Right drive shaft
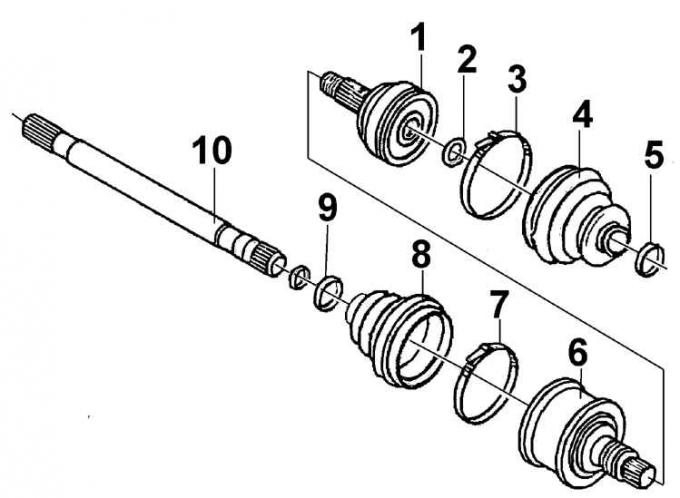
1, 6 - ball joint; 2 - retaining ring; 3, 5, 7, 9 - clamp; 4, 8 - protective cover; 10 - drive shaft
Left drive shaft
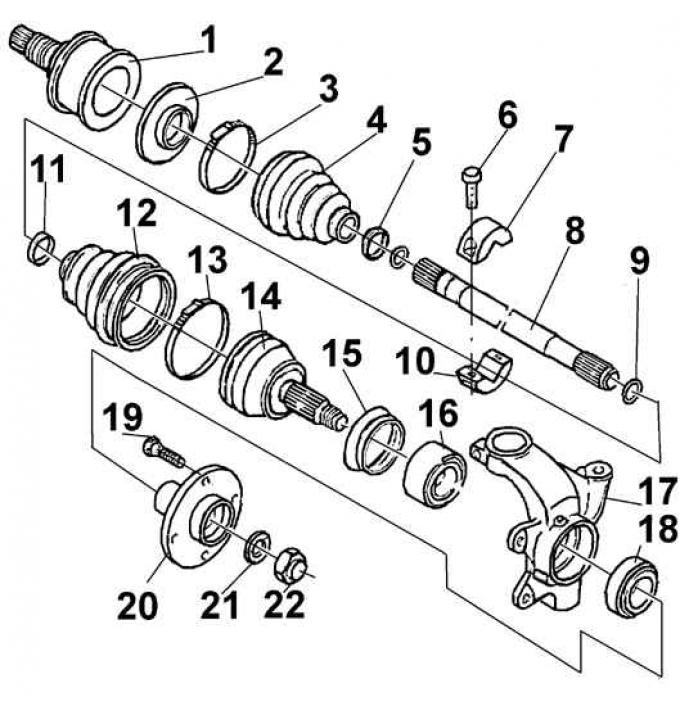
1, 14 - ball joint; 2 - flange; 3, 5, 11, 13 - collar; 4, 12 - protective cover; 6 - bolt; 7, 10 - vibration damper; 8 - drive shaft; 9 - retaining ring; 15 - sealing ring; 16, 18 - bearing; 17 - steering knuckle; 19 - bolt; 20 - hub; 21 - washer; 22 - hub nut
Outer and inner hinges of the drive shaft
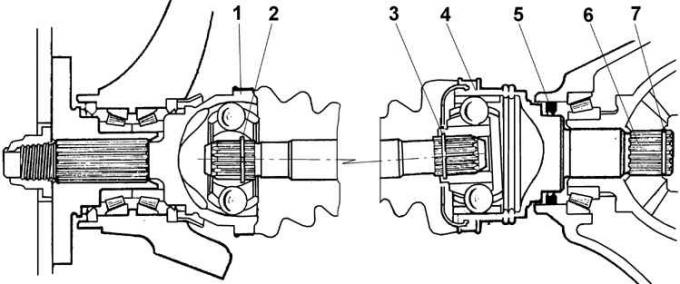
1 - outer hinge; 2 – a lock ring of the external hinge; 3 – a lock ring of the internal hinge; 4 - internal hinge; 5 - sealing ring; 6 - slotted tip of the internal hinge; 7 – a lock ring of a shaft
The transmission of torque from the gearbox to the drive wheels is carried out through drive shafts of different lengths. The right shaft is longer than the left one, has a larger diameter and has a tubular section. To eliminate vibrations, a vibration damper is installed on the right shaft. Each shaft consists of three parts: internal and external joints of equal angular velocities (SHRUS) and the central part of the shaft. The tip of the inner hinge housing with its splines enters the splines of the side gear of the differential and is fixed in it by an expanding snap ring. The splined tip of the outer hinge housing is inserted into the wheel hub and fixed with a nut. CV joints are lubricated with grease, which is replaced only when the joint is disassembled.
Visitor comments