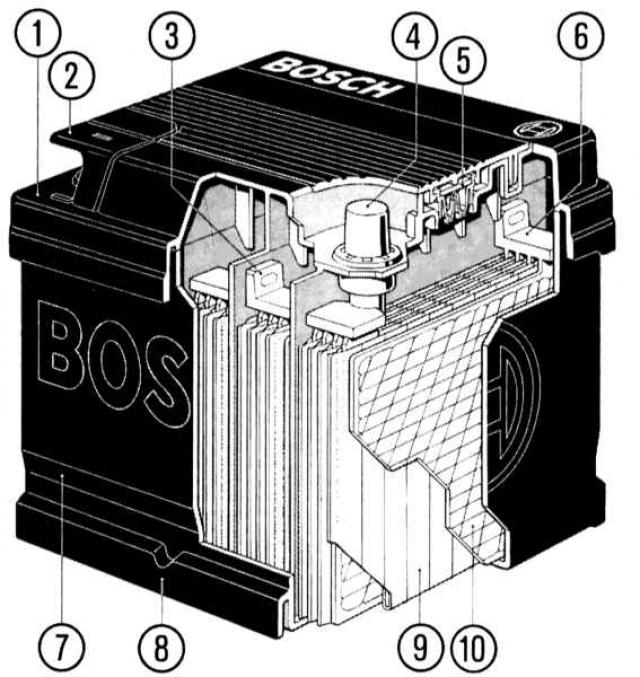
Power package: maintenance-free battery
The six connected cells in a row are the heart of the 12-volt starter battery. A single cell consists of a combination of positive and negative plates that chemically produces a voltage of about two volts. The plates, in turn, consist of gratings made of a lead-antimony alloy, which are filled with an active mass. The sides of the positive plate contain lead peroxide, the reagent of the negative plates is pure lead. Between them there is a separator - it separates the plates among themselves, however, the battery fluid (electrolyte) can circulate through microscopic pores. The electrolyte is a conductive liquid, which consists of almost 37% concentrated sulfuric acid and 67% distilled water.
Saves electrical energy - rechargeable battery
In protected «innards» energy processes take place in the battery - chemical energy is converted into electrical energy in the battery. Main consumer «power juice» is the starter. Its tractive effort depends on the stored energy that the battery produces and stores while driving: depending on the type of starter motor, the starter «sucks» up to 2000 watts - for this, the battery must be in good «physical» form.
With every cold start, most of the immense power goes to internal friction losses. On the contrary, the starter realizes the start of a heated engine with the help of a fifth of the power required to start a cold engine. All oscillating and rotating parts interact better with each other due to the greater «places», A «warm» the oil is more flexible than the cooled one, which at first circulates extremely unhappily in the circulation system.
|
TECHNICAL DICTIONARY |
Battery - concepts and norms
The designation is located on the body and characterizes the parameters of the battery. For example, «12V 70 Ah 210A» (12V (B) = rated voltage; 70 Ah (Ah) = nominal capacity; 210A = starter discharge current.
Rated voltage: Total voltage output (dimension «IN»). All Mondeo models are set to 12 V. The actual voltage depends, of course, on the degree of discharge of the battery. It may be greater or less than the nominal value.
Rated capacity: Determines the storage capacity of the battery (dimension «Ah»). This is the capacity that a fully charged battery can have at 27°C for 20 hours without the cell voltage dropping below 10.5V (final discharge voltage). The parking light in your car, for example, consumes 25 watts. With an on-board network voltage of 12 volts, the battery generates a current of 2.08 A, according to the formula «current (A) = power (Tue) /voltage (IN)». With a 70 Ah battery, your Mondeo can theoretically be left with the parking light on for about 30 hours. The emphasis here is on the word «in theory», since in practice the battery will be completely discharged and powerless after about 10–15 hours.
Capacity: Current consumption in the battery in ampere-hours (Ah). It depends primarily on the discharge current, temperature, degree of discharge and general condition (aging) battery.
Cold crank current: Determines the ability to start the battery in cold weather (dimension «A»). A certain discharge current that a 12 volt battery can produce at a temperature of -18°C. In this case, the voltage within 30 seconds will not fall below 9 Volts, within 150 seconds, respectively, 6 Volts.
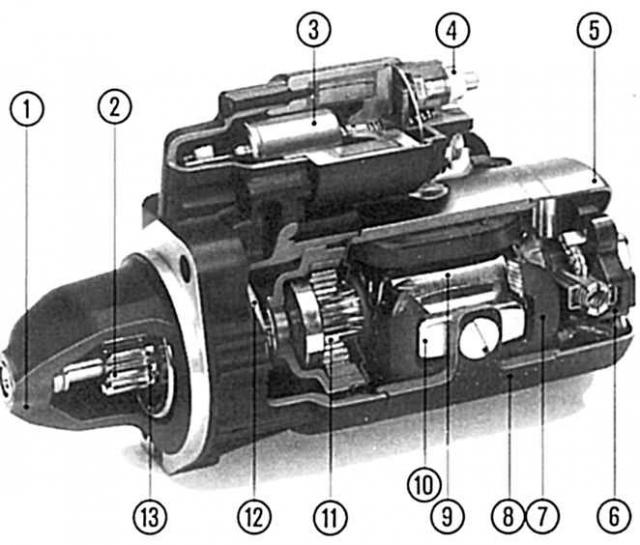
Self-discharge: The chemical processes that take place inside the battery cells cause it to discharge - even if no current consumer is connected. A charged almost new car battery loses about 0.5% of its charge daily. Large fluctuations in temperature, damage or a dirty battery case will also speed up the discharge process. Starter with forced engagement and self-disengagement with gearbox
At start-up, the forced-on-and-off starter inhales the necessary «vitality». - Turn the ignition key in the direction «Start», through the ignition switch (terminal 50) current flows to the electromagnetic switch located above the starter.
- It sets the fork in motion: it then moves the starter gear along the steep thread of the armature shaft into the toothed rim of the engine flywheel (push stroke).
- At the end of the push stroke, the starter gear «installed» directly in front of the flywheel - this is a signal for the electromagnetic switch through its main contacts «open the road» full battery current (terminal 30). The gear is screwed further into the gear rim and thereby creates a power circuit (screw-in stroke) - the starter cranks the engine.
- As soon as the engine gives the first «signs of life» and you release the ignition key, the electromagnetic field disappears in the holding winding of the electromagnetic switch - the starting signal for the return spring to bring the inclusion plug to its original position. The starter gear disengages from the flywheel, the starter itself is already de-energized.
Starter with forced inclusion and self-deactivation and a reducer. |
|
|
Visitor comments