torque converter,
|
The last resort before the drive wheels is the main gear
The final drive is the last resort that the engine-generated torque passes through on its way to the drive wheels. Its task is to ensure that the rotational speed, «incoming» from the gearbox, translate into «slow», the torque is thereby increased and evenly distributed to the drive wheels.
Visitor comments