Throttle body
throttle body (pic. 2.105) installed between the dispenser-distributor and the inlet pipeline.
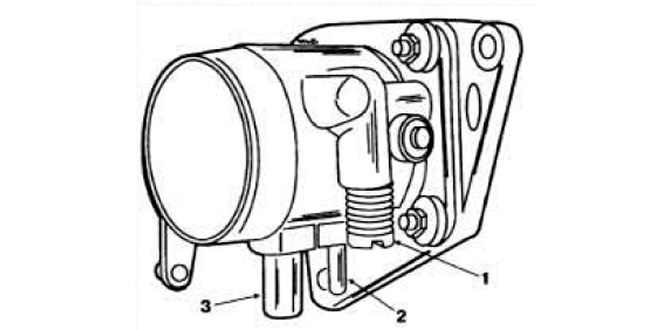 Pic. 2.105. Throttle body.
Pic. 2.105. Throttle body.
1 - idle adjustment screw; 2 - branch pipe of the vacuum supply hose to the fuel dispenser-distributor; 3 — a branch pipe of a hose of additional supply of air.
The throttle valve is never completely closed to avoid jamming it in the air intake cone when it cools. It is forbidden to violate the factory adjustment of the throttle valve opening.
Auxiliary air valve
Auxiliary air valve (pic. 2.106) It works on the principle of an accelerated idling device for carburetor engines, which provides the supply of additional air when warming up a cold engine.
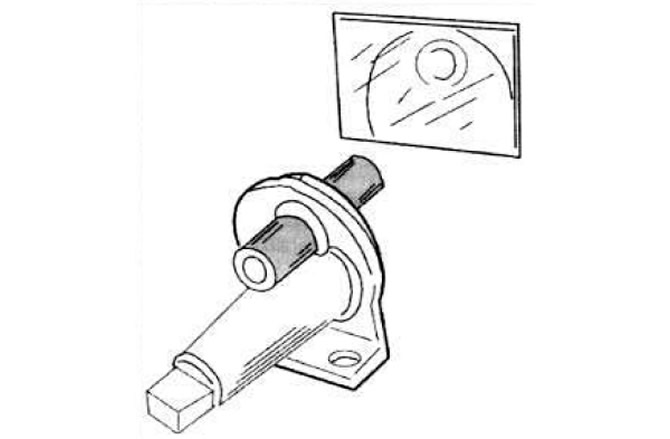 Pic. 2.106. The principle of operation of the auxiliary air supply valve.
Pic. 2.106. The principle of operation of the auxiliary air supply valve.
1 - block; 2 - winding of a bimetallic spring; 3 - bimetallic spring; 4 - rotary damper.
When starting a cold engine, the additional air supply channel is open. As the engine warms up, the bimetallic spring 3 turns the damper 4 and the air supply channel is gradually blocked. On a hot engine, the valve is closed.
In addition, the supply of additional air is regulated by the pressure plate of the air flow meter, the movement of which leads to the rise / spool of the dispenser, and therefore to an increase in the crankshaft speed (with closed throttle).
Electromagnetic starting nozzle
Electromagnetic starting nozzle (pic. 2.107) designed to inject additional fuel into the intake manifold when starting a cold engine. It is controlled by a thermostat (pic. 2.108), which closes and opens the electrical circuit of the starting injector, depending on the engine temperature and the duration of the start (pic. 2.109).
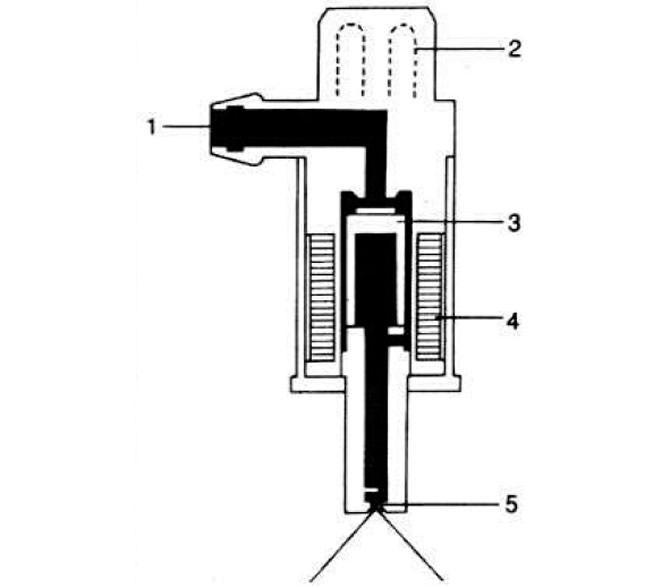 Pic. 2.107. Starter nozzle section.
Pic. 2.107. Starter nozzle section.
1 - fuel supply pipe; 2 - block; 3 - core; 4 - winding; 5 - swirl atomizer.
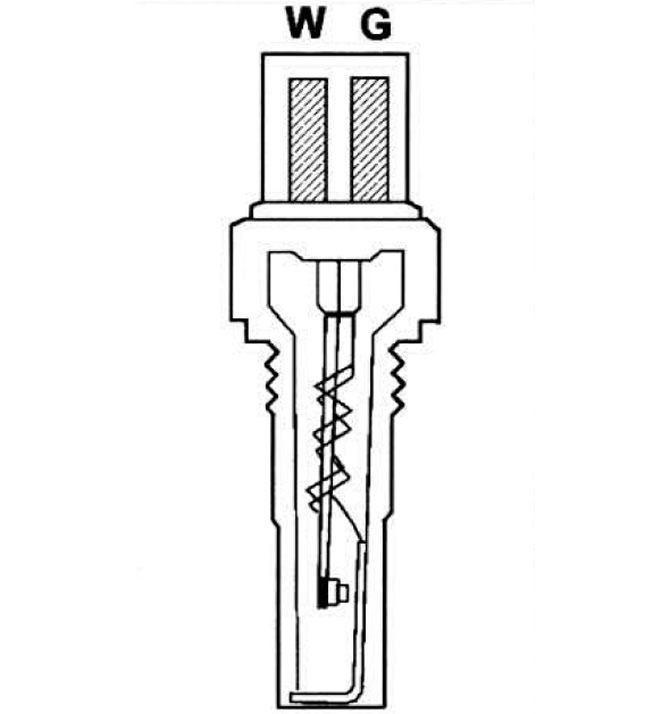 Pic. 2.108. Section of the term about the time relay.
Pic. 2.108. Section of the term about the time relay.
1 - contact; 2 - bimetallic spring; 3 - winding.
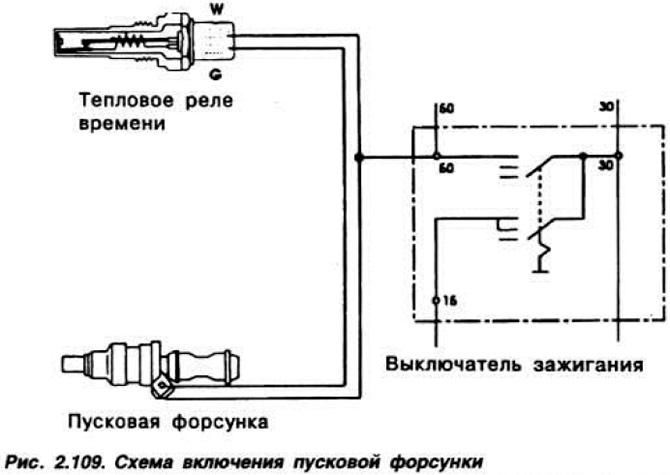
Fuel injectors
fuel injectors (pic. 2.110) fuel is injected into the cylinders at a pressure of 3.2-4.0 kgf/cm2, providing fuel atomization in the form of a cone of a certain shape.
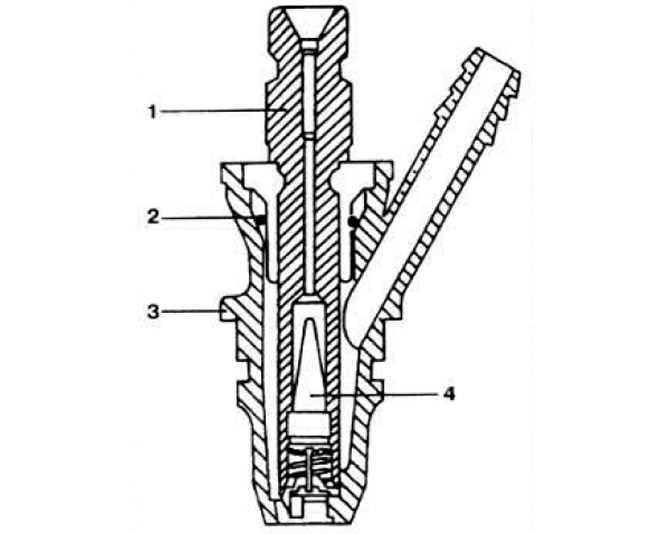 Pic. 2.110. Fuel injector section.
Pic. 2.110. Fuel injector section.
1 - sprayer body; 2 - sealing ring; 3 - fore-sunk body; 4 - conical filter.
Visitor comments