In contrast to gasoline engines, injection systems in diesel engines operate with high system pressures. Fuel pumps, including the control peripherals, are fundamentally different from their «gasoline». In technical terms, diesel engines distinguish between in-line high-pressure fuel pumps, plunger fuel distribution pumps, Common-Rail systems and «pump nozzle». Under the hoods of both Mondeos with diesel engines, fuel is supplied directly to the combustion chambers by plunger fuel distribution pumps (Bosch VP30/66 kW/90 HP; Bosch VP44/85 kW/115 hp) through pressure pipes and through nozzles with six holes. The fuel pump in DuraTorg is driven by a duplex chain from the crankshaft.
Distribution injection pump
The supply and removal of fuel is carried out separately.
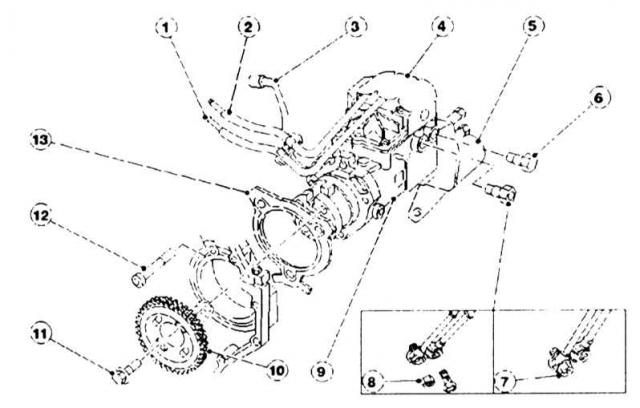 |
|
1 - supply pipeline,
|
8 - Connecting the drain pipe (only in an engine with 90 hp),
|
On the top side of the pump is an electronic pump control unit (PCU). It uses information from the steering angle sensor as well as the transmission control unit (RSM) and processes it to generate control signals for the high pressure solenoid valve and the fuel start control system.
Equal lengths - pipelines for supplying fuel to injectors
Fuel enters the injectors through pressure pipelines of the same length. The nozzles are connected by clamping screws to the cylinder head. Copper sealing rings protect their ends from direct contact with surrounding parts. The sealing washers are usually replaced after each dismantling of the nozzle.
Fuel supply
Fuel lines from pump to injectors.
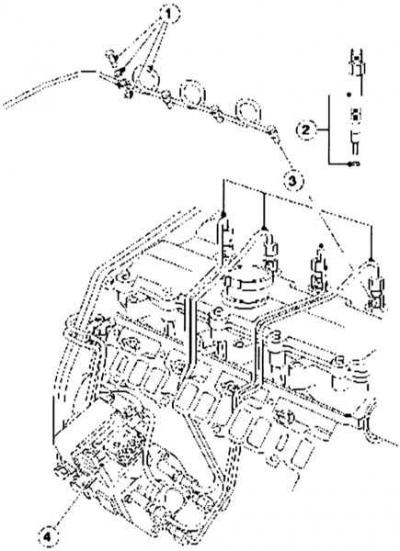 |
|
1 - Drain fuel line with connecting screw and seal,
|
3 - High pressure injection pipelines,
|
Mondeo injectors have a relatively slim design (pin nozzle). The direction of injection from six holes is oriented approximately to the center of the specially profiled cavity of the combustion chamber in the piston inside the cylinder. The 85 kW engine uses different injector options compared to the 66 kW engine. The injectors are calibrated differently, resulting in different fuel flow rates.
Electronics and mechanics
Ford's 2.0-litre DuraTorg-DI engines work with state-of-the-art control technology. Their transmission control units (RSM) use 32-bit bus and CAN bus for data transfer.
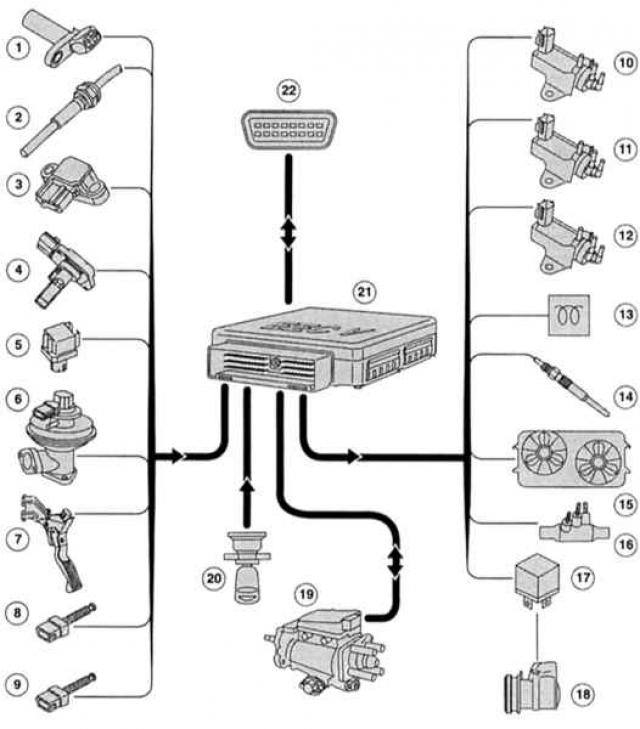 |
|
1 - Position sensor crankshaft (TFR),
|
12 — Solenoid valve boost pressure (only in 85 kW),
|
In detail - control of the DuraTorg-DI injection system
Sensors and actuators under the engine hood Mondeo with DuraTorg-DI 85 kW
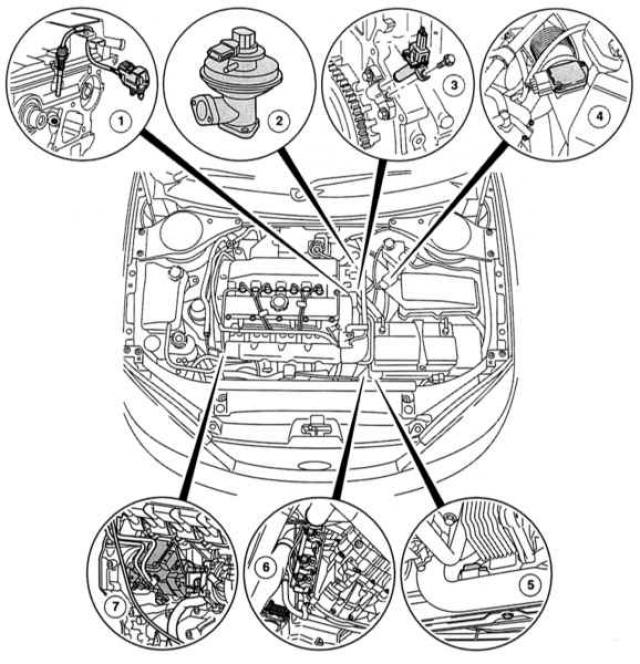 |
|
| 1 - SNT sensor,
2 - EGR valve, 3 - SKR sensor, 4 - MAF sensor, |
5 - T-MAP sensor,
|
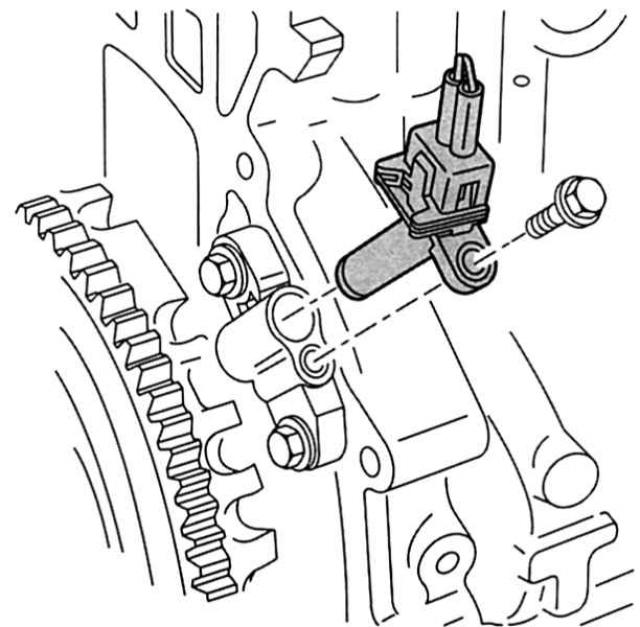 Direction of travel on the right: TFR sensor on the flange of the engine block. |
Transmission control unit (PCM/PATS integrated): «Central director's console» DuraTorg-DI engine management system is located on the side behind the side trim in the footwell at the front right. An on-board computer with 104 codes processes the current amount of data from various areas of the engine and compares them with fixed, factory-set parameters. For system analysis at Ford stations, the WDS diagnostic tool is used exclusively. Its connection is made using a 16-pole diagnostic socket (DLC) in the engine compartment.
Cylinder head temperature sensor (SNT): The CHT sensor is located on the transmission side of the cylinder head. It does not measure the coolant temperature, as is common with older Ford engines, but the actual temperature of the cylinder head. Its signals influence injection volume, start of injection, idle speed, glow plug control, EGR system, as well as the coolant temperature display and radiator fan control.
Crankshaft position sensor (TFR): The TFR sensor records the inductively precise angular position of the crankshaft as well as the current engine speed. Its signals are significant for the volume of the injected combustible mixture and the start of injection. The sensor is located on the side of the gearbox flange.
Exhaust gas recirculation sensor with valve (EGR/66 kW engine only): This position sensor sends information to the PCM about the current position of the EGR valve. It forms a separate structural unit with a valve.
Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor with intake air temperature sensor (T-MAR): It is located in the intake pipe between the charge air cooler and the intake manifold and performs the work of the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor and the intake air temperature sensor from the housing. The T-MAP sensor minimizes the power loss that occurs when driving over mountainous terrain and sloping roads by instantly ascertaining the current operating state of the engine at idle and full load. The measured value is the barometric pressure in the intake manifold. This data is recorded and processed by the PCM as a reference pressure for the respective intake manifold pressure under various load conditions.
In order to take into account the influence of temperature on charge air density, the IAT sensor records the charge air temperature. Its signals are used by PCM to obtain corrective parameters when calculating boost pressure. In such an alliance, the T-MAP sensor provides information to the PCM, on the basis of which the amount of air mass pressurized into the engine is calculated. All this also affects the amount of fuel injected and the EGR system.
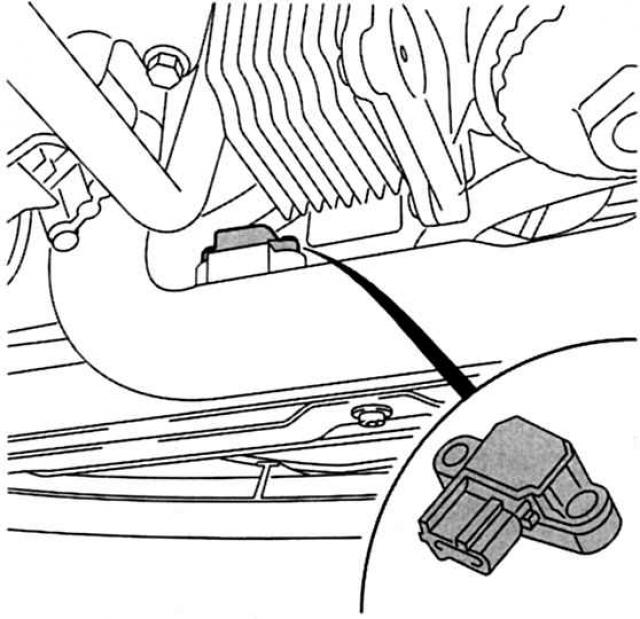 Double packed: T-MAP probe with built-in IAT probe. |
Exclusively for 85 kW motor
The 85kW variant uses a MAP signal in addition to boost pressure control in a variable turbocharger. As soon as the actual measured value deviates from the value set by the parametric characteristic in the PCM, the PCM regulates the boost pressure via the corresponding solenoid valve.
Air mass meter (MAF): The MAF sensor works on the hot wire principle. He «inserted» into the air line behind the air filter and mainly controls the EGR system.
Accelerator pedal position sensor (APP): In order to change the engine power according to the position of the accelerator pedal, the PCM is guided by the position data of the APP sensor. In principle, this sensor works in the same way as a potentiometer, which measures the angular movements of the accelerator pedal by means of three sliding contacts. If two contacts fail, the engine only runs at high idle. The APP sensor has a built-in idle switch and a foot switch. The PCM compares the signal from the idle switch to the signal from the potentiometer for plausibility.
Ambient air pressure sensor (BARO/only for 85 kW motor): The sensor is located in the passenger compartment, in the left bracket of the A-pillar reinforcing element, behind the instrument panel. To avoid black smoke, it supplies the PCM with the current values of the prevailing ambient air pressure. Based on the signals sent, the on-board computer corrects the boost pressure and the actual injection volume.
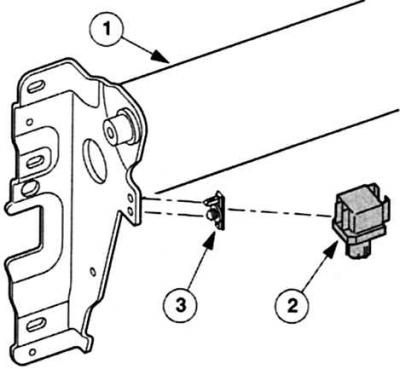 Mounted behind the instrument panel: Ambient air pressure sensor. 1 - Reinforcing element on the front pillar,
|
Brake light and brake pedal switch (WRR): The signal from the brake light switch turns on the brake lights and «controls» APP sensor (validation): during any braking operation, the engine speed automatically drops to idle speed.
Mondeo with cruise control
In order not to stop the speed control system already at «insignificant» pressure on the brake pedal, the BPP switch with a long actuation path comes to the fore. First, its signal is sent to the onboard computer, which outputs from «games» speed control system.
Clutch position switch (SRR): This element signals to the PCM whether clutch is present or not. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the amount of fuel injected is briefly reduced to avoid engine jerks.
Mondeo with cruise control
A second CPP switch is installed in combination with the speed control system. Its contacts are connected to ground by means of brake lights. In the rest position, the contacts are closed. Only when the clutch pedal is depressed does the switch open, causing the cruise control system to pause its operation.
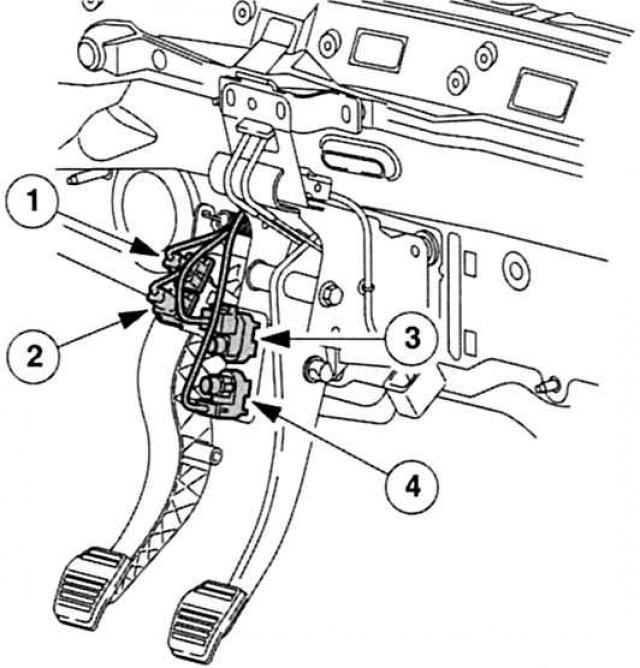 Communicate with RSM: BPP- and CPP-switches. |
Exhaust gas recirculation solenoid valve (EGR): The fresh air sucked in is mixed with part of the exhaust gas by means of the EGR valve. This reduces the content of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas. The mixing process is controlled by the PCM: its clock signals are converted by the solenoid valve into a precisely set control reduced pressure for the mechanically operating EGR valve.
Boost pressure solenoid valve (only in 85 kW motor): In order to best match the turbocharger boost pressure to the engine load condition, the 85kW engine does not have a hard vane bypass controlled supercharger, but a variable vane version. In order for these vanes to be constantly in a certain position, depending on the engine load condition, the boost pressure solenoid valve receives clock signals with the corresponding PCM spatial characteristic. It converts the electrical clock signals into a predetermined low pressure control that influences the low pressure component to control the boost pressure.
Intake manifold flap solenoid valve: As soon as the engine stops, the PCM sends an appropriate signal to the intake manifold flap solenoid valve. Based on it, the valve acts according to the vacuum dose on the intake manifold flap and closes it for a few seconds.
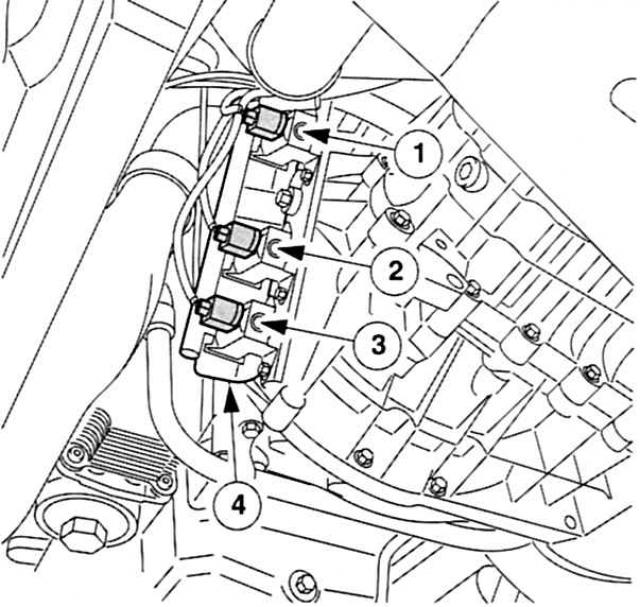 Shoulder to shoulder: 1 - Solenoid valve boost pressure (only in 85 kW motor),
|
Draining back to fuel tank - excess fuel
In terms of fuel quantity, DuraTorg-DI injection systems are constantly running more fuel than is actually needed. The injectors also do not inject the entire amount of fuel into the combustion chambers: the excess fuel is also intended to lubricate and cool the moving parts of the fuel pump and injectors, among other things.
The DuraTorg-DI Mondeo engine, however, has a function that prevents complete emptying and thus «dry» installation operation. As soon as the diesel supply reaches two percent, the PCM sets the fuel pump to zero flow. Advantage: usually needed «ventilate» Mondeo only after replacing the fuel pump, otherwise the starter will do it for you for a long starting period.
So that when the engine is running, the fuel can «travel» according to the system, diesel engines have supply and drain pipelines, respectively. The nozzles are also integrated in them: they have a drain pipe and are in contact with each other via a hose line (oil drain pipe). From the right with respect to the direction of movement of the nozzle (cylinder 1) fuel flows through the drain pipe back to the fuel tank. The drain hole of the fourth cylinder injector is sealed with a stopper in accordance with this principle.
Engine control system
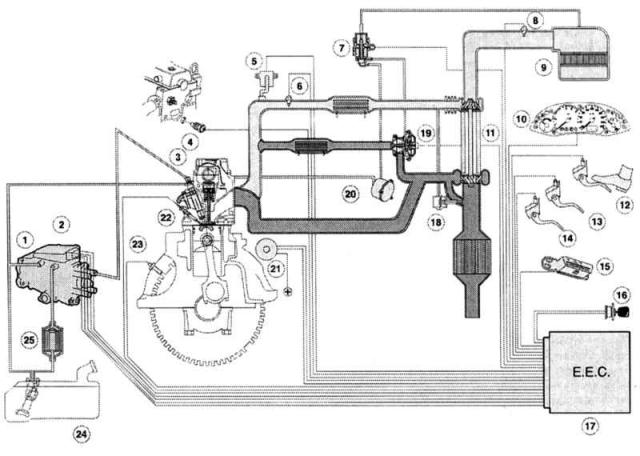 |
|
1 - Distribution fuel pump Bosch VP-30,
|
15 - Diagnostic connector (DLC),
|
Engine power - this is how fuel gets to the injectors
The fuel pump pumps through a closed piping system (supply and drain pipelines) diesel fuel from the tank through the fuel filter to the injection pump. In existing distribution injection pumps, the operation of the fuel pump is performed by a vane pump. It is located in a round hole directly in the pump housing. Since this is a suction pump and a compressor, the same pump also transports diesel fuel to the distributor injection pump's own compression zone. DuraTorg-DI 85 kW motor only «diesel turnover» the system supports an additional electric fuel priming pump, the maximum volume here is 160 liters / hour.
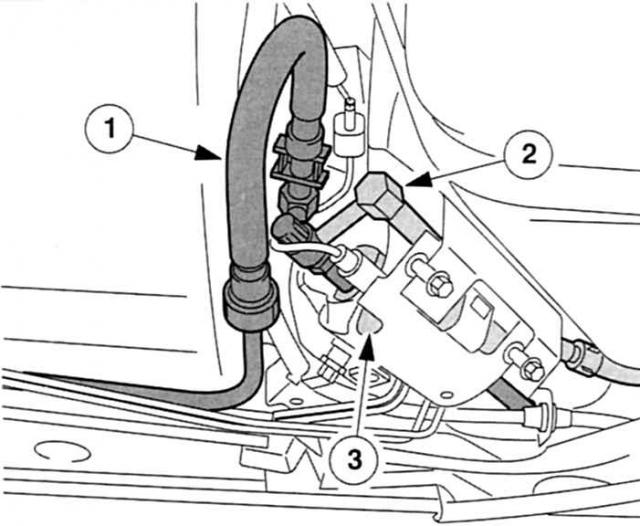 Additional fuel priming pump in the DuraTorg-DI 85 kW engine: 1 - Fuel line to the filter,
|
«Cleaner» in front of the injection pump - a fuel filter with a control valve that works depending on the temperature
The filter element is located in a well-accessible place for maintenance work at the right punch of the suspension strut under the engine hood. The fuel return line contains a temperature-dependent control valve. Advantage: Excess diesel fuel now flows back into the fuel tank if the tank temperature is above 31°C. As soon as the fuel has cooled down to 15°C, the valve brings excess fuel directly to the filter and thus maintains the fuel down to -35°C without «additional heating» in a fluid state.
Together with the connecting pipes, the control valve forms a separate unit. Disadvantage: in service centers it is necessary to completely replace the valve together with pipelines. As, however, the fuel filter - it can neither be dehydrated nor washed: therefore, the valve should be replaced regularly, therefore, for foresight from «water damage» take such a spare element with you on your travels and long trips across the southern plains.
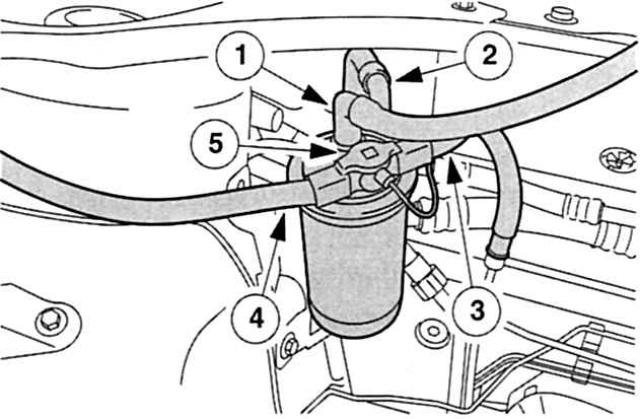 Cleaner with heat output: fuel filter in front of the injection pump. 1 - Supply pipeline to the electric pump,
|
Standard only on DuraTorg-DI 85 kW fuel cooler
Compared to the VP 30, the VP 44 injection pump has a higher pressure. Naturally, this fact determines the increase in the temperature of the circulating diesel fuel. So that the temperature level does not go beyond the limits even at high outside temperatures, a part of the drain pipe is structurally designed as «cold pipe». It cools the flowing fuel down to 10 - 12°С.
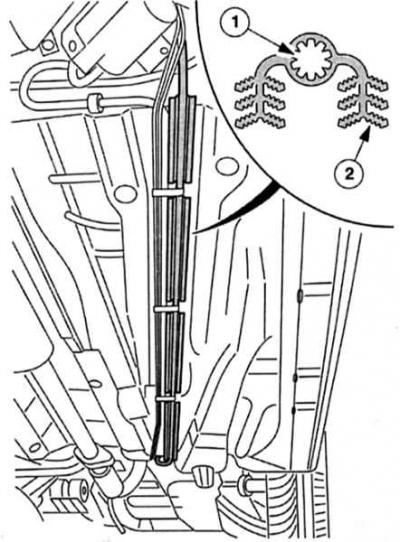 Required for DuraTorg-DI with 85 kW: underbody fuel cooler. 1 - Internal cooling profile,
|
Increases hydraulic efficiency - high pressure fuel pump
As «dispenser of instructions» all pump functions are controlled by a control box located on the top side of the pump (PCU), which is located in «electric» contact with the periphery of the engine and the accelerator pedal. The Bosch VP 30/VP 44 in the Mondeo are controlled by a high pressure solenoid valve that loads the axial pistons. The valve operates in an alternating mode, opens and closes strictly according to the parametric characteristic stored in the PCU.
However, the start of feed in the Mondeo is no longer commanded by a needle moving sensor - the command «Go» comes directly from the pump control unit and enters the hydraulic system through the high pressure electromagnetic sensor. The start of fuel delivery is determined by the closing timing point of the solenoid valve, the delivery end is determined by the opening timing point, and the fuel volume is determined by the time interval during which the high pressure solenoid valve is closed.
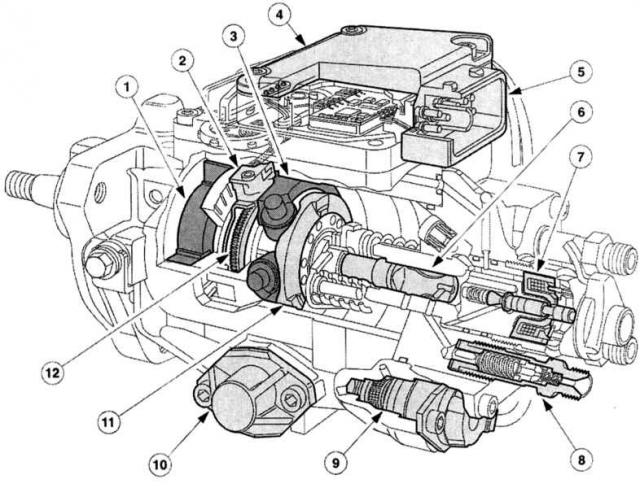
Distribution injection pump VP 30
 |
|
1 - Vane pump,
|
7 - High pressure solenoid valve,
|
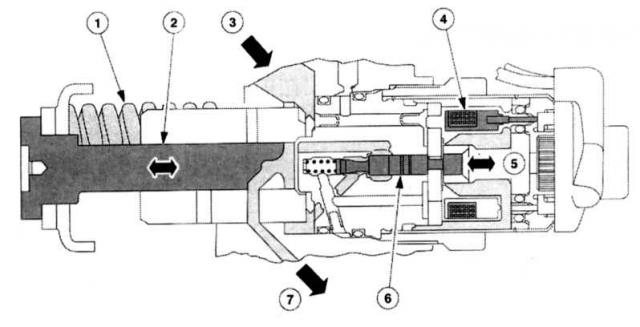
High pressure solenoid valve
 |
|
1 - Clamping spring,
|
5 - Direction of closing from opening,
|
Work Distribution - Pulse Encoder Rotor
In order for each cylinder in the correct sequence and at the right time to be «fed», the pulse encoder rotor and the angle encoder act respectively as a distributor. The pulse encoder rotor is connected directly to the motor drive shaft, and the angle encoder is firmly connected to the roller ring. As soon as the solenoid valve directs the injection controller, the roller ring and thus the angle sensor turns to position «early» or «late». The rotor of the sensor of control pulses has on each cylinder «gap between teeth». Desired «offer» for the steering angle sensor - it scans the valleys and sends the corresponding information to the PCU for later use. These signals are the basis for the current angular position of the crankshaft, the current speed of the injection pump and the control system for the start of injection.
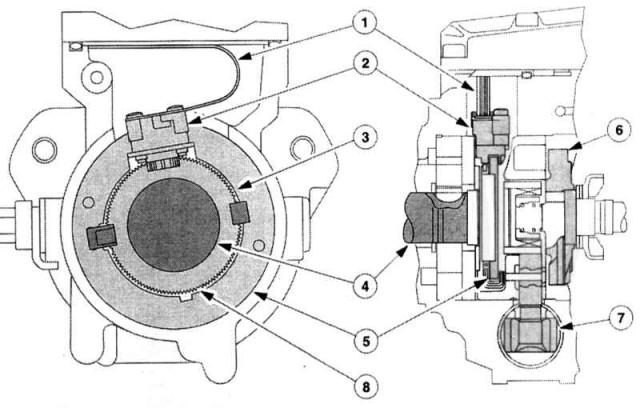
Pulse encoder rotor and angle encoder
 |
|
1 - Conductive film,
|
5 - Rotating bearing ring,
|
Makes a cold diesel frisky - a device for starting a cold engine
The cold starter serves the same purpose as the automatic starter in gasoline engines: both systems help cold engines through the transition. Thus, however, the similarity ends there. Although the device for starting a cold engine depends on the prevailing temperatures, nevertheless it does not reduce, for example, the air supply to the cylinders, but immediately sets the point of injection in the direction «early». Thus the atomized fuel has more time to ignite in compressed air and glow plugs - the engine starts «more obedient and even». In addition, the cold starter slightly increases the idling speed and - depending on the engine temperature - warms up in a certain amount of time. This reduces direct injection engine noise, improves idle performance and reduces carbon emissions during the warm-up period.
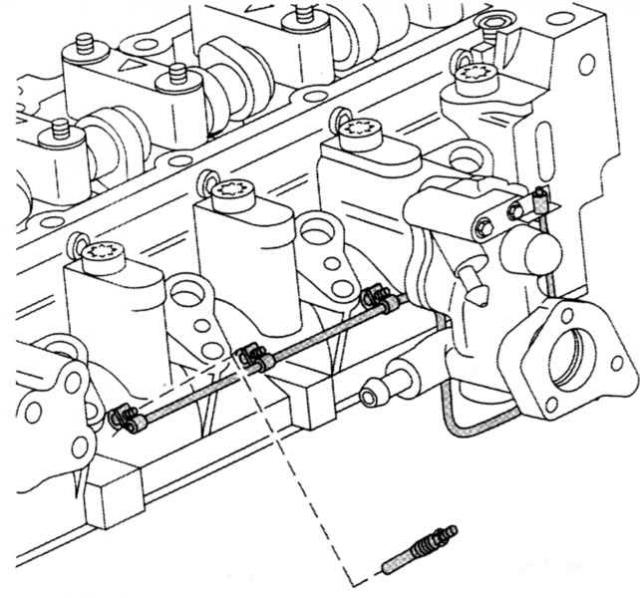 Heating a cold diesel: pin glow plugs in the cylinder head. |
Diesel fuel atomization - double spring nozzles
The injectors are exclusively the last resort of the diesel injection system. They spray fuel at high pressure into the combustion chamber. In order to minimize combustion noises and somewhat «tame» explosive pressure surges in the cylinders, Mondeo injectors are equipped with two springs. The stroke of the first spring is set in such a way that the nozzle needle is already easily lifted from its seat at 222 - 230 bar. Due to this, a small amount of fuel enters the combustion chamber and ignites.
«pre-injection» designed to smoothly increase the combustion pressure, since it acts, to some extent, as «wick» for a few milliseconds before the main injection, which occurs at 380 - 398 bar. In Mondeo, these two injection processes «smoothly» pass into each other, the high-pressure solenoid valve receives a second control pulse for this. After that, the atomizer needle fully rises and lets the main volume of fuel through six holes from the injection system into the cavity of the combustion chamber. caused «pre-combustion» the swirl of air entrains fresh fuel particles and forms an almost homogeneous and highly flammable diesel-air mixture. The high elasticity of the spring acting on the nozzle needles prevents the combustion pressure from kicking back into the fuel system. Since the entire volume of fuel is never injected, excess fuel flows - as already mentioned above - through the drain pipe back into the fuel tank. The set time between the start of injection and the ignition timing is 0.002 seconds. From this it is clear that even the slightest malfunction, for example, «jamming» atomizer needles will unbalance the physically balanced combustion process. Loss of power, black smoke or strong «needle noises» (even when the engine is warm) are undeniable and «audible» signs that the diesel engine is in such «able».
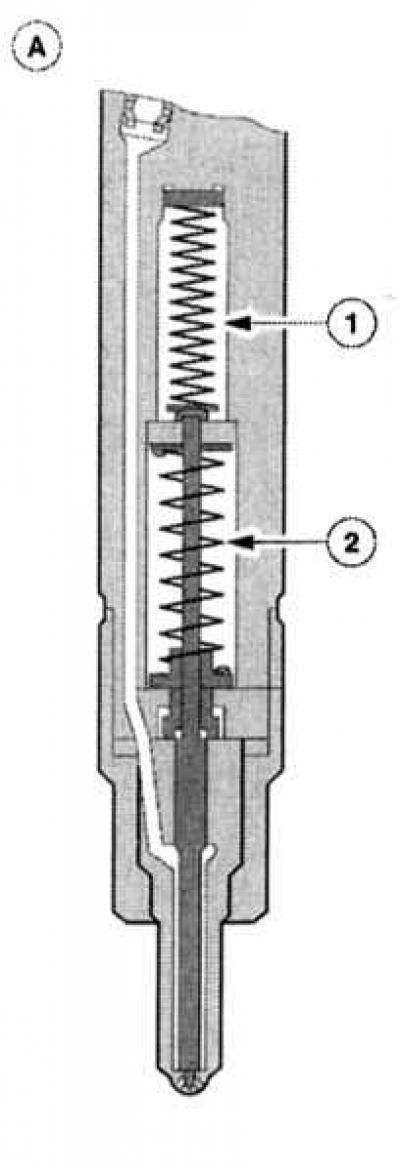 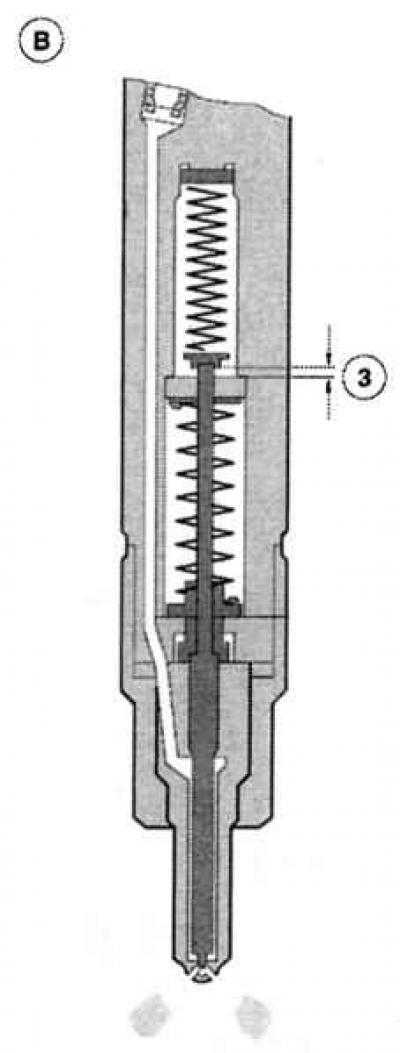 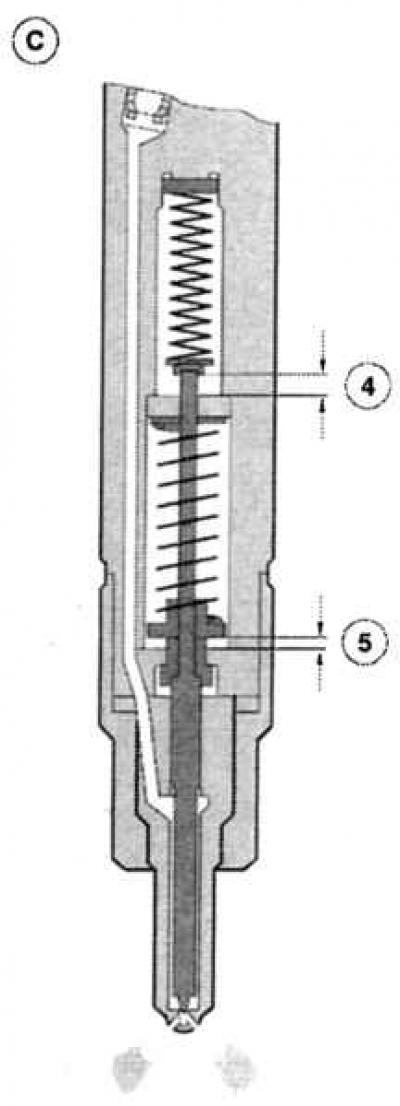 Double injection process: (A) nozzle is closed (IN) pre-injection, (WITH) main injection, 1 - Spring 1, 2 - Spring 2, 3 - Move 1, 4 - Move 1 move 2, 5 - Move 2. |
Case for experts - repair and correction of the diesel injection system
An experienced amateur can detect a separate defective nozzle on his own. To do this, you need to listen «growls» the engine is idling, and for all injectors of the row, briefly loosen the union nut of the pressure pipe. If the nozzle remains at a constant speed despite the pipe being removed, then the atomizer or valve of the corresponding cylinder is considered defective. Damaged spray nozzles can also be recognized by the following symptoms:
- regular defects in glow plugs,
- constant black smoke from the exhaust system,
- increased consumption,
- frequently overheated engine,
- harsh combustion noises (loud movement of the needle),
- power drop,
- overspending.
If you have identified the above troubles in your diesel Mondeo, look for a car repair shop and report your problems to the specialists on the spot. They will be able to provide you with information on suitable countermeasures.
Spray Nozzle Disassembly - Leave it to a Professional
Without a special test of the atomizer, one can only superficially judge its functioning. Naturally, external damage or severe contamination can be detected. Direct wear, of course, takes place inside the nozzle, on the needle, in the atomizer body or in the pressure spring. And here you have little opportunity for corrections, because for this you need to have a special test device with which you can «wring out» nozzle, install «jet picture» and adjust injection pressure. In most cases, it will be better to completely replace the atomizer. If you are still going to disassemble this part, then its «entrails» should not be left for a long time «open» on a workbench: the precision-machined surfaces of the atomizer needle and nozzle body are very sensitive to dust and rust. Always install new injectors with new O-rings in the cylinder head. The tightening torque for the nozzle holder is 24 Nm.
Visitor comments