Under the engine hood of a modern car in the intake tract of gasoline engines has long been «set the tone» electronic fuel injection systems. On the exhaust gas side, there is a three-way catalyst according to the state of the art. So no questions asked, all Mondeo powertrains: «from air filter to exhaust pipe» controlled by electronic means: the necessary fresh fuel mixture is prepared by sequential fuel injection systems, assisted in this process by a three-way catalyst. Ignition sparks are controlled by non-distributed ignition systems in a 1-3-4-2 sequence (Duratec-HE) or 1-4-2-5-3-6 (Duratec-VE). They are, like the entire electronic management of the engine, under the control of a powerful on-board computer (RSM). The new Mondeo has «Black Oak», a new generation engine control system that oversees «bits and bytes». Black Oak, developed by Ford's Visteon subsidiary, works in conjunction with a 32-bit Levanta computer, including a Motorolla processor and a CAN data bus. The operation of the Black Oak system resembles the previously used EEC engine control system.
PCM control unit with 32 bits and CAN data bus
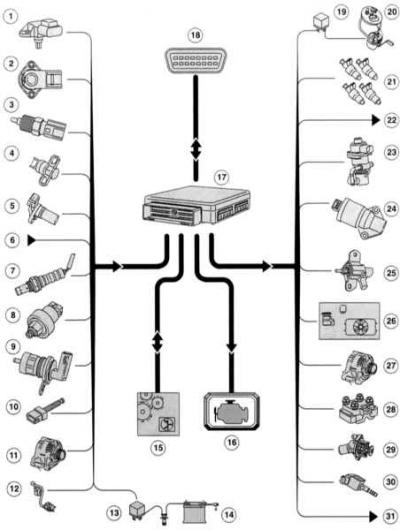 |
|
1 - Absolute pressure sensor in the intake tube with built-in intake air temperature sensor (TMAR),
|
17 - Transmission control unit (RSM),
|
Sensors and actuators under the engine hood
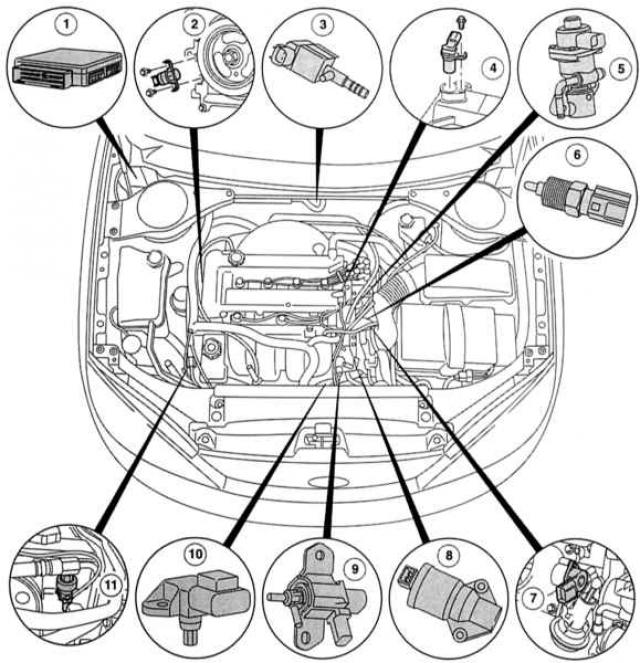 |
|
1 - Engine control unit,
|
6 - Coolant temperature sensor (EATING),
|
Electronic engine management - not for independent
New systems are largely maintenance-free - possible malfunctions, in practice, can only be detected by a competent person with the necessary measuring equipment. This fact places increased demands on those who want to do repairs themselves - Ford workshops rely on "WDS-Diagnose CD B8". Therefore, if there are malfunctions in the engine management system, it is better to entrust your Mondeo to specialists. However, you still need to know the basic principles of preparing the combustible mixture of your Mondeo. And only on this basis can you accurately classify emerging problems. Thanks to this, you will save on costly diagnostics. In addition, you will be able to clearly formulate a repair order, and the resulting cost estimate will not cause you any doubts. As an example for Ford gasoline engines, detailed information on air-fuel mixture preparation of the Duratec-HE powertrain is provided below.
Learn more about Duratec-HE injection system control
PCM control unit (built into PATS): This is the central electronic engine control unit. The on-board computer constantly uses the current «material data» from their spatial parametric characteristics (speed, intake manifold pressure, intake air and coolant temperature, and so on) and compares them with the fixed parameters in the database. After this comparison, the control unit determines and calculates, among other things, the duration of the opening of the solenoid injector, the amount of fuel required and the composition of the air-fuel mixture. At the same time, the PCM is reprogrammable: the most important criterion for situations when it proceeds to the next calibration point with modified parameters.
Advantage: with the assistance of a mobile diagnostic tool «FDS 200» Ford can easily erase electronically reprogrammable permanent memory (ROM) And «fill» her new engine management program. The corresponding service module for PCM is already installed at the factory. 16-pole diagnostic socket (DLC) «hidden» in the left footwell at the height of the fuse box.
Fuel Injection Safety Switch: Located on the side of the left door. This switch can be used to interrupt the fuel supply in the event of leaks in the fuel supply system, during an accident or in severe collisions. Electrical interruptions are recognized by the pop-up switch button. Before activating the safety button, first check the fuel system for leaks, then turn the ignition switch to the position «0» and press the button. Then turn the ignition key to the position for a few seconds «II» and then you can enter the lock in position «I».
Crankshaft position sensor (TFR): in Duratec engines, it is located on the cover of the control unit on the side of the crankshaft shock absorber. Gear sensor (36 teeth minus 1; «prong gap» for the 1st cylinder is 90°from TDC) records the inductively precise angular position of the crankshaft as well as the current engine speed, these measured values influence:
- injected fuel and start of injection,
- ignition timing and
- idle control.
If the TFR sensor fails, all engine control is transferred to «deep dream»: motor stalls and remains – until sensor is replaced – «dumb».
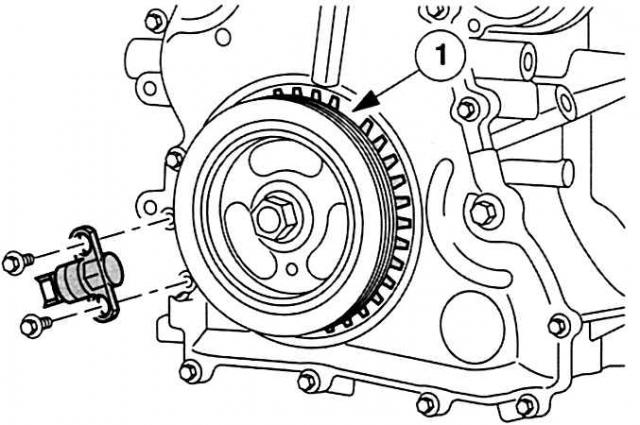 The cavity between the teeth 1: 90°from the TDC of the first cylinder. |
Camshaft position sensor (SMR): on Duratec engines, it is located in the cylinder head in front of the first cam of the intake camshaft. The sensor works on the basis of the inductive principle. Its signal uses CMP to recognize the 1st cylinder. It controls sequential fuel injection.
coolant temperature sensor (EATING): «inserted» under the ignition coil and measures the temperature of the coolant in a small circle.
Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor with built-in intake air temperature sensor (TMAR). The TMAP sensor allows you to minimize possible power losses when driving on mountainous road sections or downhill. It determines the current dominant operating state of the engine when the ignition is on and at full load. The sensor uses atmospheric pressure in the intake manifold as the measured value. These parameters are stored and processed by the PCM as a reference pressure for the respective intake manifold pressure under various load conditions. The signals from the built-in IAT sensor are initially only basic values when starting a cold engine or during a warm-up period. Additionally, they are used by the MAP sensor as correction parameters, since it aligns with its own «internal knowledge» various degrees of cylinder filling. Based on all the input signals from the TMAP sensor, the PCM calculates the air mass needed by the engine.
Knock sensor (KS). The knock sensor is «mechanical vibration remover». Due to their relatively high compression ratio, Duratec engines are equipped with such sensors. This sensor is located on the intake side directly on the engine block between the second and third cylinders. In the assembled state, it must under no circumstances come into contact with its surroundings «weight».
Once reached «detonation boundary», the KS sensor sends signals to the SKR and CMP sensors about uncontrolled combustion of the hot mixture. Based on them, the PCM shifts the ignition timing by 1.5°back. If the signals continue, the angle continues to decrease until the combustion process returns to normal. If knock noises do not occur within two seconds, the PCM regulates the ignition timing to the knock limit or, with standard fuel quality, to the prescribed ignition timing.
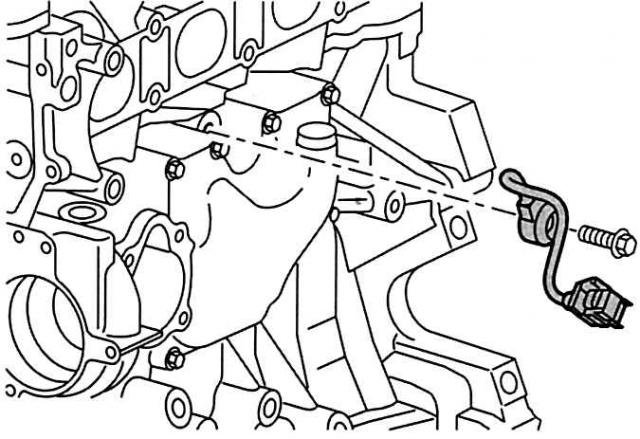 Knock sensor: constantly at the listening post. |
Throttle position sensor (TR). This sensor is screwed to the throttle body. It functions in the same way as a rotary potentiometer and affects:
- idle speed,
- the composition of the intake, combustible mixture (14,7: 1),
- exhaust gas regulation and
- opening the system control loop.
Power steering push button switch (PSP). He takes his information from the pressure pipe between the hydraulic booster pump and the steering gear. As soon as the pressure drops, for example when maneuvering the vehicle through a full turn of the steering wheels, the PSP opens and sends a signal to the PCM for a slight increase in idle speed.
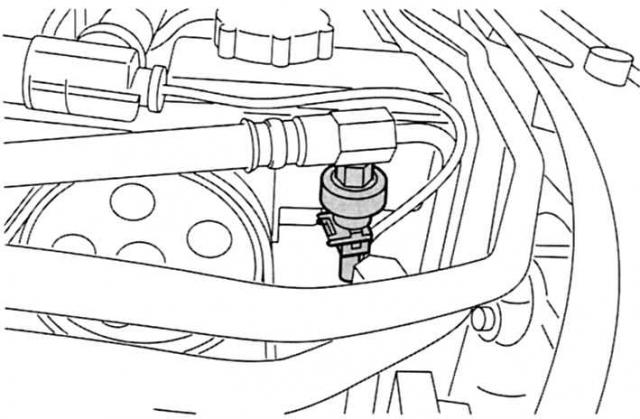 Pressure controller: Power steering push button switch. |
lambda sensor (HO2S) Note: Duratec engines are factory fitted with two lambda sensors. Sensor 1 is located directly in the exhaust gas manifold, sensor 2 in the exhaust pipe behind the catalyst. Both sensors analyze the residual oxygen content in the exhaust gas and transmit this information to the PCM. Their signals affect:
- the amount of injected air and
- functioning of the fuel mixture preparation system (EVAP).
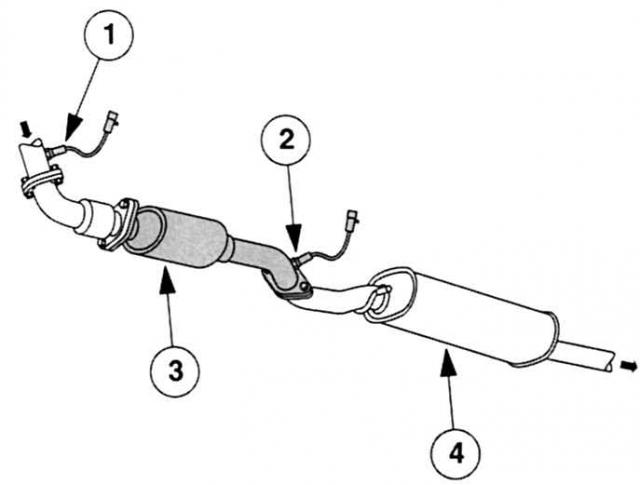 Cleaner: HO2S lambda sensors. 1 - Front lambda sensor,
|
Lambda sensors have a strong influence on the functioning and service life of the catalyst. For the proper functioning of the catalyst, they provide information about the constant change between a slightly rich and lean combustible mixture. In combination with the automatic CDE4 system, the exhaust gas is also filtered by an additional starter catalytic converter located directly in the exhaust manifold.
Idle air control valve (IAC). On Duratec engines, this valve is located near the throttle valve on the intake manifold. The PCM controls it with clock signals. Depending on the frequency of the signal, more or less fresh air bypasses the throttle valve through the diverter valve.
The swirl flap solenoid valve is located at an angle behind the IAC valve in the intake manifold. Its control pulses are based on engine speed and throttle opening angle: depending on the situation, the valve «empty» or «filled».
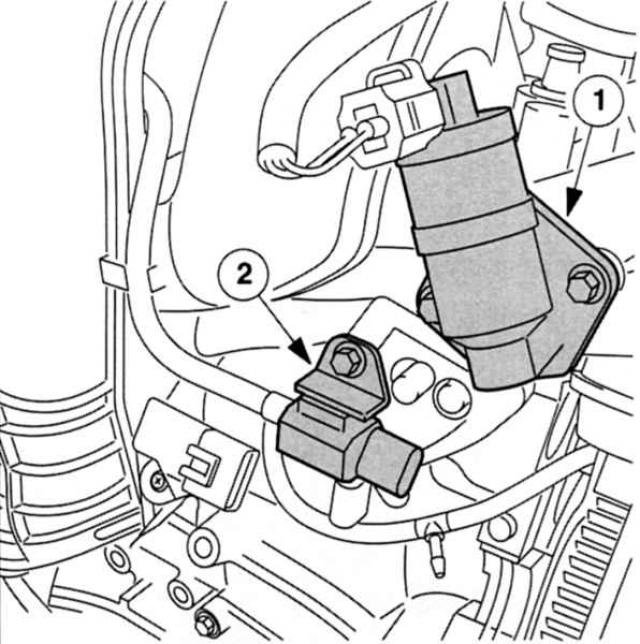 In the immediate vicinity: 1 — the Control valve of system of idling (IAC) and 2 - Swirl damper solenoid valve. |
Activated carbon filter solenoid valve. IN «leg» a redesigned solenoid valve works with the Black Oak engine control system in the 2000 Mondeo. Under certain operating conditions, it opens and releases the fuel vapors in the filter to pass into the intake manifold.
EGR-Stepper Motor: The stepper motor is located at the rear end of the cylinder head and is sensitive to digital signals from the PCM. In other words: Duratec powertrain stepper motors realize very small step movements. In addition, compared to conventional actuators, they are not sensitive to vibrations and pressure fluctuations during operation. The rotational movements of the stepper motor are converted by the spindle into lifting movements, due to which the valve is strictly opened. This feature not only improves the operating principle of the exhaust gas recirculation, but also eliminates the need for additional components, such as an exhaust gas differential valve (DPEF).
EGR stepper motor
Not sensitive to vibrations and pressure fluctuations.
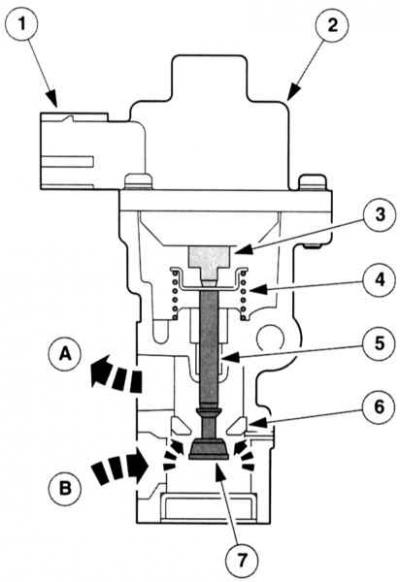 |
|
A - to the suction system,
|
4 - Pressure spring,
|
Injectors: Injectors with four holes for injection and side delivery of fuel are located in the common tube of the fuel distributor. The PCM controls the injectors in sequence. Their nozzles are set strictly at certain angles, so that accordingly «met» two holes for the right and two holes for the left valves.
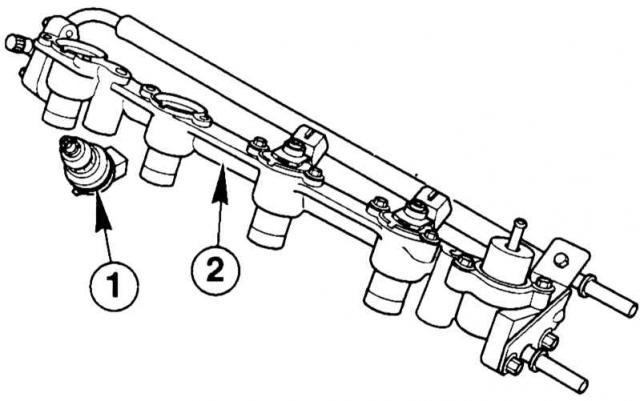 |
Outdoor temperature sensor (AAT). Outdoor temperature sensor «covertly» sits in the buffer front left. His signal governs
- outside temperature indicator on the instrument panel,
- alternator regulation (Smart Charge) And
- air conditioner.
Drive Shaft Speed Sensor (OSS) and movement speed (VS): signals from both sensors are processed by the PCM to regulate the air flow in the idle system (IAC), to enrich the air-fuel mixture during acceleration and forced idle.
Possible with restrictions – self-help with injection system
As noted in the introduction to this manual, most injection work is best left to professionals. They have the necessary control instruments and the relevant knowledge. For example, if there are malfunctions in the electronic engine control system and in order to localize them properly, it is necessary to carry out a series of tests in a certain sequence. Only in this way can defects and their consequences be established and a course of repair work can be set. The presence of conventional «domestic» knowledge is not enough to work with the Mondeo injection system. But there is no reason for «panic»: in practice, possible damage in this system is rare.
Visitor comments