Oil pump
The gear oil pump with built-in pressure relief valve is mounted at the front of the engine block and is driven by the engine crankshaft.
Oil viscosity
Viscosity characterizes the fluidity of an oil. The fluidity of oil varies with temperature. As the temperature increases, the oil becomes more fluid. This impairs the oil's ability to adhere and resist high contact pressures. As the oil cools, it thickens, fluidity decreases, and internal friction increases. Because of this property, it is necessary to use an engine oil with a viscosity that changes as little as possible with temperature changes.
When starting a cold engine, the oil must be sufficiently thin so as not to overload the engine excessively and so that after starting the oil will quickly penetrate into all places where lubrication is needed. Oil fluidity is equivalent to its internal friction and is indicated by SAE units (Society of Automotive Engineers), for example SAE 30, SAE 10. A high SAE indicates that the oil is thick, a low SAE indicates a thin oil. However, the viscosity of the oil does not fully characterize the lubricating properties of the oil.
Multigrade oils
It is preferable to use multigrade oils in Escort/Orion car engines. The advantage of all-season oils is that they do not need to be selected depending on the time of year. They are made on the basis of liquid one-season oil (type 10W). When heated, this oil is stabilized by a so-called thickener, which ensures the appropriate lubricating properties of the oil at all temperatures. When using all-weather oil, modern grades with a wide temperature viscosity range should be used, for example 10W-40, 15W-50. Letter W (winter – "winter") in the SAE designation, it characterizes the suitability of the use of oil in the winter.
Oil with enhanced lubricity
High lubricity oils are multigrade oils that, among other additives, contain substances that reduce the coefficient of friction, resulting in a 2% reduction in fuel consumption. Special raw materials are used in their production (synthetic oils). When buying such an oil, you should pay attention to the fact that this oil is approved for use by Ford (indicated on the label).
Viscosity grades and range of oil use
Since the range of use of neighboring SAE classes overlaps, short-term temperature fluctuations can be ignored. Mixing oils of different viscosity grades is allowed if topping up of oil is required, and the ambient temperature no longer corresponds to the viscosity grade of the oil filled in the engine. At long outside temperatures below -20°C, it is recommended to fill in SAE 5W-20 oil.
Viscosity grades and range of oil use
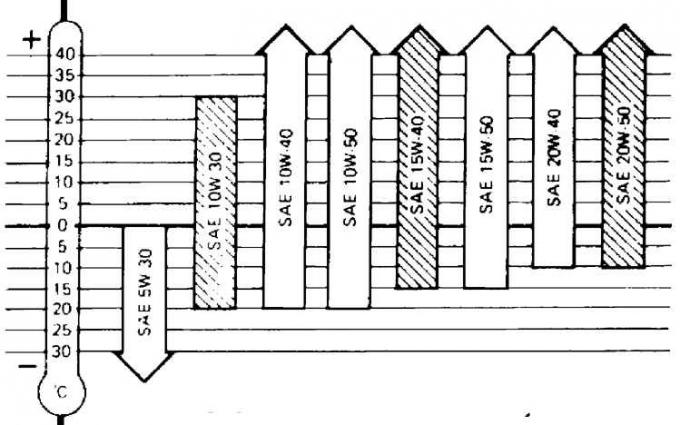
Attention! CD engine oils, which are designated by the manufacturer as diesel engine oils, are not suitable for gasoline engines. There are oils that can be used in two types of engines, in which case both designations are indicated on the oil container, for example SG / CD.
Attention! Additional oil additives, regardless of their type and purpose, should not be used.
Engine oils
For modern engines, only HD oils should be used. HD oils are oils with enhanced lubricity, improved with a variety of additives. These additives provide better anti-corrosion protection, more favorable conditions against oxidation phenomena, the least tendency to form slags, the best viscosity change, cleaning and dissolving properties. Cleaning and dissolving additives not only reduce the formation of residues in the engine, but at the same time they have the ability to dissolve and hold these residues and all other contaminants in the engine oil in a suspended state, so that when changing the oil, these contaminants are removed along with the drained oil.
The quality of HD oils is determined by the API system (American Petroleum Institut). European manufacturers also follow this system.
The designation of the oil grade is made in two letters. The first letter characterizes the scope: S - Servise, designed for carburetor engines; C - Commercial, designed for diesel engines.
The second letter identifies the grade of oil in alphabetical order.
API premium oils are SG for carbureted engines and CD for diesel engines.
| Oil pressure generated by the pump at 80°C: | |
| – at 750 rpm: | |
| • OHV | 0.6 kg/cm2 |
| • CVH | 1.0 kg/cm2 |
| • diesel engine | 1.3 kg/cm2 |
| – at 2000 rpm: | |
| • OHV | 1.5 kg/cm2 |
| • CVH | 2.8 kg/cm2 |
| • diesel engine | 3.0 kg/cm2 |
| Oil type | SAE 10W-30 |
| Oil pressure switch switch-on pressure | 0.4±0.1 bar |
| Reducing valve opening pressure | 2.41 – 2.75 kg/cm2 |
| Axial play of the pump rotor | 0.025 - 0.060 mm |
| Engine oil volume: | |
| – engine OHV 1.1 and 1.3 dm3: | |
| • without filter change | 2.75 dm3 |
| • with filter change | 3.25 dm3 |
| – CVH engines manufactured before June 1982: | |
| • without filter change | 3.5 dm3 |
| • with filter change | 3.75 dm3 |
| CVH engines manufactured since July 1982: | |
| • without filter change | 3.25dm3 |
| • with filter change | 3,5dm3 |
| XR3i and Turbo RS engines: | |
| • without filter change | 3.6 dm3 |
| • with filter change | 3.85 dm3 |
| Diesel engines: | |
| • without filter change | 4.5 dm3 |
| • with filter change | 5.0 dm3 |
| Difference between the maximum and minimum oil level on the oil level gauge | 1 dm3 |
| Oil change interval | every 10,000 km, but at least once a year |
Visitor comments