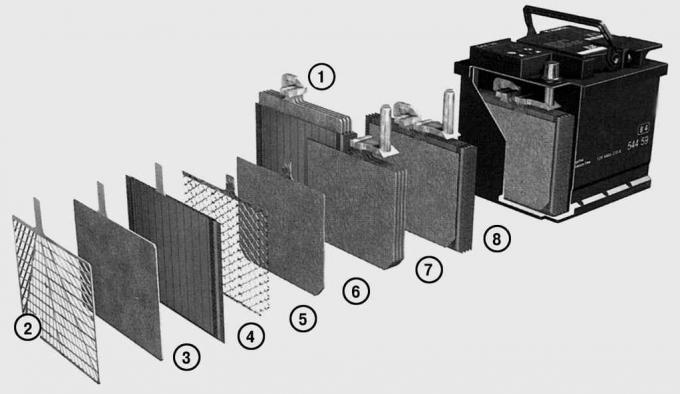
Pic. 15.1. Batteries Varta (12 V): 1 - set of positive plates; 2 - positive lattice; 3 - positive plate; 4 - separator; 5 - negative lattice; 6 - negative plate; 7 - a set of negative plates; 8 - element
Accumulator battery (pic. 15.1) designed to start the engine and power consumers when the engine is not running, when the generator does not generate electricity. Six elements connected in series (cans) form a car battery. Each element consists of alternating positive and negative plates, which, as a result of a chemical reaction, generate a voltage of approximately 2 V. The plates are made in the form of a grid filled with a porous active mass. The positive plate contains lead dioxide, the negative plate contains pure lead. Plates of the same polarity are assembled into semi-blocks and welded to common plates. Between the plates in the blocks are microporous separators. And although they separate the plates, the electrolyte can penetrate the microscopic pores of the separator. The small thickness and large porosity of the separators reduce the internal resistance of the battery and make it possible to obtain a large discharge current. The electrolyte in the battery is a solution of sulfuric acid in distilled water (37% sulfuric acid and 63% distilled water). When the battery is discharged, the sulfuric acid of the electrolyte interacts with the active mass of the plates and turns it into lead sulfate, while the amount of acid in the electrolyte decreases and its density decreases.
TECHNICAL DICTIONARY
Battery
Designation.
It is located on the battery case and contains its technical characteristics. For example: 12V 40Ah 200A (12V - nominal voltage (12 V); 40Ah - nominal capacity (40 Ah); 200A - cold discharge control current.
Rated voltage.
All Fiesta models are equipped with 12 V batteries. The voltage depends primarily on the state of charge of the battery and may be higher or lower than the nominal voltage.
Rated capacity.
The ability of a battery to store electrical energy. The capacity determines the value of the current strength that a fully charged battery can deliver with a 20-hour discharge mode, an electrolyte temperature of 27°C and a voltage of at least 10.5 V (discharge voltage). For example, the power of your Fiesta parking light is 25 watts. At a voltage of 12 V, the battery delivers an electric current of 2.08 A - current (A) = power (Tue) /voltage (IN). Theoretically, the energy of a fully charged battery is enough for 19.2 hours of parking lighting. The emphasis is on the word «in theory», since in practice the battery will be completely discharged after about 15 hours.
Capacity.
The amount of current drawn in ampere-hours. First of all, it depends on the discharge current, temperature, state of charge and general condition (age) battery.
Cold Discharge Control Current (starter discharging current).
Indicates the ability to start the engine with a battery at a negative temperature (unit A). This is the discharge current that can be obtained from a 12-volt battery at an electrolyte temperature of -18°C, and the voltage should not decrease below 9 V in 30 seconds, and below 6 V in 150 seconds.
Battery self-discharge.
The chemical processes in the battery cells lead to discharge, even if consumers of electrical energy are not connected. Every day, a new charged battery loses approximately 0.5% of its charge. High temperatures, damage and contamination of the battery cover accelerate self-discharge.
Accumulation of electrical energy by a storage battery
Inside the battery, chemical processes take place for the consumption and accumulation of electrical energy. The most important task of the battery is to supply the starter with the necessary energy during engine start-up: depending on the types of engine and starter, up to 2000 W are consumed in a short time. Most of the power when starting a cold engine goes to overcome internal friction. When starting a warm engine, the starter already operates with a consumption of about 1/5 of this power, since all the clearances in the moving and rotating units are optimal, and hot oil is more fluid than cold oil, which circulates with difficulty in the lubrication system.
TECHNICAL DICTIONARY
Starter
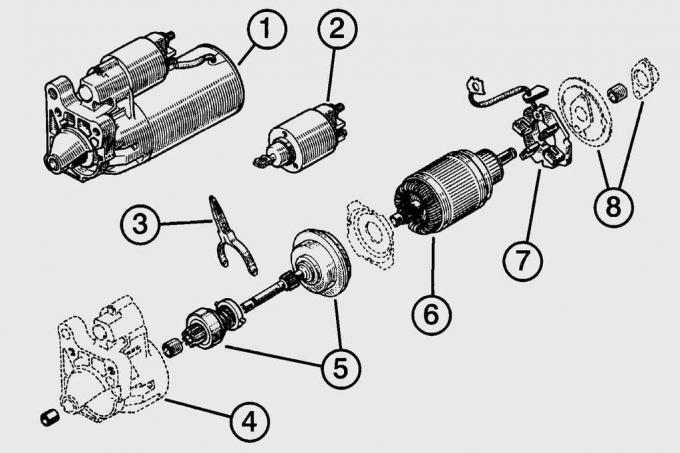
Pic. 15.2. Starter: 1 - starter assembly; 2 – traction relay; 3 – drive lever; 4 - starter cover from the drive side; 5 - freewheel with drive gear; 6 - anchor with a collector; 7 - brush holder; 8 - covers from the side of the collector with details of the mechanism for axial adjustment of the bearing
A starter is installed in the Fiesta car, which is a DC electric motor with mixed excitation and an electromagnetic two-winding traction relay (pic. 15.2).
Turn the ignition key to position «Start» - from contact «50» switch (castle) ignition, voltage is supplied to the traction relay, which is located on top of the starter.
• At the same time, the armature of the relay moves the freewheel with the gear through the lever. The freewheel hub rotates the starter armature shaft and gear on the screw splines, which facilitates its engagement with the flywheel ring gear.
• The relay armature is pulled in and the relay contacts are closed. Through the closed contacts of the traction relay, a current flows, feeding the stator and armature windings, the starter armature begins to rotate together with the hub and freewheel and turns the engine crankshaft.
• After starting the engine, the speed of the gear exceeds the speed of the starter armature. In this case, the freewheel turns freely and no torque is transmitted from the engine flywheel to the starter armature shaft. After the ignition key is released, the power circuit of the traction relay windings opens through the ignition switch, the traction relay armature is pressed by the spring to its original position, the relay contacts open and the drive gear disengages from the flywheel ring gear.
Visitor comments