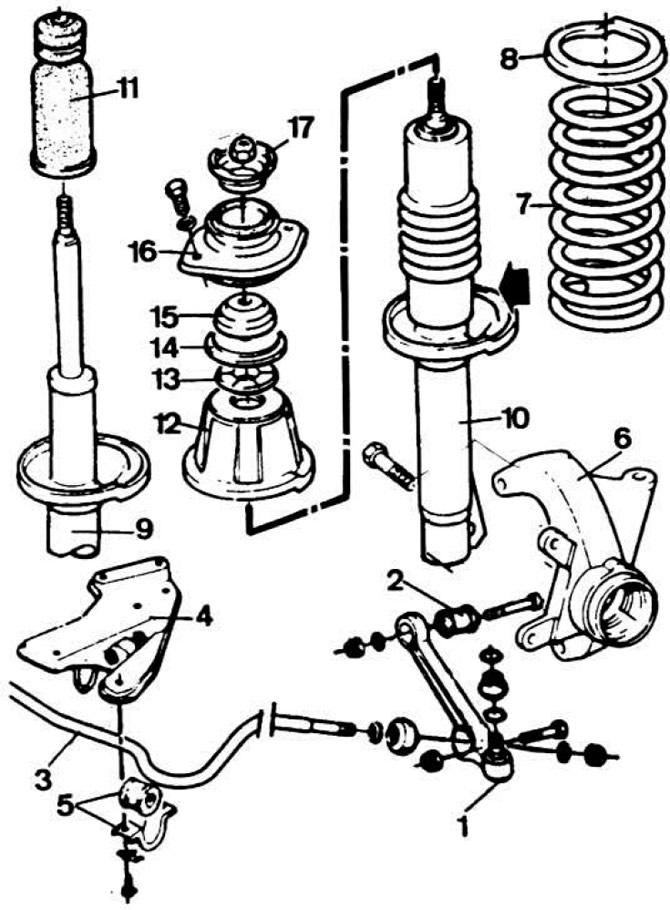
 Pic. 4.1. Details of the front suspension.
Pic. 4.1. Details of the front suspension.
1 - lower arm; 2 - rubber-metal hinge; 3 - stabilizer bar; 4 - stabilizer bracket; 5 — a pillow and a collar of fastening of the stabilizer; 6 - steering knuckle; 7 - suspension spring; 8 - anti-noise spacer; 9 - shock absorber (except XR3); 10 - shock absorber car XR3; 11 - compression stroke buffer; 12 - the upper cup of the spring; 13 - bearing; 14 - thrust washer; 15 - spacer sleeve; 16 - body of the upper support; 17 - compression stroke limiter.
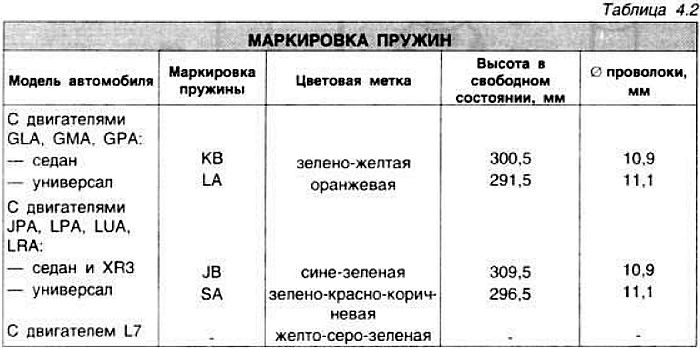
The XR3i's springs are reinforced and lower the vehicle's height by 25mm.
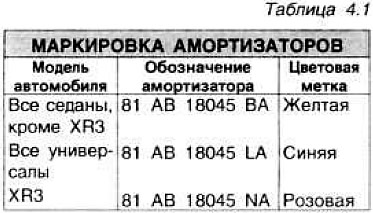
Gas-filled shock absorbers were installed on XR3i cars. Diameter of a bar of the stabilizer of cross stability of 22 mm. except for XR3 and wagon, for which it is 24 mm Front wheel hubs are mounted on two tapered roller bearings, they are filled with lithium grease according to Ford specification S-MIC-4515 A.
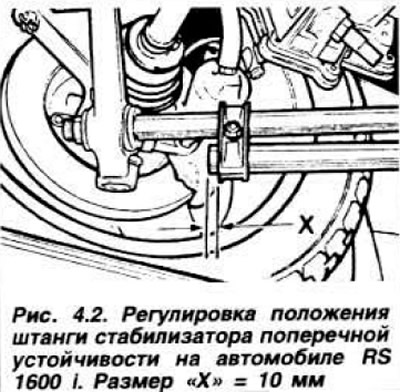
The angles of the front wheels for a car without load until May 1983, the discrepancy is 1-3 mm; tolerance in operation from 1.5 mm convergence to 5.5 mm divergence. after May 1983 discrepancy 1.5-3.5 mm; tolerance in operation from 0.5 mm convergence to 5.5 mm discrepancy. The pitch and camber angles are given in Table 4.3. For Escort RS 1600 i: front wheel divergence angle 5.0–6.0 mm, camber in operation 2°40'–0°40', pitch difference between right and left wheels 1°, camber 1°15'. You can only adjust the convergence by rotating the steering rods, and for the Escort RS 1600 i and the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation (pic. 4.2).
Visitor comments