Try to collect all possible information about the proposed purchase. This will help you with the advice of more experienced motorists, especially those who service the car on their own (however, beware of overconfident «masters», who can give peremptory advice on any occasion). Contact a car service master, especially if he will repair your car. You can read serious automotive magazines: they publish special tests of components and assemblies.
Note. Going to the store to purchase a spare part, find out the VIN code of the car, by which the seller will look for it.
When initially assessing the quality of prospective spare parts, the manufacturer of the assembly or assembly, as well as their originality, should be taken into account. Original spare parts recommended by the vehicle manufacturer and distributed through the dealer network are usually carefully packaged, have a quality certificate, an anti-counterfeiting system, a warranty period and the vehicle manufacturer's logo. These parts are more expensive, but trying to save money can result in costly repairs.
Non-original spare parts are produced by companies that specialize in one specific group (e.g. car windows, electrical components, brake pads). They are significantly cheaper than original ones, but their use in a car may lead to a denial of warranty service if there is no official approval for their use in a manufacturer's car.
Note. Purchased spare parts for the car are conditionally divided into two categories:
- spare parts depending on the mileage of the car: brake pads, tires, drive belts, fuel, air and oil filters, spark plugs;
- spare parts, the condition of which depends on the operating conditions of the car: brake mechanisms, optics, engine parts, transmissions, suspension joints, steering parts and engine exhaust systems.
Engine oil
When choosing engine oil, first of all, you should be guided by the recommendations and requirements of the manufacturer for the quality and manufacturer of engine oil.
Modern motor oils, consisting of base oils and a selected set of additives, are divided into two main types:
- mineral (obtained by distillation from petroleum) Their viscosity is highly dependent on temperature. To stabilize the properties, various additives are used, which, in turn, are quickly destroyed due to high mechanical and thermal loads, reducing the life of the oil;
- synthetic (obtained by chemical synthesis) – possess high uniformity and stability of properties. They remain thinner in cold weather and thicker in hot weather, burn less in the engine, form fewer deposits, and last longer.
Note. Synthetic oils do not destroy engine seals, however, when they are used, leakage through worn seals may occur due to the greater fluidity of synthetic oils compared to mineral oils.
Note. The service life of synthetic oils is only slightly longer than mineral oils. The rapid darkening of the oil only indicates its good cleaning properties and a contaminated lubrication system.
An intermediate position is occupied by the so-called semi-synthetic oils. They are made on a mineral basis, but with the addition of synthetic components, so they are close in quality to synthetic oils, but much cheaper than them.
One of the main properties of engine oil is its viscosity, which determines the temperature range of application of engine oil. At low ambient temperatures, engine oil must have a low viscosity in order to start the engine and supply engine oil to its components. At high temperatures, the engine oil must be more viscous in order to maintain the required oil pressure in the lubrication system. By viscosity, motor oils are divided into three types:
- winter - due to their low viscosity, they provide engine start-up and lubrication of the main components at negative ambient temperatures;
- summer - due to their high viscosity, they provide lubrication of engine parts at high ambient temperatures;
- all-weather - at low ambient temperatures they have the viscosity of winter oils, and at high temperatures they have the viscosity of summer oils.
Attention! The use of motor oils is strictly prohibited:
- not intended for gasoline automobile engines;
- with inappropriate performance characteristics;
- viscosity not appropriate for the season (according to SAE classifications).
Greases
Greases are used to reduce friction and, as a result, to reduce wear of parts in vehicle components in which it is impossible or impractical to create oil circulation. Grease easily penetrates into the contact zone of rubbing parts and is held on their surface. The main advantages of greases are a wide temperature range of application compared to motor oils, the ability not to flow out or be squeezed out of unsealed friction units. The disadvantage of greases is the retention of mechanical and corrosive wear products, which increase the rate of destruction of rubbing surfaces, and therefore worsen heat removal from lubricated parts.
When choosing greases for a specific vehicle component, one should know their physical characteristics, the effectiveness of lubrication of rubbing surfaces and compatibility with materials in contact with the lubricant.
Attention! Greases of different compositions must not be mixed with each other due to a possible change in their physical characteristics (thinning and lowering the dropping point).
Coolants
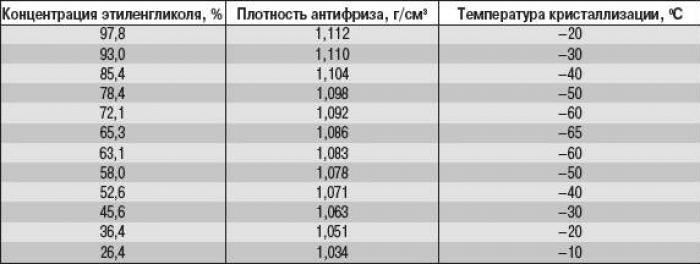
It is recommended to fill in the cooling system of Ford Fusion vehicles with a low-freezing liquid - antifreeze - an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol with the addition of additives and a neutral dye.
Ethylene glycol in concentrated form is highly corrosive, its boiling point is +170°C. Due to the fact that the crystallization temperature of ethylene glycol in concentrated form is -20°C, it is diluted with distilled water to lower the crystallization temperature (tab. 13.1).
To neutralize corrosive activity, special additives are added to ethylene glycol. To distinguish it from other operating fluids and to make it easier to determine the level in the expansion tank of the engine cooling system, a dye is added to the antifreeze.
Table 13.1. Ethylene glycol concentration depending on the required antifreeze crystallization temperature
Brake fluid
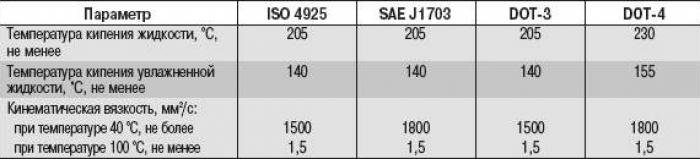
In accordance with the operating instructions in the brake system of your car, brake fluids are used that comply with the international DOT-4 class and are designed for use in vehicles with increased dynamic characteristics. When buying brake fluid, you should be guided by the following recommendations:
- purchase brake fluid only of the class recommended by the car manufacturer;
- carefully inspect the container, it must be airtight, and the protective membrane must be made of foil.
Brake fluids are classified according to their boiling point and viscosity (tab. 13.2).
Table 13.2. Classification of brake fluids by viscosity and boiling point
Fuel fine filter
Gasoline poured into the fuel tank may contain water, dirt, metal particles, rust, which, if the fuel is not cleaned, lead not only to contamination of the engine power system, but also to wear of the fuel equipment, and a decrease in vehicle performance. The main function of the fuel filter is to keep various contaminants from entering the engine power system.
The fuel fine filter must meet the following requirements:
- effectively capture fuel contaminating particles;
- to separate water entering the fuel to prevent corrosion of fuel injectors.
- The fuel filter is mounted on the bottom of the vehicle on the fuel tank and can be replaced separately.
Air filter
The air filter, installed in the central part of the engine compartment, serves to clean the air entering the intake pipe. It must meet the following requirements:
- effectively retain particles that pollute the incoming air;
- have low airflow resistance.
For information on the type of air filter element, contact your Ford dealer or parts dealer.
Engine oil filter
An oil filter installed in the engine lubrication system serves to clean the engine oil. It must meet the following requirements:
- accumulate and retain metal-containing and carbon-containing particles formed in engine oil during engine operation;
- have low hydraulic resistance, which allows, with a high degree of purification of engine oil, to supply it to the rubbing pairs of the engine;
- the oil filter housing must be strong enough not to collapse with a sharp increase in pressure in the engine lubrication system and abnormal mechanical impact.
For information on the type of oil filter, contact your Ford dealer or parts dealer.
Spark plug
Information about the applied spark plugs is presented in sec. «Maintenance» (see «Replacement and maintenance of spark plugs»).
Visitor comments