In a non-turbocharged engine (1.8 D) this system includes:
- thermal switch with vacuum servomotor. located on the thermostat housing, which turns off the exhaust gas recirculation when the engine coolant temperature is below 60°C;
- vacuum control valve located on the fuel pump;
- vacuum limiting valve;
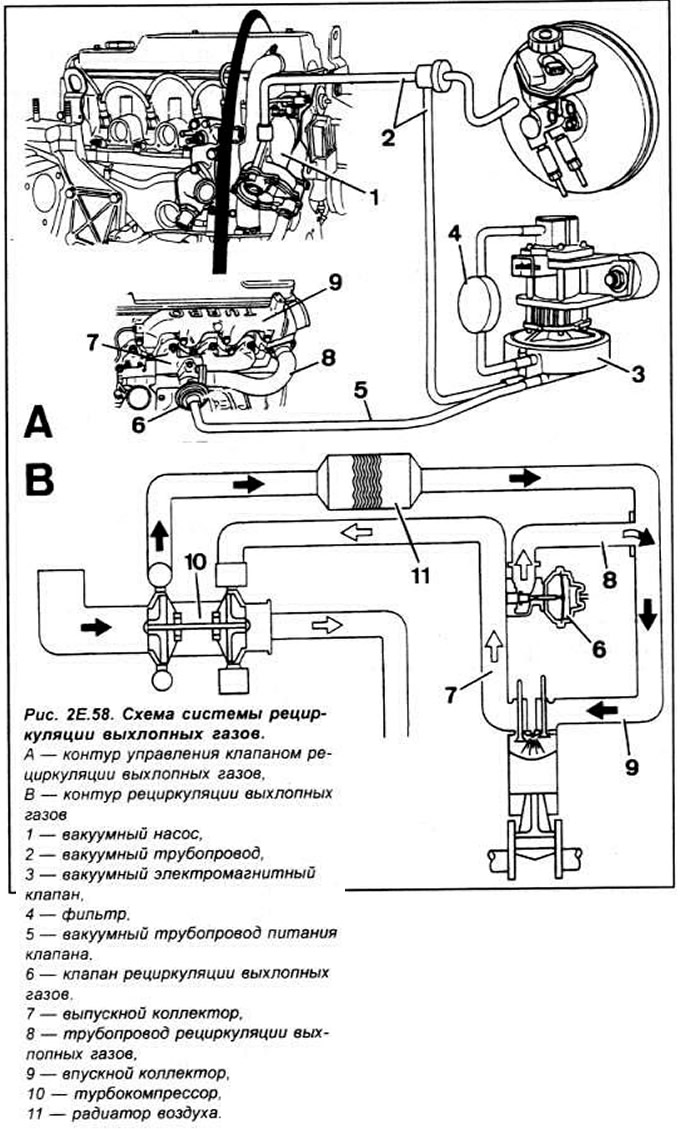
- exhaust gas recirculation valve. located on the intake manifold of the engine, which, under vacuum, opens or closes the connection between the exhaust manifold and the intake manifold In a turbocharged engine (1.8 TD) the exhaust gas recirculation system is controlled by an electronic control device and includes;
- coolant temperature sensor located on the thermostat housing;
- solenoid vacuum valve located on the left front side of the engine compartment, this valve is exposed to the vacuum generated by the vacuum pump, the solenoid valve receives a voltage signal from the electronic control device and makes it possible to supply vacuum to the EGR valve servomotor;
- under vacuum, the diaphragm of the EGR valve servomotor causes it to open. allowing the flow of exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold into the intake manifold.
Visitor comments