Despite their perfect design, Mondeo engines are naturally not free from annoying defects: Ford certifies power units for mileage of 240,000 kilometers for at least ten years. It is better, of course, to transfer the adjustment work going into depth to the workshop. Trained «specialists in blue uniforms» have at their disposal the necessary specialist knowledge, they have practical experience and, as a rule, a large set of special tools in order to «put on your feet» your Mondeo.
For example, an improperly replaced camshaft drive chain can cause irreparable damage to pistons and valves. It is better not to require yourself to carry out any repair of cylinder head gaskets or valves; high demands are also sometimes placed on independent actions for repair work on the crank mechanism. If you are not so sure that you can properly service or check «entrails» your Mondeo, it is best to close the toolbox for your own safety. However, do not hide «finally» engine compartment: there are enough inspection and repair work that you can do yourself.
|
TECHNICAL DICTIONARY |
Engine parts
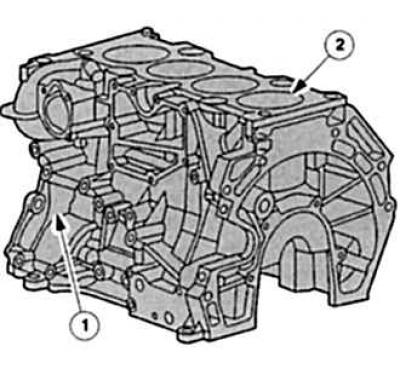
Engine block: here are collected all the rotating and swinging elements of the crank mechanism and the oil supply system. In its periphery, it also carries auxiliary units, such as a generator, a servo pump, a starter and an ignition system. Duratec engine blocks are cast aluminum, gray cast iron is favored by DuraTorg DI.
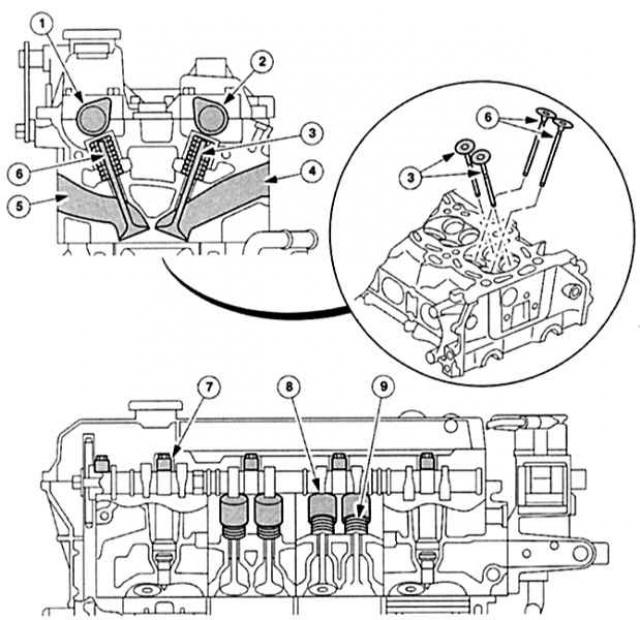
Cylinder head: in modern engines in general today is made from light metal alloys. The cylinder head covers the top of the engine block, it contains intake and exhaust channels, water channels, oil channels, valve seat insert rings, valve guides, camshaft bearings and other valve actuators, combustion chambers, as well as holes for spark plugs and nozzles. From oil, coolant and «outsider» air from the inside and outside is sealed by the engine cylinder head gasket, located between the cylinder block and the engine cylinder head.
Cylinder: the piston moves between bottom dead center (UT) and top dead center (FROM): the working surfaces of the cylinders are strictly coordinated with the diameter of the pistons in their diameter and additionally the surfaces are specially processed. They are cooled indirectly via cooling ducts or, in the case of wet cylinder liners, directly flushed by the coolant.
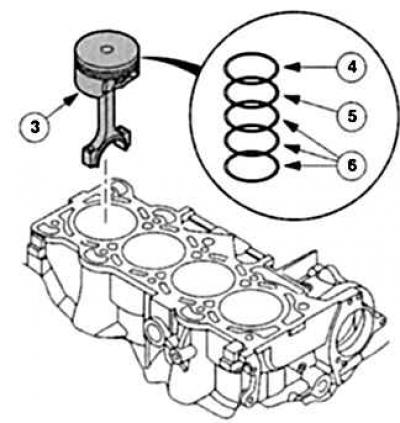
Piston: moves in the cylinder and transfers the combustion energy through the connecting rod to the crankshaft. The pistons are made of particularly light and heat-resistant light metal alloys. Their main components are: bottoms, annular zones with piston rings, holes for the piston pin and guide part. The piston pin connects the piston to the connecting rod. Top piston ring (sealing ring) seals the combustion chamber almost gas-tight from the crank mechanism. bottom ring (scraper oil scraper piston ring) diverts excess lubricating oil away from the cylinder walls to a waste oil sump (oil sump).
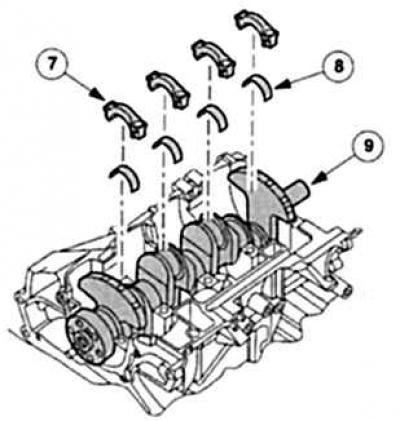
Connecting rod: connects the piston to the crankshaft. It consists of: connecting rod head (guides the piston pin), rod, connecting rod base and base cover (base and cover surround crankshaft crankpins with bearing shells).
Crank mechanism:
3 - piston with connecting rod,
4 - top sealing ring,
5 - lower sealing ring,
6 - scraper oil scraper piston ring (of 3 elements),
7 - connecting rod cap, 8 lower connecting rod bearing,
9 - crankshaft,
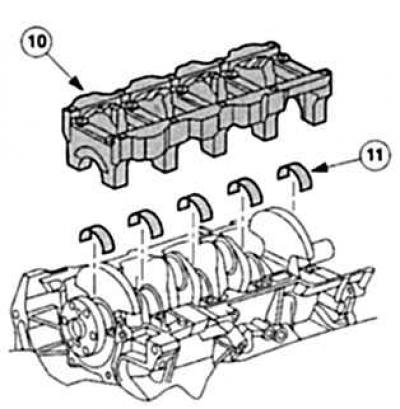
10 - bridge of main bearings,
11 - the lower loose leaf of the bearing of a cranked shaft. |
Crankshaft: through «Connecting rod connecting rod» converts kinetic energy (piston movement from TDC to BDC) into rotational energy (rotary motion). A modern crankshaft consists of a forged rod that rotates in the main bearing shells of the cylinder block. Depending on the number of cylinders with a strictly defined shift (angular degrees) each time two cheeks of the crank lead to the crankpins (location of connecting rod bearings).
Mondeo's four-cylinder crankshafts have five main bearings and four eccentric 90°connecting rod bearings. All bearing locations «inserted» replaceable three-component plain bearings. V6 is enough to have 4 main bearings, here the places of the connecting rod bearings are located eccentrically with angles of 60°.
Valves: in a four-stroke engine are designed to control gas exchange (suction, compression, combustion, expulsion). Valves in Mondeo engines «hanging» V-shape at 42°below the camshafts. All moving parts in the cylinder head complete the valve train.
Camshaft: opens and closes the valves - depending on the engine speed and the position of the pistons - in a strictly defined time sequence.
Basic concepts of engine technology
Four stroke principle:
Inlet (1st measure): piston slips from top dead center (TDC) to bottom dead center (NMT). The intake valve opens, the air-fuel mixture rushes into the cylinder.
Compression (2nd measure): The piston slides from TDC to BDC and, as it moves, compresses the incoming fresh fuel mixture. The intake valve and exhaust valve are closed.
Combustion (3rd measure): already at TDC, the compressed fresh fuel mixture is ignited by the igniting sparks of the spark plugs: the mixture burns explosively, due to the increase in pressure, the piston is displaced to BDC. The connecting rod transfers energy further to the crankshaft and causes it to rotate.
Release (4th measure): the rotating mass of the flywheel moves the piston from BDC back to TDC. The exhaust valve is already open, so the burnt gas (waste gas) exits the exhaust system. Together, these four strokes in a four-stroke engine form a gas exchange cycle.
In general, a diesel engine operates on the same principle. However, on the intake stroke, it sucks in only clean air, compresses it much more strongly, so that the fuel injected at the end of the compression stroke (diesel fuel) in hot air without forced ignition (igniting sparks) could ignite on its own. The rest of the gas exchange cycle is identical to the carburetor engine.
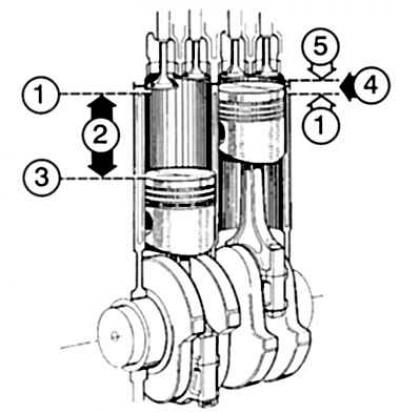
Working volume: the space that the piston passes during its movement from BDC to TDC. The combustion chamber has nothing to do with the working volume. The working volume and the combustion chamber together form the volume of the cylinder.
Compression ratio: parameter that determines how compressed the intake fresh combustible mixture in the combustion chamber. The size of the combustion chamber has a direct effect on the compression ratio. The compression ratio indicates how much of the fuel mixture at 100% filling (throttle valve fully open) must be in the combustion chamber by the time of ignition. DuraTorg engines have a compression ratio of 19.0. Duratec-HE engines operate at a compression ratio of 10.8:1 and the V6 compresses the fresh fuel mixture at a ratio of 9.8:1 (ST220 10,25:1).
The working volume 2 extends from the top 1 to the bottom dead center 3. Between the TDC, which in the right cylinder is limited directly by the piston crown, and the deflection of the cylinder head 5, a combustion chamber 4 is formed. |
|
|
Visitor comments