K-Jetronic fuel injection system
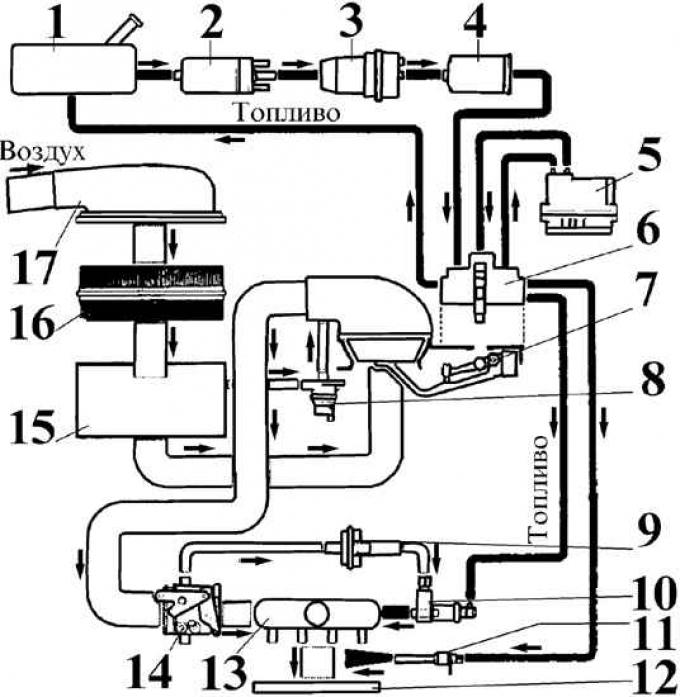
1 - fuel tank; 2 - fuel pump; 3 – pressure accumulator; 4 - fuel filter; 5 - temperature controller; 6 – distributor-dispenser of fuel; 7 - air flow meter; 8 - cut-off valve; 9 - additional air supply; 10 - starting nozzle; 11 - nozzle; 12 - intake manifold; 13 - air chamber; 14 - throttle valve; 15 - air intake chamber; 16 - air filter; 17 - air intake
The Bosch K-Jetronic system is a mechanical fuel injection system with constant fuel injection into the intake manifold ahead of the intake valves.
Fuel under pressure developed by the fuel pump is supplied through the pressure accumulator and the fuel filter.
The air flow is regulated by the throttle valve depending on the position of the accelerator pedal. The amount of air entering the engine cylinders through the flow meter is the main quantity that controls the mixture formation process.
The fuel quantity distributor delivers a certain amount of fuel in accordance with the measured amount of air to the respective injectors.
Sensors located on the engine provide accurate fuel metering in all engine operating modes at any ambient temperature.
To save fuel, there is a fuel cut-off system in engine braking mode.
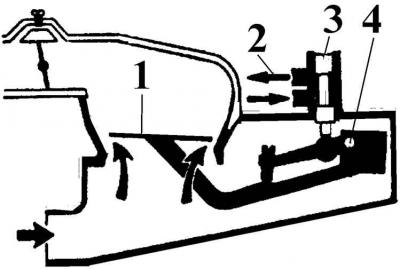
The principle of operation of the vane roller pump
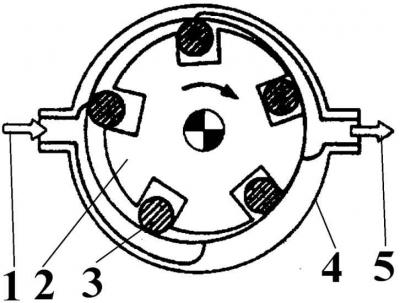
1 - fuel supply from the fuel tank; 2 - rotor; 3 - roller; 4 - pump housing; 5 - fuel outlet under pressure
Electric fuel pump
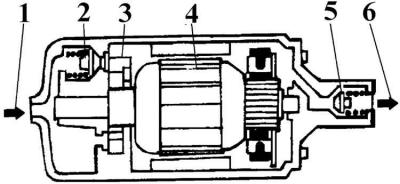
1 - fuel supply from the fuel tank; 2 - pressure reducing valve; 3 - sliding-roller pump; 4 - electric motor; 5 - check valve; 6 - fuel outlet under pressure
An electric fuel pump with a pressure reducing valve is installed near the gas tank.
Pressure accumulator
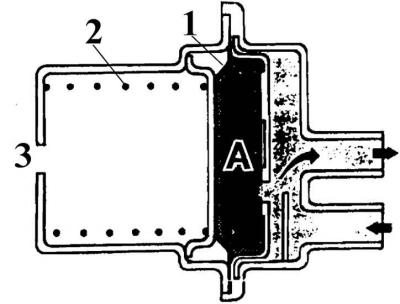
A is the accumulated volume of fuel; 1 - diaphragm; 2 - spring; 3 - hole
The pressure accumulator reduces fuel pulsations generated by the fuel pump and maintains pressure in the fuel line after the engine has been switched off.
Fuel lines connected to the fuel distributor
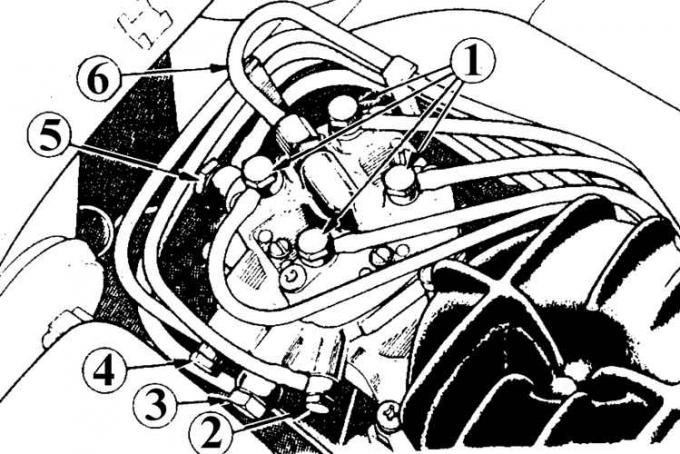
1 - to nozzles; 2 - to the starting valve; 3 - return line; 4 - to the thermostat; 5 - fuel supply line; 6 - to the thermostat
The fuel filter consists of two paper filter elements that perfectly clean the fuel supplied to the injectors.
The fuel distributor controls the amount and uniformity of distribution of fuel entering the engine cylinders.
Air mass meter
1 – pressure plate of the flowmeter; 2 - distribution plunger; 3 - axis; 4 - direction of fuel flows
Control plunger
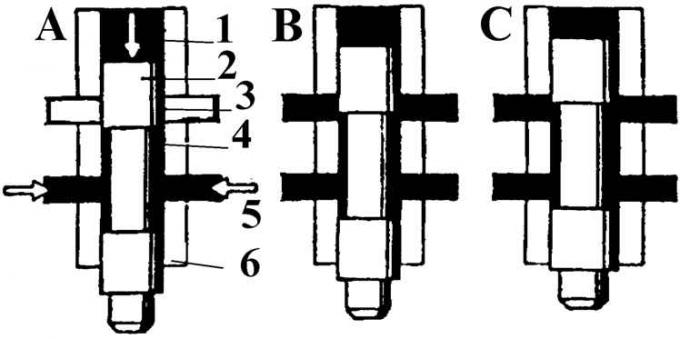
A - a state of rest; B - partial load; C - full load; 1 - control pressure; 2 - control plunger; 3 - control edge; 4 - control face; 5 – fuel supply; 6 - holder
The adjustment block includes a flow meter plate and a control plunger. In idle mode, the air flow lifts the pressure plate of the flow meter, which in turn moves up the control plunger, which passes fuel to the injectors. As the engine speed increases, the air flow increases, as a result of which the control plunger moves up accordingly, which in turn changes the amount of fuel entering the injectors
Attention! Near each connector of the fuel pipe that injects fuel into the injectors, on the distributor head there are special 4 screws of the initial installation, which are not adjusting and cannot be rotated.
Throttle valve
1 - throttle valve; 2 - bypass air channel; 3 – the screw of adjustment of turns of idling
The throttle valve is installed in the main air path and is actuated from the accelerator cable. When installed at the factory, the throttle actuator mechanism is adjusted so that the throttle is initially partially open to prevent it from possibly jamming in the fully closed position. Throttle valve adjustment during operation is not allowed. Idle speed adjustment is performed by a screw, which, depending on its position, to a greater or lesser extent restricts the flow of air passing through the air bypass channel located in the throttle body.
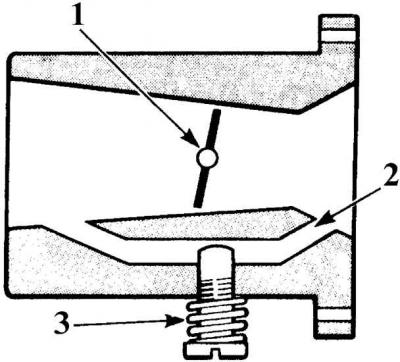
Fuel burner
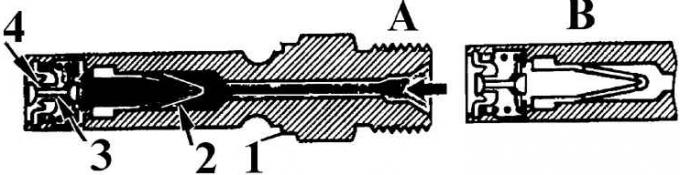
A - the nozzle is open; B - the nozzle is closed; 1 – nozzle body; 2 - filter; 3 - needle valve; 4 - valve seat
The injectors are installed in the intake manifold and open at a pressure of 3.5 bar. They atomize fuel by oscillating a needle valve and inject it continuously into the intake manifold before the intake valve of each cylinder. After the engine is stopped, the pressure in the fuel system drops and the injectors close at a pressure below 3.5 bar.
The thermostat is located on the intake manifold and consists of two springs, a bimetallic plate and a control pressure valve. The regulator controls the fuel supply to the control line, which regulates the pressure drops during the movements of the control plunger. The compression of the springs is regulated by a bimetallic plate, the amount of expansion of which depends on the temperature of the engine.
The auxiliary metering device is located on the intake manifold and consists of a rotating plate, a bimetal plate and a heating element. This device supplies an additional amount of fuel-air mixture when the engine is idling at low air temperatures.
Starting nozzle in working position
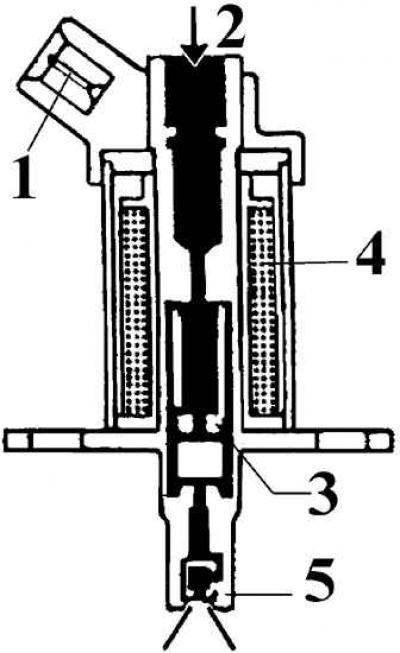
1 - electrical connector; 2 - fuel supply through the fuel filter; 3 - valve; 4 - winding; 5 - centrifugal atomizer
The starting injector is electrically controlled and has a start mode switch and is designed to supply fuel to the air chamber in the cold start mode of the engine. Since July 1988, a starter nozzle of an improved design has been installed.
The fuel pump protector is located under the dashboard on the driver's side and is purple. The purpose of the unit is to disconnect the power supply from the fuel pump in the event of a sudden stop of the engine.
Shut-off valve
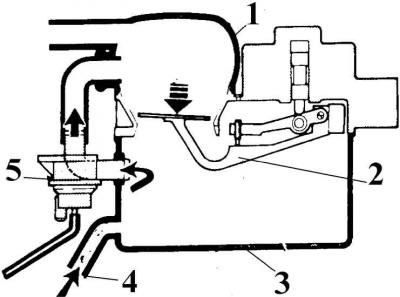
1 - suction air line; 2 – sensor plate; 3 - air filter housing; 4 - air channel; 5 - open shut-off valve
The shut-off valve is used to save fuel when the engine is warming up and in certain modes of vehicle movement.
Visitor comments