Voltage measurement
The presence of voltage can already be proven with a simple test light or voltage indicator. True, in this case it is only determined whether voltage is applied at all. In order to determine the magnitude of the applied voltage, it is necessary to connect a voltmeter. First of all, when using a voltmeter, you need to set the measurement range in which the measured voltage is supposed to be. As a rule, the voltage in the car does not exceed 14 V. The exception is the ignition system: here the secondary voltage of the ignition system can reach up to 30,000 V. This high voltage can only be measured using a special measuring device - an oscilloscope. First of all, the DCV voltage range is set with the selector switch, as opposed to the ACV voltage range. Then the measurement range is selected. Since the car, in addition to the ignition system, does not have a voltage above 14 Volts, the upper limit of the set measuring range should be set slightly higher (about 15-20 V). If the measured voltage is known to be significantly lower, for example, it is in the range of two Volts, then you can switch to a narrower range in order to achieve greater readout accuracy. If higher voltages are applied than specified by the instrument's measuring range, the latter may be damaged.
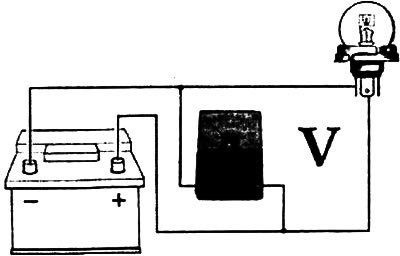
Connect the wires of the meter in parallel with the consumer according to the figure. In this case, the red test lead is connected to the wire coming from the positive pole of the battery, and the black test lead is connected to the wire connecting the battery and the car body, or directly to the vehicle ground, for example, to the engine block.
Control example: If the engine does not start properly because the starter is turning too slowly, it is advisable to check the battery voltage while the starter is pressed. For this red wire (+) connect the voltmeter to the red terminal of the positive pole of the battery, and the black wire to the vehicle ground (-). Then instruct the assistant to press the starter and read the voltage. If the voltage is less than about 10 V (at battery temperature +20°С), it is necessary to check the battery and, possibly, before the next attempts to start the engine, charge it.
Current measurement
In a car, it is relatively rare to need to check the current strength. For example, see section "Battery self-discharge". This requires an ammeter, which is also built into the combination measuring instrument.
Before measuring the current strength, the measuring device is set to a range in which the measured current strength approximately lies. If this is not known, then set the highest measuring range and, if there is no indication, successively switch the device to lower ranges.
To measure the current strength, it is necessary to disconnect the electrical circuit and connect the measuring device to the open circuit (ammeter). To do this, the plug is pulled together, and the red wire (+) ammeter is connected to a conductive wire. black wire (-) connects to the pin to which the broken line is connected. In this case, the earth contacts of the consumer and the plug must be connected using an auxiliary cable.
Attention! Never measure the current with an ordinary ammeter in the wire going to the starter (about 150 A), or in glow plugs for diesel engines (up to 60 A). The resulting high currents can burn the measuring device. In car workshops, an ammeter equipped with DC clamps is used for such measurements. In this case, the current clamp clamps an insulated electrical wire, and the current value is measured using induction.
Resistance measurement
Before measuring the resistance, you must be sure that the structural element to which the ohmmeter is connected is not energized. Therefore, each time, pull off the plug in advance, turn off the ignition, disconnect the wire, for example, from the unit or disconnect the battery. Otherwise, the meter may be damaged.
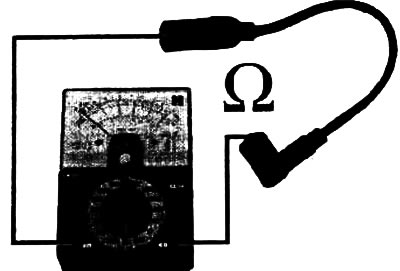
The ohmmeter is connected to two terminals of the consumer (load) or to two ends of an electrical line. It does not matter which wire (±) measuring device is connected to the terminals.
Measuring resistance in a vehicle falls into two main areas:
1. Checking a resistor or structural element built into an electrical target.
2. "Current flow test" in the electric line, in the switch or heating coil of the heater. This checks whether the electrical circuit in the vehicle has been interrupted and therefore the connected electrical device cannot function. For measurement, an ohmmeter is connected to both ends of the corresponding electrical line. If the resistance is 0, then in this case an electric current passes, i.e. electrical line is ok. In the case of a broken line, the meter shows infinity (in ohms)
Visitor comments